COVID-19-associated anemia: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Main|COVID-19}} | |||
'''For COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions, click [[COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions|here]]'''<br> | '''For COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions, click [[COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions|here]]'''<br> | ||
'''For COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions, click [[COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions|here]]'''<br> | '''For COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions, click [[COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions|here]]'''<br> | ||
{{ | {{SI}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{SHA}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{SHA}} | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
[[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] is caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]], which caused a respiratory illness [[outbreak]] that was first detected in Wuhan, China. Anemia in general is defined as a hemoglobin level of less than 13 | [[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] is caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]], which caused a [[respiratory]] illness [[outbreak]] that was first detected in Wuhan, China. [[Anemia]] in general is defined as a [[hemoglobin]] level of less than 13 gm/dL in men and less than 12 gm/dL in women by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. Although [[anemia]] is not a common finding in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection, decrease in [[hemoglobin]] in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] infection has been reported. The [[pathophysiology]] of decrease in [[hemoglobin]] in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection are hypothetically affected [[erythropoiesis]] due to [[inflammation]] during [[COVID-19]] infection which leads to decrease in [[hemoglobin]]. | ||
==Historical Perspective== | ==Historical Perspective== | ||
* [[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] is caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]], which caused a respiratory illness [[outbreak]] that was first detected in Wuhan, China.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/about/index.html|title=|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref><ref name="LuCui2020">{{cite journal|last1=Lu|first1=Jian|last2=Cui|first2=Jie|last3=Qian|first3=Zhaohui|last4=Wang|first4=Yirong|last5=Zhang|first5=Hong|last6=Duan|first6=Yuange|last7=Wu|first7=Xinkai|last8=Yao|first8=Xinmin|last9=Song|first9=Yuhe|last10=Li|first10=Xiang|last11=Wu|first11=Changcheng|last12=Tang|first12=Xiaolu|title=On the origin and continuing evolution of SARS-CoV-2|journal=National Science Review|year=2020|issn=2095-5138|doi=10.1093/nsr/nwaa036}}</ref> | * [[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] is caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]], which caused a respiratory illness [[outbreak]] that was first detected in Wuhan, China.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/about/index.html|title=|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref><ref name="LuCui2020">{{cite journal|last1=Lu|first1=Jian|last2=Cui|first2=Jie|last3=Qian|first3=Zhaohui|last4=Wang|first4=Yirong|last5=Zhang|first5=Hong|last6=Duan|first6=Yuange|last7=Wu|first7=Xinkai|last8=Yao|first8=Xinmin|last9=Song|first9=Yuhe|last10=Li|first10=Xiang|last11=Wu|first11=Changcheng|last12=Tang|first12=Xiaolu|title=On the origin and continuing evolution of SARS-CoV-2|journal=National Science Review|year=2020|issn=2095-5138|doi=10.1093/nsr/nwaa036}}</ref> | ||
* On January 30, 2020, the [[outbreak]] was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. | * On January 30, 2020, the [[outbreak]] was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. | ||
* On March 12, 2020, the [[COVID-19]] outbreak was declared a [[pandemic]] by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | * On March 12, 2020, the [[COVID-19]] outbreak was declared a [[pandemic]] by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
*[[Anemia]], in general, is defined as a [[hemoglobin]] level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | |||
* Anemia in general is defined as a [[hemoglobin]] level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | |||
* The following is the classification of [[anemia]] in general by red blood cell size with [[Mean corpuscular volume|mean corpuscular volume (MCV)]]: | * The following is the classification of [[anemia]] in general by red blood cell size with [[Mean corpuscular volume|mean corpuscular volume (MCV)]]: | ||
**[[Macrocytic anemia]] (MCV>100) | **[[Macrocytic anemia]] ([[Mean corpuscular volume|MCV]]>100) | ||
**[[Normocytic anemia]] (80<MCV<100) | **[[Normocytic anemia]] (80<[[Mean corpuscular volume|MCV]]<100) | ||
*** High [[reticulocyte]] count | *** High [[reticulocyte]] count | ||
*** Low [[reticulocyte]] count | *** Low [[reticulocyte]] count | ||
** [[Microcytic anemia]] (MCV<80) | ** [[Microcytic anemia]] (MCV<80) | ||
Here is a schematic representation of how to consider anemia with [[Mean corpuscular volume|MCV]] as the starting point: | |||
[[File:Covid19 anemia 2.jpg|center|800px]] | |||
Other characteristics visible on the [[peripheral smear]] may provide valuable clues about a more specific diagnosis; for example, abnormal [[white blood cell]]s may point to a cause in the [[bone marrow]]. | |||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
The [[pathophysiology]] of decrease in hemoglobin and rarity of anemia in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection are as the followings:<ref name="pmid32495027">{{cite journal| author=Liu X, Zhang R, He G| title=Hematological findings in coronavirus disease 2019: indications of progression of disease. | journal=Ann Hematol | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=32495027 | doi=10.1007/s00277-020-04103-5 | pmc=7266734 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32495027 }} </ref> | The [[pathophysiology]] of decrease in [[hemoglobin]] and rarity of [[anemia]] in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection are as the followings:<ref name="pmid32495027">{{cite journal| author=Liu X, Zhang R, He G| title=Hematological findings in coronavirus disease 2019: indications of progression of disease. | journal=Ann Hematol | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=32495027 | doi=10.1007/s00277-020-04103-5 | pmc=7266734 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32495027 }} </ref> | ||
*[[Erythropoiesis]] may be affected by [[inflammation]] during [[COVID-19]] infection which leads to decrease in [[hemoglobin]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | *[[Erythropoiesis]] may be affected by [[inflammation]] during [[COVID-19]] infection which leads to decrease in [[hemoglobin]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | ||
*[[Anemia]] is not a common finding probably due to the compensation of [[Red blood cell|erythrocyte]] proliferation caused by [[pneumonia]]-induced [[Hypoxemia|hypoxia]] and the long life span of [[erythrocytes]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | *[[Anemia]] is not a common finding probably due to the compensation of [[Red blood cell|erythrocyte]] proliferation caused by [[pneumonia]]-induced [[Hypoxemia|hypoxia]] and the long life span of [[erythrocytes]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | ||
[[ File:COVID 19 anemia.jpg|center|600px]] | |||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
[[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]] is the cause of [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | |||
* [[COVID-19|Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)]] caused by a novel [[coronavirus]] called [[SARS-CoV-2]] is the cause of [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | |||
==Differentiating COVID-19-associated Anemia from other Diseases== | ==Differentiating COVID-19-associated Anemia from other Diseases== | ||
Differential diagnosis of [[anemia]] in general may include:<ref name="pmid28189170">{{cite journal| author=Cascio MJ, DeLoughery TG| title=Anemia: Evaluation and Diagnostic Tests. | journal=Med Clin North Am | year= 2017 | volume= 101 | issue= 2 | pages= 263-284 | pmid=28189170 | doi=10.1016/j.mcna.2016.09.003 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28189170 }} </ref> | * Differential diagnosis of [[anemia]] in general may include: [[Iron deficiency anemia]], [[thalassemia]], [[sideroblastic anemia]], anemia of [[inflammation]], [[aplastic anemia]], [[hypothyroidism]], [[Liver diseases|liver disease]], [[renal disease]], [[reticulocytosis]], [[thyroid disease]], [[vitamin]] [[Vitamin B12|B12]] and [[folate deficiency]], [[chemotherapy]], [[myelodysplastic syndrome]], acute onset [[hemolysis]] or [[blood loss]].<ref name="pmid28189170">{{cite journal| author=Cascio MJ, DeLoughery TG| title=Anemia: Evaluation and Diagnostic Tests. | journal=Med Clin North Am | year= 2017 | volume= 101 | issue= 2 | pages= 263-284 | pmid=28189170 | doi=10.1016/j.mcna.2016.09.003 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28189170 }} </ref> | ||
For complete differential diagnosis of anemia please click [[Anemia#Differentiating Anemia from Other Diseases|here]]. | |||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
*[[Anemia]] is a very rare [[Complication (medicine)|complication]] of [[COVID-19]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | |||
* Anemia is a very rare complication of [[COVID-19]].<ref name="pmid32495027" /> | * There is no new update about COVID-19 associated [[anemia]]. | ||
* There is no new update about COVID-19 associated anemia. | |||
==Risk Factors== | ==Risk Factors== | ||
There is no associated risk factor | * There is no associated [[risk factor]] for [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]]. | ||
==Screening== | ==Screening== | ||
There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for [[anemia]] in [[COVID-19]] infection. | * There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine [[Screening (medicine)|screening]] for [[anemia]] in [[COVID-19]] infection. | ||
==Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis== | ==Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis== | ||
* Although [[anemia]] is not a common finding in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection, but decrease in [[hemoglobin]] in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] infection has been reported.<ref name="pmid32495027" /><ref name="pmid32109013">{{cite journal| author=Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX | display-authors=etal| title=Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2020 | volume= 382 | issue= 18 | pages= 1708-1720 | pmid=32109013 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 | pmc=7092819 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32109013 }} </ref> | * Although [[anemia]] is not a common finding in patients with [[COVID-19]] infection, but decrease in [[hemoglobin]] in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] infection has been reported.<ref name="pmid32495027" /><ref name="pmid32109013">{{cite journal| author=Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX | display-authors=etal| title=Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2020 | volume= 382 | issue= 18 | pages= 1708-1720 | pmid=32109013 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 | pmc=7092819 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32109013 }} </ref> | ||
* The median [[hemoglobin]] is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 | * The median [[hemoglobin]] is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 gm/dL) compared to patients with non-severe [[infection]] (13.5 gm/dL).<ref name="pmid32109013" /> | ||
* Decrease in [[hemoglobin]] is seen more in critically ill patients with severe [[COVID-19]] infection.<ref name="pmid32109013" /> | * Decrease in [[hemoglobin]] is seen more in critically ill patients with severe [[COVID-19]] infection.<ref name="pmid32109013" /> | ||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
===Diagnostic Study of Choice=== | ===Diagnostic Study of Choice=== | ||
* The [[diagnostic study of choice]] for [[anemia]] is [[complete blood count]] ([[Complete blood count|CBC]]). | |||
* The [[diagnostic study of choice]] for [[anemia]] is | *[[Anemia]], in general, is defined as a [[hemoglobin]] level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | ||
* Anemia in general is defined as a [[hemoglobin]] level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the [[World Health Organization|World Health Organization (WHO)]]. | * The median [[hemoglobin]] is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL).<ref name="pmid32109013" /> | ||
* The median hemoglobin is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL).<ref name="pmid32109013" /> | |||
===History and Symptoms=== | ===History and Symptoms=== | ||
*There is insufficient information about the symptoms of [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | |||
*There is insufficient information about the symptoms of | |||
* Patients with [[anemia]] in general should be asked about:<ref name="pmid27866575">{{cite journal| author=Powell DJ, Achebe MO| title=Anemia for the Primary Care Physician. | journal=Prim Care | year= 2016 | volume= 43 | issue= 4 | pages= 527-542 | pmid=27866575 | doi=10.1016/j.pop.2016.07.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27866575 }} </ref> | * Patients with [[anemia]] in general should be asked about:<ref name="pmid27866575">{{cite journal| author=Powell DJ, Achebe MO| title=Anemia for the Primary Care Physician. | journal=Prim Care | year= 2016 | volume= 43 | issue= 4 | pages= 527-542 | pmid=27866575 | doi=10.1016/j.pop.2016.07.006 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=27866575 }} </ref> | ||
** Blood loss | **[[Blood loss]] | ||
** Duration of the anemia | ** Duration of the [[anemia]] | ||
** Any associated features | ** Any associated features | ||
**[[Infection]] | **[[Infection]] | ||
**[[Cancer]] | **[[Cancer]] | ||
** Comorbidities that cause [[anemia]] (such as [[Renal insufficiency|renal failure]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]], and [[inflammatory bowel disease]]) | **[[Comorbidities]] that cause [[anemia]] (such as [[Renal insufficiency|renal failure]], [[rheumatoid arthritis]], and [[inflammatory bowel disease]]) | ||
** Past medical history | ** Past [[medical history]] | ||
** Patient’s ethnicity may influence the differential | ** Patient’s ethnicity may influence the differential | ||
**[[Family history]] | **[[Family history]] | ||
** Drug history ([[aspirin]] and [[Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug|NSAIDs]]) | ** Drug history ([[aspirin]] and [[Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug|NSAIDs]]) | ||
===Physical Examination=== | ===Physical Examination=== | ||
*There is insufficient information about the signs found on [[physical examination]] of [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | *There is insufficient information about the signs found on [[physical examination]] of [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | ||
* The [[physical examination]] in patients with [[anemia]] in general may include checking for:<ref name="pmid27866575" /> | * The [[physical examination]] in patients with [[anemia]] in general may include checking for:<ref name="pmid27866575" /> | ||
** Pallor of the [[conjunctiva]] | **[[Pallor]] of the [[conjunctiva]] | ||
**[[Lymphadenopathy]] | **[[Lymphadenopathy]] | ||
**[[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | **[[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | ||
** Bone tenderness | **[[Bone]] [[tenderness]] | ||
**[[Petechia|Petechiae]] | **[[Petechia|Petechiae]] | ||
**[[Bruise|Ecchymose]] | **[[Bruise|Ecchymose]] | ||
===Laboratory Findings=== | ===Laboratory Findings=== | ||
*[[Complete blood count]] ([[Complete blood count|CBC]])''':'''<ref name="pmid28189170" /><ref name="pmid32109013" /> | |||
* | |||
** The median [[hemoglobin]] is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL). | ** The median [[hemoglobin]] is lower in patients with severe [[COVID-19]] (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL). | ||
*[[Blood film|Peripheral blood smear]]: | |||
*[[Blood film|Peripheral blood smear]]: | **Maybe helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]]. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine [[Blood film|peripheral blood smear]] in [[COVID-19]] patients. | ||
*[[Reticulocyte]] count : | *[[Reticulocyte]] count: | ||
*Red cell indices: May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]] | **Maybe helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]]. | ||
*Red cell indices: May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]] which includes: | |||
**[[Mean corpuscular volume|MCV]] | **[[Mean corpuscular volume|MCV]] | ||
**[[Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration|Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)]] | **[[Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration|Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)]] | ||
**[[Mean corpuscular hemoglobin|Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)]] | **[[Mean corpuscular hemoglobin|Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH)]] | ||
* To view the laboratory findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 laboratory findings|click here]]. | |||
===Electrocardiogram=== | ===Electrocardiogram=== | ||
There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with [[COVID-19|COVID-1]]9-associated anemia. | * There are no [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] findings associated with [[COVID-19|COVID-1]]9-associated [[anemia]]. | ||
* However, the following findings may be seen on [[The electrocardiogram|ECG]] in patients with [[anemia]]: | |||
**[[Tachycardia]], ST depression, [[T wave]] changes ([[T wave]] flattening and [[T wave inversion|inversion]]), and [[QRS complex|QRS]] abnormalities (indicating [[Left ventricular hypertrophy|LVH]] and cardiac enlargement).<ref name="pmid24959433">{{cite journal| author=Gv S, Pk S, Herur A, Chinagudi S, Patil SS, Ankad RB | display-authors=etal| title=Correlation Between Haemoglobin Level and Electrocardiographic (ECG) Findings in Anaemia: A Cross-Sectional Study. | journal=J Clin Diagn Res | year= 2014 | volume= 8 | issue= 4 | pages= BC04-6 | pmid=24959433 | doi=10.7860/JCDR/2014/8966.4202 | pmc=4064835 | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=24959433 }} </ref> | |||
*To view the electrocardiogram findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 electrocardiogram|click here]]. | |||
===X-ray=== | ===X-ray=== | ||
There are no [[X-rays|x-ray]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated anemia. | *There are no [[X-rays|x-ray]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated anemia. | ||
*To view X-ray findings of COVID-19 ,click [[COVID-19 x ray|here]].<br /> | |||
===Echocardiography or Ultrasound=== | ===Echocardiography or Ultrasound=== | ||
There are no [[echocardiography]]/[[ultrasound]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]]-associated anemia. | *There are no [[echocardiography]]/[[ultrasound]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]]-associated anemia. | ||
* To view the [[Echocardiography|echocardiographic]] findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 echocardiography and ultrasound|click here]].<br /> | |||
===CT scan=== | ===CT scan=== | ||
There are no [[Computed tomography|CT]] scan findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | *There are no [[Computed tomography|CT]] scan findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | ||
*To view the [[Computed tomography|CT]] scan findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 CT scan|click here]]. | |||
===MRI=== | ===MRI=== | ||
There are no [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | *There are no [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | ||
* To view the [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]] findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 MRI|click here]].<br /> | |||
===Other Imaging Findings=== | ===Other Imaging Findings=== | ||
There are no other [[imaging]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | *There are no other [[imaging]] findings associated with [[COVID-19]] associated-anemia. | ||
* To view other imaging findings on COVID-19, [[COVID-19 other imaging findings|click here]].<br /> | |||
===Other Diagnostic Studies=== | ===Other Diagnostic Studies=== | ||
* [[Bone marrow examination]]: | |||
* [[Bone marrow examination]]: | **May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]]. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine [[bone marrow examination]] in [[COVID-19]] patients.<ref name="pmid28189170" /> | ||
* [[Cytogenetics|Cytogenetic]] and [[Molecule|molecular]] tests : | * [[Cytogenetics|Cytogenetic]] and [[Molecule|molecular]] tests: | ||
**May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of [[anemia]]. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine [[Cytogenetics|cytogenetic]] and [[Molecule|molecular]] in [[COVID-19]] patients. | |||
* To view other diagnostic studies for COVID-19, [[COVID-19 other diagnostic studies|click here]].<br /> | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
===Medical Therapy=== | ===Medical Therapy=== | ||
Treatment of [[anemia]] in general depends on the cause of anemia.<ref name="pmid27866575" /> No specific treatment has been reported for [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | *Treatment of [[anemia]] in general depends on the cause of anemia.<ref name="pmid27866575" /> | ||
*No specific treatment has been reported for [[COVID-19]]-associated-[[anemia]]. | |||
===Surgery=== | ===Surgery=== | ||
Surgery is not a treatment option for patients with [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]]. | *Surgery is not a treatment option for patients with [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]]. | ||
===Primary Prevention=== | ===Primary Prevention=== | ||
There are no established measures for the primary prevention of [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]]. | *There are no established measures for the [[primary prevention]] of [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]]. | ||
===Secondary Prevention=== | ===Secondary Prevention=== | ||
Minimal amount of blood should be drawn for [[Blood test|blood tests]] and only clinically necessary tests should be ordered in order to prevent aggregation of [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]].<ref name="pmid32339260">{{cite journal| author=Baron DM, Franchini M, Goobie SM, Javidroozi M, Klein AA, Lasocki S | display-authors=etal| title=Patient blood management during the COVID-19 pandemic: a narrative review. | journal=Anaesthesia | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=32339260 | doi=10.1111/anae.15095 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32339260 }} </ref> | *Minimal amount of blood should be drawn for [[Blood test|blood tests]] and only clinically necessary tests should be ordered in order to prevent [[aggregation]] of [[COVID-19]] associated [[anemia]].<ref name="pmid32339260">{{cite journal| author=Baron DM, Franchini M, Goobie SM, Javidroozi M, Klein AA, Lasocki S | display-authors=etal| title=Patient blood management during the COVID-19 pandemic: a narrative review. | journal=Anaesthesia | year= 2020 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=32339260 | doi=10.1111/anae.15095 | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=32339260 }} </ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | |||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:52, 21 July 2020
For COVID-19 frequently asked inpatient questions, click here
For COVID-19 frequently asked outpatient questions, click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Shakiba Hassanzadeh, MD[2]
Synonyms and keywords: Hemoglobin changes in COVID 19, anemia in COVID 19, effects on erythropoiesis in COVID 19
Overview
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by a novel coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2, which caused a respiratory illness outbreak that was first detected in Wuhan, China. Anemia in general is defined as a hemoglobin level of less than 13 gm/dL in men and less than 12 gm/dL in women by the World Health Organization (WHO). Although anemia is not a common finding in patients with COVID-19 infection, decrease in hemoglobin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection has been reported. The pathophysiology of decrease in hemoglobin in patients with COVID-19 infection are hypothetically affected erythropoiesis due to inflammation during COVID-19 infection which leads to decrease in hemoglobin.
Historical Perspective
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by a novel coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2, which caused a respiratory illness outbreak that was first detected in Wuhan, China.[1][2]
- On January 30, 2020, the outbreak was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
- On March 12, 2020, the COVID-19 outbreak was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Classification
- Anemia, in general, is defined as a hemoglobin level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The following is the classification of anemia in general by red blood cell size with mean corpuscular volume (MCV):
- Macrocytic anemia (MCV>100)
- Normocytic anemia (80<MCV<100)
- High reticulocyte count
- Low reticulocyte count
- Microcytic anemia (MCV<80)
Here is a schematic representation of how to consider anemia with MCV as the starting point:

Other characteristics visible on the peripheral smear may provide valuable clues about a more specific diagnosis; for example, abnormal white blood cells may point to a cause in the bone marrow.
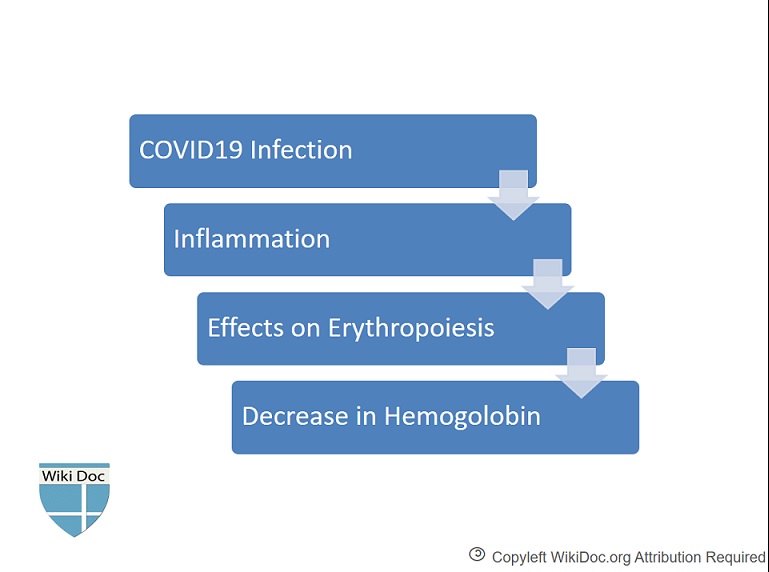
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of decrease in hemoglobin and rarity of anemia in patients with COVID-19 infection are as the followings:[3]
- Erythropoiesis may be affected by inflammation during COVID-19 infection which leads to decrease in hemoglobin.[3]
- Anemia is not a common finding probably due to the compensation of erythrocyte proliferation caused by pneumonia-induced hypoxia and the long life span of erythrocytes.[3]
Causes
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by a novel coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2 is the cause of COVID-19-associated-anemia.
Differentiating COVID-19-associated Anemia from other Diseases
- Differential diagnosis of anemia in general may include: Iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, anemia of inflammation, aplastic anemia, hypothyroidism, liver disease, renal disease, reticulocytosis, thyroid disease, vitamin B12 and folate deficiency, chemotherapy, myelodysplastic syndrome, acute onset hemolysis or blood loss.[4]
For complete differential diagnosis of anemia please click here.
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Anemia is a very rare complication of COVID-19.[3]
- There is no new update about COVID-19 associated anemia.
Risk Factors
- There is no associated risk factor for COVID-19 associated anemia.
Screening
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
- Although anemia is not a common finding in patients with COVID-19 infection, but decrease in hemoglobin in patients with severe COVID-19 infection has been reported.[3][5]
- The median hemoglobin is lower in patients with severe COVID-19 (12.8 gm/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 gm/dL).[5]
- Decrease in hemoglobin is seen more in critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 infection.[5]
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
- The diagnostic study of choice for anemia is complete blood count (CBC).
- Anemia, in general, is defined as a hemoglobin level of less than 13 g/dL in men and less than 12 g/dL in women by the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The median hemoglobin is lower in patients with severe COVID-19 (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL).[5]
History and Symptoms
- There is insufficient information about the symptoms of COVID-19-associated-anemia.
- Patients with anemia in general should be asked about:[6]
- Blood loss
- Duration of the anemia
- Any associated features
- Infection
- Cancer
- Comorbidities that cause anemia (such as renal failure, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease)
- Past medical history
- Patient’s ethnicity may influence the differential
- Family history
- Drug history (aspirin and NSAIDs)
Physical Examination
- There is insufficient information about the signs found on physical examination of COVID-19-associated-anemia.
- The physical examination in patients with anemia in general may include checking for:[6]
Laboratory Findings
- Complete blood count (CBC):[4][5]
- The median hemoglobin is lower in patients with severe COVID-19 (12.8 g/dL) compared to patients with non-severe infection (13.5 g/dL).
- Peripheral blood smear:
- Maybe helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of anemia. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine peripheral blood smear in COVID-19 patients.
- Reticulocyte count:
- Maybe helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of anemia.
- Red cell indices: May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of anemia which includes:
- To view the laboratory findings on COVID-19, click here.
Electrocardiogram
- There are no ECG findings associated with COVID-19-associated anemia.
- However, the following findings may be seen on ECG in patients with anemia:
- To view the electrocardiogram findings on COVID-19, click here.
X-ray
- There are no x-ray findings associated with COVID-19 associated anemia.
- To view X-ray findings of COVID-19 ,click here.
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
- There are no echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with COVID-19-associated anemia.
- To view the echocardiographic findings on COVID-19, click here.
CT scan
- There are no CT scan findings associated with COVID-19 associated-anemia.
- To view the CT scan findings on COVID-19, click here.
MRI
- There are no MRI findings associated with COVID-19 associated-anemia.
- To view the MRI findings on COVID-19, click here.
Other Imaging Findings
- There are no other imaging findings associated with COVID-19 associated-anemia.
- To view other imaging findings on COVID-19, click here.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- Bone marrow examination:
- May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of anemia. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine bone marrow examination in COVID-19 patients.[4]
- Cytogenetic and molecular tests:
- May be helpful if there is a suspicion of other causes of anemia. However, there is insufficient evidence recommending routine cytogenetic and molecular in COVID-19 patients.
- To view other diagnostic studies for COVID-19, click here.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- Treatment of anemia in general depends on the cause of anemia.[6]
- No specific treatment has been reported for COVID-19-associated-anemia.
Surgery
Primary Prevention
- There are no established measures for the primary prevention of COVID-19 associated anemia.
Secondary Prevention
- Minimal amount of blood should be drawn for blood tests and only clinically necessary tests should be ordered in order to prevent aggregation of COVID-19 associated anemia.[8]
References
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/about/index.html. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Lu, Jian; Cui, Jie; Qian, Zhaohui; Wang, Yirong; Zhang, Hong; Duan, Yuange; Wu, Xinkai; Yao, Xinmin; Song, Yuhe; Li, Xiang; Wu, Changcheng; Tang, Xiaolu (2020). "On the origin and continuing evolution of SARS-CoV-2". National Science Review. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa036. ISSN 2095-5138.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Liu X, Zhang R, He G (2020). "Hematological findings in coronavirus disease 2019: indications of progression of disease". Ann Hematol. doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04103-5. PMC 7266734 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32495027 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Cascio MJ, DeLoughery TG (2017). "Anemia: Evaluation and Diagnostic Tests". Med Clin North Am. 101 (2): 263–284. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2016.09.003. PMID 28189170.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX; et al. (2020). "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China". N Engl J Med. 382 (18): 1708–1720. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. PMC 7092819 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 32109013 Check|pmid=value (help). - ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Powell DJ, Achebe MO (2016). "Anemia for the Primary Care Physician". Prim Care. 43 (4): 527–542. doi:10.1016/j.pop.2016.07.006. PMID 27866575.
- ↑ Gv S, Pk S, Herur A, Chinagudi S, Patil SS, Ankad RB; et al. (2014). "Correlation Between Haemoglobin Level and Electrocardiographic (ECG) Findings in Anaemia: A Cross-Sectional Study". J Clin Diagn Res. 8 (4): BC04–6. doi:10.7860/JCDR/2014/8966.4202. PMC 4064835. PMID 24959433.
- ↑ Baron DM, Franchini M, Goobie SM, Javidroozi M, Klein AA, Lasocki S; et al. (2020). "Patient blood management during the COVID-19 pandemic: a narrative review". Anaesthesia. doi:10.1111/anae.15095. PMID 32339260 Check
|pmid=value (help).