Behçet's disease physical examination: Difference between revisions
Hamid Qazi (talk | contribs) |
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{ | {{Behçet's disease}} | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{HQ}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{HQ}}, {{JH}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Patients with | Patients with Behçet disease usually appear normal. Vital signs of patients with Behçet disease are usually normal. The presence of [[Oral ulcer|mouth sores]], [[Genital ulcer|genital ulcers]], and [[Visual impairment|vision problems]] on physical examination are diagnostic of Behçet disease. [[Skin]] examination of patients with Behçet disease shows [[erythema nodosum]] [[Lesion|lesions]] typically occur on the [[Limb (anatomy)|extremities]], especially the lower legs, but they can also be observed on the [[face]], [[neck]], and [[buttocks]]. The [[Lesion|lesions]] are [[Pain|painful]] and resolve spontaneously, although some may [[Ulcer|ulcerate]] or leave [[hyperpigmentation]]. A [[folliculitis]] like [[rash]], resembling [[Acne vulgaris|acne]] [[Acne Vulgaris|vulgaris]], appears on the [[face]], [[neck]], [[chest]], [[Human back|back]], and [[Stress fracture|hairline]] of patients. Some lesions become more [[Rash|pustular]]; 24-48 hours after a [[Sterility|sterile]] [[needle]] prick, some patients develop [[erythema]] with a [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] or [[Abscess|pustule]] at the prick site. Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of [[retinal]] [[vasculitis]], and vaso-occlusive [[Lesion|lesions]]. [[Uveitis]] of anterior and posterior chambers diagnosed with [[Slit lamp|slit-lamp]] examination. [[Erythema|Erythematous]] throat with [[Tonsillitis|tonsillar]] [[Edema|swelling]], and [[Exudate|exudates]]. [[Ulcer|Ulcers]] 2-15 mm in diameter, with a [[Necrosis|necrotic]] center and surrounding red rim. A white or yellow pseudomembrane covers the surface of the [[ulcer]]. The [[Ulcer|ulcers]] are typically [[Pain|painful]], nonscarring, and found on the lips, [[buccal mucosa]], [[tongue]], [[Tonsil|tonsils]], and [[larynx]]. Most last 7-14 days and occur in crops. [[Hypopyon]] may be observed in the [[anterior chamber]]. [[Genitourinary system|Genitourinary]] examination of patients with Behçet disease will show [[Ulcer|ulcers]] on the [[scrotum]] and [[vulva]], [[Pain|painful]] and heal with [[Scar|scarring]]. [[Sex organ|Genital]] [[Ulcer|ulcerations]] tend to be deeper and larger than the [[oral lesions]]. Females can have asymptomatic [[Ulcer|ulcers]]. [[Neuromuscular junction|Neuromuscular]] examination of patients with Behçet disease will show [[CNS]] involvement in 25% of the cases. [[Immune-mediated disease|Immune-mediated]] [[meningoencephalitis]] predominantly involves the [[Brain stem|brainstem]]. [[Meningitis]], [[encephalitis]], focal [[Neurology|neurological]] deficits, and [[psychiatric]] symptoms can be present. Irreversible [[dementia]] can occur. | ||
The | |||
The | |||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
Physical examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually remarkable for: [[Skin lesion|skin lesions]], [[Genital ulcer|genital lesions]], and [[Neuromuscular disease|neuromuscular]] complications.<ref name="pmid14727454">{{cite journal| author=Zouboulis CC, Vaiopoulos G, Marcomichelakis N, Palimeris G, Markidou I, Thouas B et al.| title=Onset signs, clinical course, prognosis, treatment and outcome of adult patients with Adamantiades-Behçet's disease in Greece. | journal=Clin Exp Rheumatol | year= 2003 | volume= 21 | issue= 4 Suppl 30 | pages= S19-26 | pmid=14727454 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=14727454 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19026127">{{cite journal| author=Moses Alder N, Fisher M, Yazici Y| title=Behçet's syndrome patients have high levels of functional disability, fatigue and pain as measured by a Multi-dimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ). | journal=Clin Exp Rheumatol | year= 2008 | volume= 26 | issue= 4 Suppl 50 | pages= S110-3 | pmid=19026127 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19026127 }} </ref><ref name="pmid1970380">{{cite journal| author=| title=Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. | journal=Lancet | year= 1990 | volume= 335 | issue= 8697 | pages= 1078-80 | pmid=1970380 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=1970380 }} </ref> | |||
===Appearance of the Patient=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
*Patients with | *Patients with Behçet disease usually appear normal. | ||
===Vital Signs=== | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
*Vital signs of patients with | *Vital signs of patients with Behçet disease are usually normal. | ||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
* Skin examination of patients with | * [[Skin]] examination of patients with Behçet disease shows the following: | ||
**Erythema nodosum lesions typically occur on the extremities, especially the lower legs, but they can also be observed on the face, neck, and buttocks | **[[Erythema nodosum]] lesions typically occur on the [[Limb (anatomy)|extremities]], especially the lower [[Leg|legs]], but they can also be observed on the [[face]], [[neck]], and [[buttocks]] | ||
**The lesions are painful and resolve spontaneously, although some may ulcerate or leave hyperpigmentation | **The [[Lesion|lesions]] are [[Pain|painful]] and resolve spontaneously, although some may [[Ulcer|ulcerate]] or leave [[hyperpigmentation]] | ||
**A | **A [[folliculitis]] like [[rash]], resembling [[acne vulgaris]], appears on the [[face]], [[neck]], [[chest]], [[Human back|back]], and hairline of patients | ||
**Some lesions become more pustular; 24-48 hours after a sterile needle prick, some patients develop erythema with a nodule or pustule at the prick site | **Some lesions become more [[Rash|pustular]]; 24-48 hours after a [[Sterility|sterile]] needle prick, some patients develop [[erythema]] with a [[Nodule (medicine)|nodule]] or [[Abscess|pustule]] at the prick site | ||
===HEENT=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
*Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of [[retinal]] [[vasculitis]], vaso-occlusive lesions: | |||
**[[Uveitis]] of anterior and posterior chambers diagnosed with [[Slit lamp|slit-lamp]] examination<ref name="pmid12544711">{{cite journal| author=Kural-Seyahi E, Fresko I, Seyahi N, Ozyazgan Y, Mat C, Hamuryudan V et al.| title=The long-term mortality and morbidity of Behçet syndrome: a 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center. | journal=Medicine (Baltimore) | year= 2003 | volume= 82 | issue= 1 | pages= 60-76 | pmid=12544711 | doi= | pmc= | url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=12544711 }} </ref> | |||
*Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of retinal vasculitis, vaso-occlusive lesions | * [[Erythema|Erythematous]] throat with [[Tonsillitis|tonsillar]] [[Edema|swelling]], and [[Exudate|exudates]]: | ||
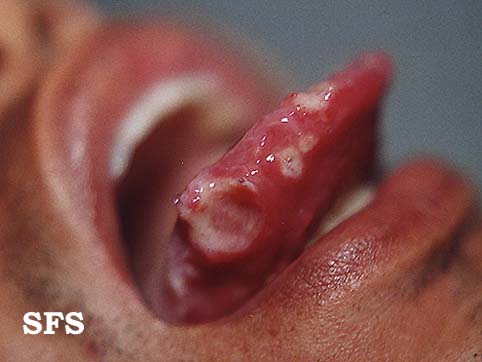
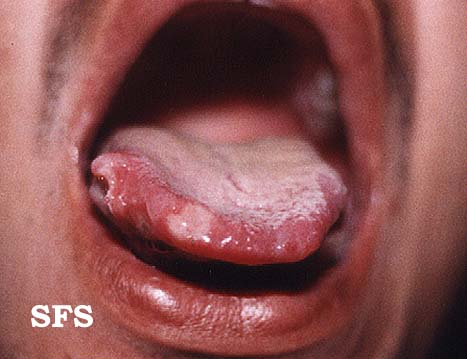
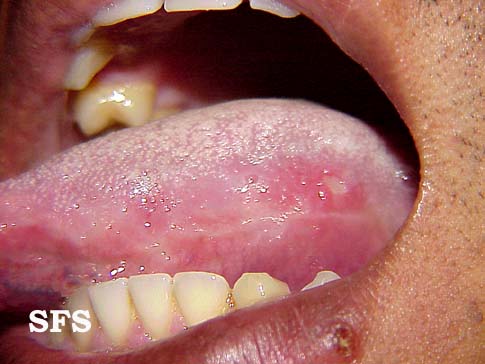
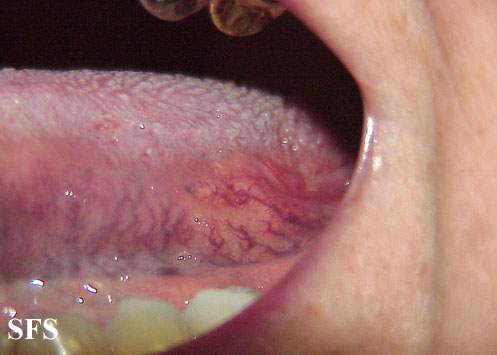
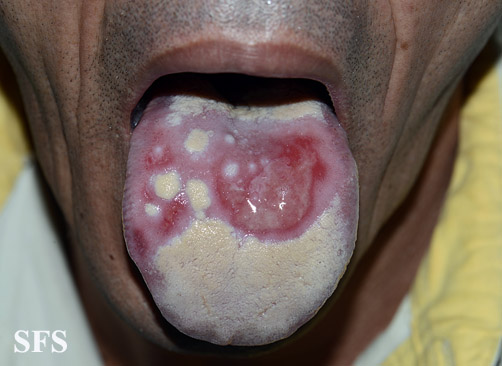
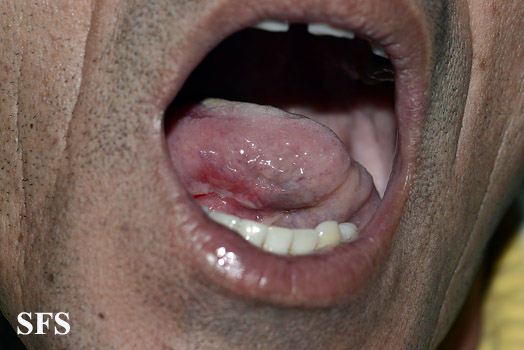
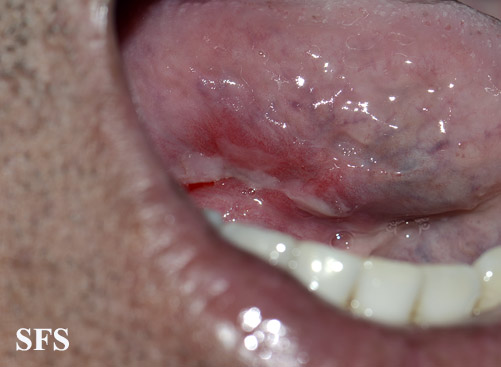
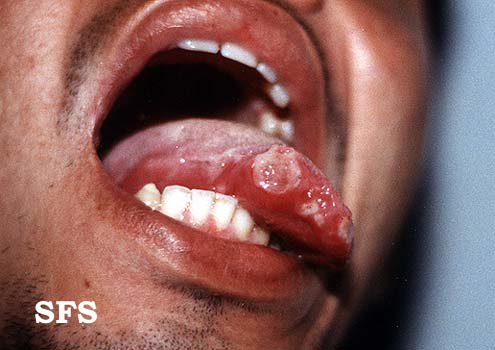
**Uveitis of anterior and posterior chambers diagnosed with slit-lamp examination | **[[Ulcer|Ulcers]] 2-15 mm in diameter, with a [[Necrosis|necrotic]] center and surrounding red rim | ||
* Erythematous throat with tonsillar swelling, and exudates | **A white or yellow pseudomembrane covers the surface of the [[ulcer]] | ||
**Ulcers 2-15 mm in diameter, with a necrotic center and surrounding red rim | **The [[Ulcer|ulcers]] are typically [[Pain|painful]], nonscarring, and found on the lips, [[buccal mucosa]], [[tongue]], [[Tonsil|tonsils]], and [[larynx]] | ||
**A white or yellow pseudomembrane covers the surface of the ulcer | |||
**The ulcers are typically painful, nonscarring, and found on the lips, buccal mucosa, tongue, tonsils, and larynx | |||
**Most last 7-14 days and occur in crops | **Most last 7-14 days and occur in crops | ||
* | *[[Hypopyon]] may be observed in the [[anterior chamber]]. | ||
===Neck=== | ===Neck=== | ||
* Neck examination of patients with | * Neck examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal. | ||
===Lungs=== | ===Lungs=== | ||
* Pulmonary examination of patients with | * Pulmonary examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal. | ||
===Heart=== | ===Heart=== | ||
*[[Circulatory system|Cardiovascular]] examination of patients with | *[[Circulatory system|Cardiovascular]] examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal. | ||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
Abdominal examination of patients with | * Abdominal examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal. | ||
===Back=== | ===Back=== | ||
* Back examination of patients with | * Back examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal. | ||
===Genitourinary=== | ===Genitourinary=== | ||
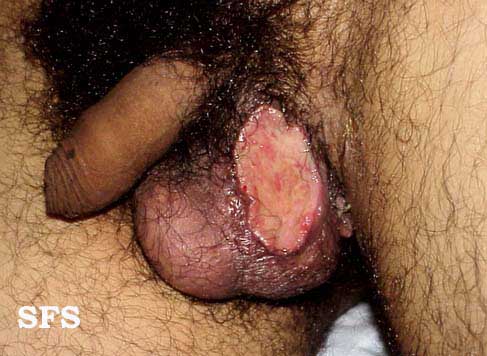
* Genitourinary examination of patients with | * Genitourinary examination of patients with Behçet disease will show: | ||
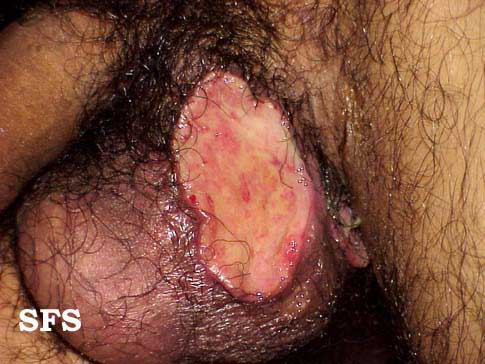
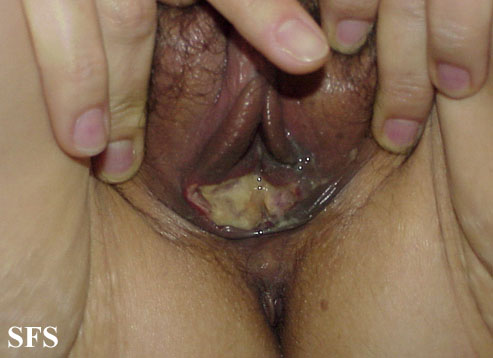
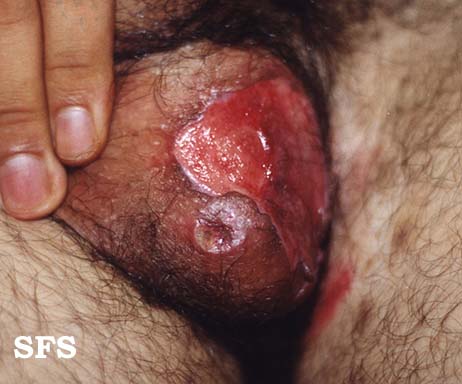
**Ulcers on the scrotum and vulva, painful and heal with scarring | **[[Ulcer|Ulcers]] on the [[scrotum]] and [[vulva]], [[Pain|painful]] and heal with [[Scar|scarring]] | ||
**Genital ulcerations tend to be deeper and larger than the oral lesions | **[[Sex organ|Genital]] [[Ulcer|ulcerations]] tend to be deeper and larger than the oral lesions | ||
**Females can have asymptomatic ulcers | **[[Female|Females]] can have asymptomatic [[Ulcer|ulcers]] | ||
===Neuromuscular=== | ===Neuromuscular=== | ||
* Neuromuscular examination of patients with | * [[Neuromuscular]] examination of patients with Behçet disease will show the following: | ||
**[[CNS]] involvement occurs in 25% of the cases | |||
**[[Immune-mediated disease|Immune-mediated]] [[meningoencephalitis]] predominantly involves the [[brain stem]] | |||
**[[Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis|Dural venous sinus thrombosis]] | |||
**[[Meningitis]], [[encephalitis]], focal [[Neurology|neurological]] deficits, and [[psychiatric]] symptoms | |||
**Irreversible [[dementia]] | |||
* | |||
* | |||
CNS involvement occurs in | |||
===Extremities=== | ===Extremities=== | ||
*Monoarthritis or polyarthritis | *[[Monoarthritis]] or [[polyarthritis]] | ||
*Knees are the most commonly affected joints, followed by wrists, ankles, and elbows | *[[Knee|Knees]] are the most commonly affected [[Joint|joints]], followed by [[Wrist|wrists]], [[Ankle|ankles]], and [[Elbow|elbows]] | ||
*The arthritis is typically nonerosive | *The [[arthritis]] is typically nonerosive | ||
===Gallery=== | ===Gallery=== | ||
==== | [[File:Behcet's syndrome 01.jpeg|200x200px|thumb|left|Oral ulcer [http://atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=53 Source:Created by Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D. in homage to The Master And Professor Delso Bringel Calheiros]]] | ||
<br clear="left" /> | |||
[[File:Behcet's syndrome 03.jpeg|200x200px|thumb|left|Genital ulcer [http://atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=53 Source:Created by Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D. in homage to The Master And Professor Delso Bringel Calheiros]]] | |||
<br clear="left" /> | |||
[[File:Behcet's syndrome 10.jpeg|200x200px|thumb|left|Penile ulcer [http://atlasdermatologico.com.br/disease.jsf?diseaseId=53 Source:Created by Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D. in homage to The Master And Professor Delso Bringel Calheiros]]] | |||
<br clear="left" /> | |||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
| Line 137: | Line 115: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
{{WH}} | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | {{WS}} | ||
[[Category: | |||
[[Category:Medicine]] | |||
[[Category:Up-To-date]] | |||
[[Category:Dermatology]] | [[Category:Dermatology]] | ||
[[Category:Rheumatology]] | [[Category:Rheumatology]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:36, 29 July 2020
|
Behçet's disease Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Behçet's disease physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Behçet's disease physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Behçet's disease physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Hamid Qazi, MD, BSc [2], Jesus Rosario Hernandez, M.D. [3]
Overview
Patients with Behçet disease usually appear normal. Vital signs of patients with Behçet disease are usually normal. The presence of mouth sores, genital ulcers, and vision problems on physical examination are diagnostic of Behçet disease. Skin examination of patients with Behçet disease shows erythema nodosum lesions typically occur on the extremities, especially the lower legs, but they can also be observed on the face, neck, and buttocks. The lesions are painful and resolve spontaneously, although some may ulcerate or leave hyperpigmentation. A folliculitis like rash, resembling acne vulgaris, appears on the face, neck, chest, back, and hairline of patients. Some lesions become more pustular; 24-48 hours after a sterile needle prick, some patients develop erythema with a nodule or pustule at the prick site. Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of retinal vasculitis, and vaso-occlusive lesions. Uveitis of anterior and posterior chambers diagnosed with slit-lamp examination. Erythematous throat with tonsillar swelling, and exudates. Ulcers 2-15 mm in diameter, with a necrotic center and surrounding red rim. A white or yellow pseudomembrane covers the surface of the ulcer. The ulcers are typically painful, nonscarring, and found on the lips, buccal mucosa, tongue, tonsils, and larynx. Most last 7-14 days and occur in crops. Hypopyon may be observed in the anterior chamber. Genitourinary examination of patients with Behçet disease will show ulcers on the scrotum and vulva, painful and heal with scarring. Genital ulcerations tend to be deeper and larger than the oral lesions. Females can have asymptomatic ulcers. Neuromuscular examination of patients with Behçet disease will show CNS involvement in 25% of the cases. Immune-mediated meningoencephalitis predominantly involves the brainstem. Meningitis, encephalitis, focal neurological deficits, and psychiatric symptoms can be present. Irreversible dementia can occur.
Physical Examination
Physical examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually remarkable for: skin lesions, genital lesions, and neuromuscular complications.[1][2][3]
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with Behçet disease usually appear normal.
Vital Signs
- Vital signs of patients with Behçet disease are usually normal.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with Behçet disease shows the following:
- Erythema nodosum lesions typically occur on the extremities, especially the lower legs, but they can also be observed on the face, neck, and buttocks
- The lesions are painful and resolve spontaneously, although some may ulcerate or leave hyperpigmentation
- A folliculitis like rash, resembling acne vulgaris, appears on the face, neck, chest, back, and hairline of patients
- Some lesions become more pustular; 24-48 hours after a sterile needle prick, some patients develop erythema with a nodule or pustule at the prick site
HEENT
- Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of retinal vasculitis, vaso-occlusive lesions:
- Erythematous throat with tonsillar swelling, and exudates:
- Hypopyon may be observed in the anterior chamber.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal.
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal.
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal.
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal.
Back
- Back examination of patients with Behçet disease is usually normal.
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with Behçet disease will show:
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with Behçet disease will show the following:
- CNS involvement occurs in 25% of the cases
- Immune-mediated meningoencephalitis predominantly involves the brain stem
- Dural venous sinus thrombosis
- Meningitis, encephalitis, focal neurological deficits, and psychiatric symptoms
- Irreversible dementia
Extremities
- Monoarthritis or polyarthritis
- Knees are the most commonly affected joints, followed by wrists, ankles, and elbows
- The arthritis is typically nonerosive
Gallery
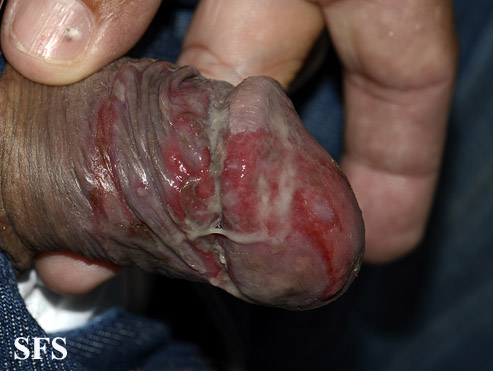
Genital area
References
- ↑ Zouboulis CC, Vaiopoulos G, Marcomichelakis N, Palimeris G, Markidou I, Thouas B; et al. (2003). "Onset signs, clinical course, prognosis, treatment and outcome of adult patients with Adamantiades-Behçet's disease in Greece". Clin Exp Rheumatol. 21 (4 Suppl 30): S19–26. PMID 14727454.
- ↑ Moses Alder N, Fisher M, Yazici Y (2008). "Behçet's syndrome patients have high levels of functional disability, fatigue and pain as measured by a Multi-dimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ)". Clin Exp Rheumatol. 26 (4 Suppl 50): S110–3. PMID 19026127.
- ↑ "Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease". Lancet. 335 (8697): 1078–80. 1990. PMID 1970380.
- ↑ Kural-Seyahi E, Fresko I, Seyahi N, Ozyazgan Y, Mat C, Hamuryudan V; et al. (2003). "The long-term mortality and morbidity of Behçet syndrome: a 2-decade outcome survey of 387 patients followed at a dedicated center". Medicine (Baltimore). 82 (1): 60–76. PMID 12544711.