Bradycardia resident survival guide: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Adding CME Category::Cardiology) |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
==FIRE: Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation== | ==FIRE: Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation== | ||
A Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation (FIRE) should be performed to identify patients in need of immediate intervention.<br> | A Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation (FIRE) should be performed to identify patients in need of immediate intervention. The initial rapid evaluation is based on the 2005 AHA guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia|journal=Circulation|volume=112|issue=24_suppl|year=2005|pages=IV-67–IV-77|issn=0009-7322|doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558}}</ref> | ||
<span style="font-size:85%">Boxes in | <br> | ||
<span style="font-size:85%">Boxes in red signify that an urgent management is needed.</span> | |||
<span style="font-size:85%">'''Abbreviations:''' '''IV:''' [[Intravenous]]; '''ECG:''' [[Electrocardiogram]]</span> | |||
{{familytree/start}} | {{familytree/start}} | ||
{{familytree | {{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''Identify cardinal findings that increase the pretest probability of bradycardia''' <br> ❑ [[Heart rate]] < 50 beats/min </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | {{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | ||
{{familytree | {{familytree | | | | | C01 | | | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''Does the patient have any of the following findings of hemodyanamic instability that require urgent treatment?'''<br> ❑ [[Shock]] <br> ❑ [[Altered mental status]] <br> ❑ [[Hypotension]] <br> ❑ [[Hypothermia]] <br> ❑ [[Oliguria]] </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | | |,|-| | {{familytree | | | |,|-|^|-|.| }} | ||
{{familytree | | | D01 | | D02| |D01=<div style=" width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''Yes'''}}</div>|D02='''No'''}} | |||
{{familytree | | |! | {{familytree | | | |!| | | |!| }} | ||
{{familytree | | |! | {{familytree | | | |!| | | E02 |E02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;"> '''[[Bradycardia resident survival guide#Complete Diagnostic Approach|Continue with the complete diagnostic approach below]]''' </div>}} | ||
{{familytree | | E01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |E01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''Initial Stabilization'''<br> ❑ Maintain patent airway <br> ❑ Assist breathing if required <br> ❑ Place patient on cardiac monitor <br> ❑ Give supplemental oxygen <br> ❑ Monitor blood pressure and evaluate oxyhemoglobin saturation <br> ❑ Establish IV access <br> ❑ Obtain [[ECG|<span style="color:white;">ECG</span>]] to define rhythm <br> ❑ Evaluate clinical status and identify reversible causes simultaneously}}</div>}} | {{familytree | | | E01 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |E01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''Initial Stabilization'''<br> ''Do the following simultaneously without delaying the treatment''<br><br>❑ Maintain patent airway <br> ❑ Assist breathing if required <br> ❑ Place patient on cardiac monitor <br> ❑ Give supplemental oxygen <br> ❑ Monitor blood pressure and evaluate oxyhemoglobin saturation <br> ❑ Establish IV access <br> ❑ Obtain [[ECG|<span style="color:white;">ECG</span>]] to define rhythm <br> ❑ Evaluate clinical status and identify reversible causes simultaneously}}</div>}} | ||
{{familytree | | |! | {{familytree | | | |!| | | | | |}} | ||
{{familytree | | P01 | {{familytree | | | P01 | | | | | P01=<div style=" width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|Is there an [[AV block|<span style="color:white;">AV block</span>]]?}}</div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |,|^|-|-|-|.| | | | }} | {{familytree | | |,|^|-|-|-|.| | | | }} | ||
{{familytree | V01 | | | V02 | | | | |V01=<div style=" width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''No'''}}</div>|V02='''Yes'''}} | {{familytree | | V01 | | | V02 | | | | |V01=<div style=" width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''No'''}}</div>|V02=<div style=" width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''Yes'''}}</div>}} | ||
{{familytree | |!| | | | | {{familytree | | |!| | |,|-|^|-|.| | | | | | | | | | |}} | ||
{{familytree | | {{familytree |boxstyle=background: #FA8072; color: #F8F8FF; | | |!| | F01 | | F02 | | F01= [[Second degree AV block]]/[[Third-degree AV block]]| F02= [[First degree AV block|<span style="color:white;">First degree AV block</span>]]}} | ||
{{familytree | | |!| | |!| | | |!| | | }} | |||
{{familytree |boxstyle=background: #FA8072; color: #F8F8FF; | G01 | | G02 | | G03 | | | | | | | | | | |G01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; line-height: 150%; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''First Line Treatment Option'''<br> ❑ Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV bolus and repeat every 3-5 mins with a maximum dose of 3 mg <br><br> '''Second Line Treatment Options''' <br> | |||
❑ | ❑ Administer [[dopamine|<span style="color:white;">Dopamine</span>]] infusion (2-10 mcg/kg/min) <br> OR <br> | ||
❑ Administer [[epinephrine|<span style="color:white;">Epinephrine</span>]] infusion (2-10 mcg/min) <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ Proceed with [[transcutaneous pacing|<span style="color:white;">transcutaneous pacing</span>]] <br> ([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme|Class IIa, level of evidence B]]) }}</div>|G02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF| '''DO NOT GIVE ATROPINE''' <br> ❑ Proceed with [[transcutaneous pacing|<span style="color:white;">transcutaneous pacing</span>]]}}</div> |G03=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; line-height: 150%; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''First Line Treatment Option'''<br> ❑ Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV bolus and repeat every 3-5 mins with a maximum dose of 3 mg <br><br> '''Second Line Treatment Options''' <br> | |||
❑ Administer [[dopamine|<span style="color:white;">Dopamine</span>]] infusion (2-10 mcg/kg/min) <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ Administer [[epinephrine|<span style="color:white;">Epinephrine</span>]] infusion (2-10 mcg/min) <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ Proceed with [[transcutaneous pacing|<span style="color:white;">transcutaneous pacing</span>]] <br> ([[ACC AHA guidelines classification scheme|Class IIa, level of evidence B]]) }} </div>}} | |||
{{familytree | | |`|-|v|-|'| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |}} | |||
{{familytree |boxstyle=background: #FA8072; color: #F8F8FF; | | | | H01 | | | | | | | | | |H01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 20em; background: #FA8072"> {{fontcolor|#F8F8FF|'''Are the signs of poor perfusion or shock persisting?'''}} </div>}} | |||
{{familytree | | |,|-|^|-|.| | }} | |||
{{familytree | | I01 | | I02 | I01= Yes| I02= No}} | |||
{{familytree | | |!| | | |!| | }} | |||
{{familytree | | J01 | | J02 | J01= ❑ Consult a cardiologist and <br>❑ Prepare patient for [[transvenous pacing|<span style="color:white;">transvenous pacing</span>]]| J02= <div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;"> '''[[Bradycardia resident survival guide#Complete Diagnostic Approach|Continue with the complete diagnostic approach below]]''' </div>}} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | {{familytree/end}} | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 88: | Line 101: | ||
==Complete Diagnostic Approach== | ==Complete Diagnostic Approach== | ||
A complete diagnostic approach should be carried out after a focused initial rapid evaluation is conducted and following initiation of any urgent intervention.<ref name="Neumar-2010">{{Cite journal | last1 = Neumar | first1 = RW. | last2 = Otto | first2 = CW. | last3 = Link | first3 = MS. | last4 = Kronick | first4 = SL. | last5 = Shuster | first5 = M. | last6 = Callaway | first6 = CW. | last7 = Kudenchuk | first7 = PJ. | last8 = Ornato | first8 = JP. | last9 = McNally | first9 = B. | title = Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. | journal = Circulation | volume = 122 | issue = 18 Suppl 3 | pages = S729-67 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970988 | PMID = 20956224 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia|journal=Circulation|volume=112|issue=24_suppl|year=2005|pages=IV-67–IV-77|issn=0009-7322|doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558}}</ref> | A complete diagnostic approach should be carried out after a focused initial rapid evaluation is conducted and following initiation of any urgent intervention.<ref name="Neumar-2010">{{Cite journal | last1 = Neumar | first1 = RW. | last2 = Otto | first2 = CW. | last3 = Link | first3 = MS. | last4 = Kronick | first4 = SL. | last5 = Shuster | first5 = M. | last6 = Callaway | first6 = CW. | last7 = Kudenchuk | first7 = PJ. | last8 = Ornato | first8 = JP. | last9 = McNally | first9 = B. | title = Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. | journal = Circulation | volume = 122 | issue = 18 Suppl 3 | pages = S729-67 | month = Nov | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970988 | PMID = 20956224 }}</ref><ref>{{cite journal|title=Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia|journal=Circulation|volume=112|issue=24_suppl|year=2005|pages=IV-67–IV-77|issn=0009-7322|doi=10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558}}</ref> | ||
<span style="font-size:85%">'''Abbreviations:''' '''CK-MB:''' [[Creatine kinase myocardial type]]; '''ECG:''' [[Electrocardiogram]]; '''TSH:''' [[Thyroid stimulating hormone]]</span> | |||
{{Family tree/start}} | {{Family tree/start}} | ||
{{family tree | | | | V01 | {{family tree | | | | V01 | |V01= <div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 35em">'''Characterize the symptoms:''' <br> | ||
❑ [[Lightheadedness]] or [[dizziness]] <br> ❑ [[Dyspnea]] <br> ❑ [[Chest pain]] <br> ❑ [[Altered mental status]] <br> | |||
❑ [[Syncope]] <br> ❑ [[Fatigue]] <br> ❑ [[Exercise intolerance]]<br> | ❑ [[Syncope]] <br> ❑ [[Fatigue]] <br> ❑ [[Exercise intolerance]]<br> | ||
'''Obtain a detailed history''': <br> | '''Obtain a detailed history''': <br> | ||
❑ [[Age]] | ❑ [[Age]] (bradycardia is commonly seen in the elderly) <br> | ||
❑ | ❑ Use of negative chronotropic medications <br> | ||
:❑ [[Beta blockers]] | :❑ [[Beta blockers]] | ||
:❑ [[Calcium channel blockers]] | :❑ [[Calcium channel blockers]] | ||
:❑ [[Digoxin]] <br> | :❑ [[Digoxin]] <br> | ||
❑ Past medical history <br> | ❑ Past medical history <br> | ||
:❑ Disease in the sinus node | :❑ [[Sinus node disease|Disease in the sinus node]] | ||
:❑ [[atrioventricular block|AV nodal disease]] | :❑ [[atrioventricular block|AV nodal disease]] | ||
:❑ Age-related fibrosis and sclerosis | :❑ Age-related fibrosis and sclerosis | ||
| Line 109: | Line 124: | ||
:❑ [[Surgery]] | :❑ [[Surgery]] | ||
:❑ [[Heart transplant]] | :❑ [[Heart transplant]] | ||
:❑[[Sleep apnea]] | :❑ [[Sleep apnea]] | ||
:❑ [[Myocardial infarction]] | :❑ [[Myocardial infarction]] | ||
:❑ [[Hypothyroidism]]</div>}} | :❑ [[Hypothyroidism]]</div>}} | ||
{{family tree | | | | |! | {{family tree | | | | |!| | }} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | A01 | {{Family tree | | | | A01 | |A01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em; width: 35em"> '''Examine the patient:'''<br> | ||
'''Vitals'''<br> | '''Vitals'''<br> | ||
❑ [[Pulse]] <br> | ❑ [[Pulse]] <br> | ||
| Line 132: | Line 147: | ||
:❑ Facial edema (not common) <br> | :❑ Facial edema (not common) <br> | ||
❑ Palpation <br> | ❑ Palpation <br> | ||
:❑ Cool lower extremities | :❑ Cool lower extremities (due to poor [[cardiac output]]) <br> | ||
'''Neck'''<br> | '''Neck'''<br> | ||
:❑ [[Jugular venous distension]] (suggestive of [[heart failure]]) <br> | :❑ [[Jugular venous distension]] (suggestive of [[heart failure]]) <br> | ||
:❑ [[Cannon a waves]] in [[jugular venous pulse]] | :❑ [[Cannon a waves]] in [[jugular venous pulse]] (suggestive of [[complete heart block]]) <br> | ||
'''Respiratory examination'''<br> | '''Respiratory examination'''<br> | ||
❑ Assessment of respiratory effort movement <br> | ❑ Assessment of respiratory effort movement <br> | ||
| Line 141: | Line 156: | ||
:❑ Suprasternal retractions <br> | :❑ Suprasternal retractions <br> | ||
❑ Auscultation <br> | ❑ Auscultation <br> | ||
:❑ [[Rales]] | :❑ [[Rales]] (uncommon) <br> | ||
'''Cardiovascular examination'''<br> | '''Cardiovascular examination'''<br> | ||
❑ Auscultation <br> | ❑ Auscultation <br> | ||
| Line 148: | Line 163: | ||
'''Abdominal examination'''<br> | '''Abdominal examination'''<br> | ||
❑ Percussion<br> | ❑ Percussion<br> | ||
:❑ | :❑ [[Ascites]] - suggestive of [[heart failure]] (uncommon)<br> | ||
'''Extremities'''<br> | '''Extremities'''<br> | ||
❑ Inspection/palpation <br> | ❑ Inspection/palpation <br> | ||
:❑ Lower extremity edema (uncommon)</div>}} | :❑ Lower extremity edema - suggestive of [[heart failure]] (uncommon)</div>}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | |! | {{Family tree | | | | |!| | }} | ||
{{family tree | | | | P01 | {{family tree | | | | P01 | |P01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 35em">'''Consider alternative diagnosses''':<br> ❑ [[Ventricular bigeminy]] <br> ❑ [[premature ventricular contraction|Frequent premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)]] <br> ❑ [[Atrial fibrillation]] <br> ❑ [[premature atrial contraction|Blocked premature atrial contractions (PACs)]] <br> ❑ [[Cardiac tamponade]] </div>}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | |! | {{Family tree | | | | |!| | | }} | ||
{{family tree | | | | R01 | {{family tree | | | | R01 | |R01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150%; width: 35em">'''Order tests''':<br> '''First initial test''' <br> | ||
❑ [[ECG|12-lead ECG]] (to determine rhythm) | ❑ [[ECG|12-lead ECG]] (to determine rhythm) | ||
| Line 173: | Line 188: | ||
❑ [[Cardiac enzymes]] ([[creatine kinase]], [[CK-MB]] and [[troponin]]) <br> | ❑ [[Cardiac enzymes]] ([[creatine kinase]], [[CK-MB]] and [[troponin]]) <br> | ||
❑ [[creatinine|Serum creatinine]] (elevated in renal impairment) <br> | ❑ [[creatinine|Serum creatinine]] (elevated in renal impairment) <br> | ||
❑ Serum digoxin | ❑ Serum digoxin (for junctional bradycardia)<br> | ||
'''Other Investigations''' <br> | '''Other Investigations''' <br> | ||
❑ [[Tilt-table testing]] (to evaluate autonomic system and diagnosis of [[neurocardiogenic syncope]]) <br> | ❑ [[Tilt-table testing]] (to evaluate autonomic system and diagnosis of [[neurocardiogenic syncope]]) <br> | ||
| Line 183: | Line 198: | ||
{{family tree/start}} | {{family tree/start}} | ||
{{family tree | | | | A01 | | | |A01=[[Bradycardia]] | {{family tree | | | | A01 | | | |A01=[[Bradycardia]]/[[Bradyarrhythmia]] with [[heart rate]] <br> < 60/min}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | |!| | | | | }} | {{Family tree | | | | |!| | | | | }} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''Identify | {{Family tree | | | | B01 | | | |B01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''Identify underlying causes:'''<br> | ||
❑ [[Acidosis]]<br> | ❑ [[Acidosis]]<br> | ||
❑ [[ | ❑ [[Carotid sinus hypersensitivity]]<br> | ||
❑ [[Hyperkalemia]]<br> | ❑ [[Electrolyte imbalance]] e.g. [[Hyperkalemia]]<br> | ||
❑ [[Hypoglycemia]]<br> | ❑ [[Hypoglycemia]]<br> | ||
❑ [[Hypothermia]]<br> | ❑ [[Hypothermia]]<br> | ||
❑ [[Hypoxemia]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Sick sinus syndrome]]<br> | |||
❑ [[Toxins]]<br> | ❑ [[Toxins]]<br> | ||
</div>}} | </div>}} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | |!| | | | | }} | {{Family tree | | | | |!| | | | | }} | ||
{{Family tree | | | | C01 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% "> '''Determine signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability''' <br> ❑ [[Hypotension]] <br> ❑ Acutely altered mental status <br> ❑ Signs of [[shock]] <br> ❑ [[Ischemia|Ischemic]] chest discomfort <br> ❑ Acute [[heart failure]]</div>}} | {{Family tree | | | | C01 | | | |C01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% "> '''Determine signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability''' <br> ❑ [[Hypotension]] <br> ❑ Acutely altered mental status <br> ❑ Signs of [[shock]] <br> ❑ [[Ischemia|Ischemic]] chest discomfort <br> ❑ Acute [[heart failure]]</div>}} | ||
{{Family tree | |,|-|-|^|-|-|.| | }} | {{Family tree | |,|-|-|^|-|-|.| | }} | ||
{{Family tree | D01 | | | | D02 |D01= '''Unstable'''| D02= '''Stable'''}} | {{Family tree | D01 | | | | D02 |D01= '''Unstable'''| D02= '''Stable'''}} | ||
{{ | {{family tree | |!| | | | | |!| |}} | ||
{{ | {{family tree | X01 | | | | X02 | |X01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; width: 20em; padding:1em;">'''<br> | ||
'''[[Bradycardia resident survival guide#Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation|Continue with focused initial rapid evaluation above]]''' </div>|X02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% "> <br> ❑ Close follow up and monitoring <br> ❑ Identify and treat underlying causes</div>}} | |||
{{ | {{family tree | |,|-|-|-|v|-|^|-|v|-|-|-|.| |}} | ||
{{ | {{family tree | Y01 | | Y02 | | Y03 | | Y04 | |Y01=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''[[Sinus node dysfunction]]''' <br> | ||
❑ Treat underlying cause <br> | |||
:❑ Withdrawal of [[medication]] <br> | |||
:❑ Administer electrolytes to correct for imbalance <br> | |||
:❑ Correction of thyroid dysfunction <br> | |||
:❑ Correction of [[hypoglycemia]] <br> | |||
❑ Give [[Theophylline]] 200-400mg PO twice daily for [[fatigue]] and/or [[dizziness]] <br> ❑ [[artificial pacemaker|Temporary pacing]] for severe symptoms <br> ❑ [[artificial pacemaker|Permanent pacing]] for irreversible causes with severe symptoms (e.g. [[Sinus node dysfunction]] with [[AV block]] or [[Afib]]</div>|Y02=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''[[AV Block]]''' <br> '''Acquired or Congenital''' <br> ❑ Treat underlying cause <br> ❑ [[artificial pacemaker|Temporary pacing]] if indicated <br> ❑ Reassurance for irreversible causes without indication for pacing <br> ❑ [[artificial pacemaker|Permanent pacing]] for symptomatic irreversible causes</div>|Y03= '''[[Carotid sinus hypersensitivity]]''' <br> [[artificial pacemaker|Permanent pacing]]|Y04=<div style="float: left; text-align: left; line-height: 150% ">'''[[Neurocardiogenic syncope]]''' <br> | |||
❑ Lifestyle modification <br> | |||
:❑ Adequate salt and fluid intake <br> | |||
:❑ Elevation of legs, lying down and tensing maneuvers <br> | |||
:❑ Avoid precipitating factors <br> | |||
❑ [[Fludrocortisone]] 0.1-0.2mg PO once daily <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ [[Midodrine]] 2.5-10mg PO tid <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ [[Fluoxetine]] 20mg PO once daily <br> OR <br> | |||
❑ [[artificial pacemaker|Permanent pacing]]</div>}} | |||
{{Family tree/end}} | {{Family tree/end}} | ||
| Line 232: | Line 250: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | |||
{{WS}} | |||
</div> | |||
[[CME Category::Cardiology]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | [[Category:Disease]] | ||
[[Category:Resident survival guide]] | [[Category:Resident survival guide]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
[[Category:Emergency medicine]] | [[Category:Emergency medicine]] | ||
[[Category:Arrhythmia]] | [[Category:Arrhythmia]] | ||
| Line 242: | Line 264: | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date cardiology]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date cardiology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:23, 15 March 2016
| Bradycardia Resident Survival Guide Microchapters |
|---|
| Overview |
| Causes |
| FIRE |
| Diagnosis |
| Treatment |
| Do's |
| Don'ts |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]: Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ogheneochuko Ajari, MB.BS, MS [2]; Vidit Bhargava, M.B.B.S [3]
Overview
Bradycardia is defined as a sinus rhythm with a rate < 60 beats per minute. A heart rate of < 50 beats per minute is used as a working definition of bradycardia causing symptoms.[1] The evaluation of bradycardia includes assessment of heart rhythm, symptoms and associated medical conditions. The management of symptomatic bradycardia typically involves treating the underlying causes, the use of medications (e.g. atropine) or insertion of temporary or permanent pacemaker. Nevertheless, some asymtomatic bradycardias may require treatment to prevent complications.
Causes
Life Threatening Causes
Life-threatening causes include conditions which may result in death or permanent disability within 24 hours if left untreated.
Common Causes
Click here for the complete list of causes.
FIRE: Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation
A Focused Initial Rapid Evaluation (FIRE) should be performed to identify patients in need of immediate intervention. The initial rapid evaluation is based on the 2005 AHA guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care.[2]
Boxes in red signify that an urgent management is needed.
Abbreviations: IV: Intravenous; ECG: Electrocardiogram
Identify cardinal findings that increase the pretest probability of bradycardia ❑ Heart rate < 50 beats/min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Does the patient have any of the following findings of hemodyanamic instability that require urgent treatment? ❑ Shock ❑ Altered mental status ❑ Hypotension ❑ Hypothermia ❑ Oliguria | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Initial Stabilization Do the following simultaneously without delaying the treatment ❑ Maintain patent airway ❑ Assist breathing if required ❑ Place patient on cardiac monitor ❑ Give supplemental oxygen ❑ Monitor blood pressure and evaluate oxyhemoglobin saturation ❑ Establish IV access ❑ Obtain ECG to define rhythm ❑ Evaluate clinical status and identify reversible causes simultaneously | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Is there an AV block? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
No | Yes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Second degree AV block/Third-degree AV block | First degree AV block | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
First Line Treatment Option ❑ Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV bolus and repeat every 3-5 mins with a maximum dose of 3 mg Second Line Treatment Options ❑ Administer Dopamine infusion (2-10 mcg/kg/min) (Class IIa, level of evidence B) | DO NOT GIVE ATROPINE ❑ Proceed with transcutaneous pacing | First Line Treatment Option ❑ Administer atropine 0.5 mg IV bolus and repeat every 3-5 mins with a maximum dose of 3 mg Second Line Treatment Options ❑ Administer Dopamine infusion (2-10 mcg/kg/min) (Class IIa, level of evidence B) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Are the signs of poor perfusion or shock persisting? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ❑ Consult a cardiologist and ❑ Prepare patient for transvenous pacing | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Complete Diagnostic Approach
A complete diagnostic approach should be carried out after a focused initial rapid evaluation is conducted and following initiation of any urgent intervention.[1][3]
Abbreviations: CK-MB: Creatine kinase myocardial type; ECG: Electrocardiogram; TSH: Thyroid stimulating hormone
Characterize the symptoms: ❑ Lightheadedness or dizziness ❑ Past medical history
| |||||||||||||||
Examine the patient: Vitals
Skin
❑ Palpation
Neck
Respiratory examination
❑ Auscultation
Cardiovascular examination
Abdominal examination
Extremities
| |||||||||||||||
Consider alternative diagnosses: ❑ Ventricular bigeminy ❑ Frequent premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) ❑ Atrial fibrillation ❑ Blocked premature atrial contractions (PACs) ❑ Cardiac tamponade | |||||||||||||||
Order tests: First initial test ❑ 12-lead ECG (to determine rhythm) 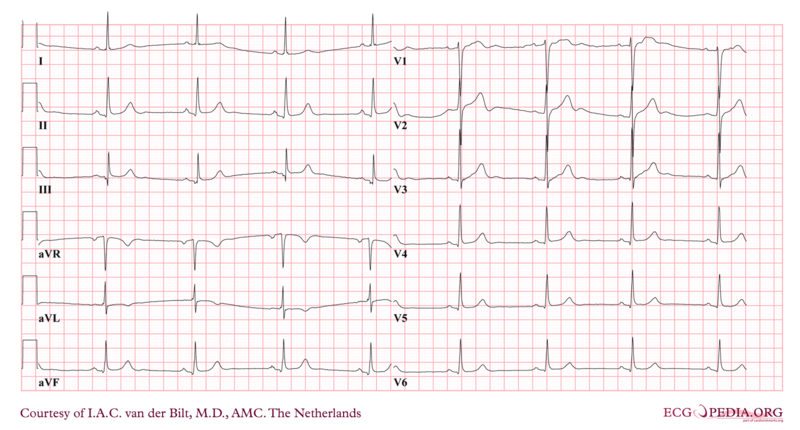 Other initial tests
❑ Exercise stress testing (for diagnoses of sick sinus syndrome and ischemic heart disease) | |||||||||||||||
Treatment
Shown below is an algorithm depicting the treatment of bradycardia based on the 2010 AHA guidelines for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care.[1]
| Bradycardia/Bradyarrhythmia with heart rate < 60/min | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Identify underlying causes: ❑ Acidosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Determine signs and symptoms of hemodynamic instability ❑ Hypotension ❑ Acutely altered mental status ❑ Signs of shock ❑ Ischemic chest discomfort ❑ Acute heart failure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unstable | Stable | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
❑ Close follow up and monitoring ❑ Identify and treat underlying causes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sinus node dysfunction ❑ Treat underlying cause
❑ Temporary pacing for severe symptoms ❑ Permanent pacing for irreversible causes with severe symptoms (e.g. Sinus node dysfunction with AV block or Afib | AV Block Acquired or Congenital ❑ Treat underlying cause ❑ Temporary pacing if indicated ❑ Reassurance for irreversible causes without indication for pacing ❑ Permanent pacing for symptomatic irreversible causes | Carotid sinus hypersensitivity Permanent pacing | Neurocardiogenic syncope ❑ Lifestyle modification
❑ Fludrocortisone 0.1-0.2mg PO once daily | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Do's
- Prepare for transcutaneous pacing if perfusion is poor.
- Consider using sodium bicarbonate for severe metabolic acidosis.
- Use atropine with caution in the presence of myocardial ischemia and acute coronary syndrome because it increases oxygen demand and could worsen the ischemia and increase infarction size.[1]
- Consider immediate pacing in unstable patients with high degree AV block when IV access isn't available.(Class IIb, level of evidence C)[1]
Don'ts
- Do not treat asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic patients, unless the rhythm is likely to progress to symptoms or become life threatening.[1]
- Do not delay pacing if the rhythm is Mobitz type II second degree block or third-degree AV block even if the patient is asymptomatic.
- Do not use atropine in hypothermic patients with either bradycardia or Mobitz type II second degree AV block.
- Do not use atropine to treat bradycardia in cardiac transplant patients as the transplanted heart lacks vagal innervation.[1]
- Do not use atropine to treat type II second degree and third degree heart blocks since their management requires transcutaneous/transvenous pacing.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Neumar, RW.; Otto, CW.; Link, MS.; Kronick, SL.; Shuster, M.; Callaway, CW.; Kudenchuk, PJ.; Ornato, JP.; McNally, B. (2010). "Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation. 122 (18 Suppl 3): S729–67. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970988. PMID 20956224. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ "Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia". Circulation. 112 (24_suppl): IV-67–IV-77. 2005. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558. ISSN 0009-7322.
- ↑ "Part 7.3: Management of Symptomatic Bradycardia and Tachycardia". Circulation. 112 (24_suppl): IV-67–IV-77. 2005. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.166558. ISSN 0009-7322.