Bradycardia: Difference between revisions
(→Causes) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
===Causes in Alphabetical Order=== | ===Causes in Alphabetical Order=== | ||
Revision as of 03:58, 27 August 2012
| Bradycardia | |
| ICD-10 | R00.1 |
|---|---|
| ICD-9 | 427.81, 659.7, 785.9, 779.81 |
|
Bradycardia Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Bradycardia On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Bradycardia |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: M.Umer Tariq [2]
Overview
Causes
Causes in Alphabetical Order
Epidemiology and Demographics
Bradycardia is more common in older patients.
Diagnosis
Evaluation of bradycardia includes assessment of the heart rhythm, symptoms, medications, and associated medical conditions (reversible and irreversible). Symptomatic bradycardias are treated by removal of the underlying causes, medications (atropine) or insertion of a temporary or permanent pacemaker. The term relative bradycardia is used to explain a heart rate that, while not technically below 60 beats per minute, is considered too slow for the individual's current medical condition.
Symptoms
- Presyncope
- Syncope
- Fatigue
- Angina
- Symptoms of congestive heart failure
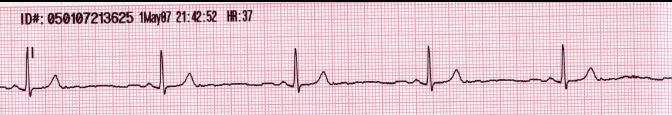
Resting EKG
The heart rate is < 60 beats per minute.
24 Hour Ambulatory Electrocardiogram Monitoring
The diagnosis is usually made with the help of a 24-hour ambulatory electrocardiogram (ECG) or telemetry.
Treatment
Urgent Treatment
- Check drug list and remove drugs predisposing to bradycardia like beta blockers, calcium channel blocker, anti-arrhythmic drug.
- Drug treatment for bradycardia is typically not indicated for patients who are asymptomatic.
- In symptomatic patients, underlying electrolyte or acid-base disorders or hypoxia should be corrected first.
- IV atropine may provide temporary improvement in symptomatic patients, although its use should be balanced by an appreciation of the increase in myocardial oxygen demand this agent causes. Atropine 0.5-1 mg IV or ET q3-5min up to 3 mg total (0.04 mg/kg)
Indications For a Temporary Pacemaker
Advanced heart block such as complete heart block is an indication for a temporary pacemaker insertion.
Chronic Management
There are two main reasons for treating brandycardia:
- With bradycardia, the first is to address the associated symptoms, such as fatigue, limitations on how much an individual can physically exert, fainting (syncope), dizziness or lightheadedness, or other vague and non-specific symptoms.
- The other reason to treat bradycardia is if the person's ultimate outcome (prognosis) will be changed or impacted by the bradycardia.
Treatment in this vein depends on whether any symptoms are present, and what the underlying cause is. Primary or idiopathic bradycardia is treated symptomatically if it is significant, and the underlying cause is treated if the bradycardia is secondary.
See also
References
- ↑ Pagon RA, Bird TD, Dolan CR; et al. PMID 20301600. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - ↑ Goldstein S, Qazi QH, Fitzgerald J, Goldstein J, Friedman AP, Sawyer P (1985). "Distichiasis, congenital heart defects and mixed peripheral vascular anomalies". Am. J. Med. Genet. 20 (2): 283–94. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320200212. PMID 3976722. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help)
de:Bradykardie it:Bradicardia nl:Bradycardie nn:Bradykardi sk:Bradykardia sv:Bradykardi