Endocarditis physical examination: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
==Physical Examination== | ==Physical Examination== | ||
===Appearance of the Patient=== | ===Appearance of the Patient=== | ||
*Patients with | *Patients with endocarditis usually appear ill. | ||
===Vital Signs=== | ===Vital Signs=== | ||
| Line 191: | Line 37: | ||
Examine the oral cavity: | Examine the oral cavity: | ||
* Poor oral hygiene<ref name="pmid19797553">{{cite journal| author=Lockhart PB, Brennan MT, Thornhill M, Michalowicz BS, Noll J, Bahrani-Mougeot FK et al.| title=Poor oral hygiene as a risk factor for infective endocarditis-related bacteremia. | journal=J Am Dent Assoc | year= 2009 | volume= 140 | issue= 10 | pages= 1238-44 | pmid=19797553 | doi= | pmc=PMC2770162 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19797553 }} </ref><br> | * Poor oral hygiene<ref name="pmid19797553">{{cite journal| author=Lockhart PB, Brennan MT, Thornhill M, Michalowicz BS, Noll J, Bahrani-Mougeot FK et al.| title=Poor oral hygiene as a risk factor for infective endocarditis-related bacteremia. | journal=J Am Dent Assoc | year= 2009 | volume= 140 | issue= 10 | pages= 1238-44 | pmid=19797553 | doi= | pmc=PMC2770162 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19797553 }} </ref><br> | ||
* [[Teeth]] looking for [[periodontitis]], [[plaque]] and [[calculus]]<ref name="pmid19797553" | * [[Teeth]] looking for [[periodontitis]], [[plaque]] and [[calculus]]<ref name="pmid19797553" /><BR> | ||
* [[Gingiva]] looking for [[gingivitis]]<ref name="pmid19797553" | * [[Gingiva]] looking for [[gingivitis]]<ref name="pmid19797553" /><BR> | ||
* Recent dental procedure | * Recent dental procedure | ||
=== | * | ||
===HEENT=== | |||
*[[Conjunctival hemorrhage]] | *[[Conjunctival hemorrhage]] | ||
*[[Roth's spot]]s in the [[retina]] | *[[Roth's spot]]s in the [[retina]] | ||
<br | *Bobbing of the [[uvula]] may be present among patients with new onset [[aortic regurgitation]]. | ||
<br />[[Image:Roth-spot (white-centered hemorrhage - endocarditis).jpg|left|150px|[[Roth's spot]]s (white centered hemorrhage)|thumb]] | |||
=== | <br /> | ||
* | ===Neck=== | ||
* Neck examination of patients with endocarditis is usually normal. | |||
===Lungs=== | ===Lungs=== | ||
*Signs of [[heart failure]] such as [[rales]] may present | *Signs of [[heart failure]] such as [[rales]] may present | ||
===Heart=== | |||
*Heart [[murmur]]s are present in 80% to 85% of patients including that of [[aortic insufficiency]], [[tricuspid regurgitation]] and [[mitral regurgitation]]. | |||
===Abdomen=== | ===Abdomen=== | ||
| Line 215: | Line 78: | ||
* Left upper quadrant pain (LUQ pain) may be present as a result of a [[splenic infarct]] from embolization. | * Left upper quadrant pain (LUQ pain) may be present as a result of a [[splenic infarct]] from embolization. | ||
* [[Flank pain]] may be present as a result of an [[embolus to the kidney]]. | * [[Flank pain]] may be present as a result of an [[embolus to the kidney]]. | ||
===Back=== | |||
* Back examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal. | |||
OR | |||
*Point tenderness over __ vertebrae (e.g. L3-L4) | |||
*Sacral edema | |||
*Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally | |||
*Buffalo hump | |||
===Genitourinary=== | |||
* Genitourinary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal. | |||
OR | |||
*A pelvic/adnexal mass may be palpated | |||
*Inflamed mucosa | |||
*Clear/(color), foul-smelling/odorless penile/vaginal discharge | |||
===Neurologic=== | |||
*[[Septic emboli]] may result in [[stroke]] and focal neurologic findings | |||
*[[Seizures]] may be present | |||
*[[Intracranial hemorrhage]] may occur | |||
* Signs of a [[brain abscess]] may be present | |||
===Extremities=== | ===Extremities=== | ||
| Line 222: | Line 113: | ||
* [[Osler's node]]s ([[lesions|painful subcutaneous lesions in the distal fingers]]) | * [[Osler's node]]s ([[lesions|painful subcutaneous lesions in the distal fingers]]) | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 16:33, 6 January 2020
|
Endocarditis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Valvular Heart Disease |
|
Case Studies |
|
Endocarditis physical examination On the Web |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Endocarditis physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editors-in-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
Common signs on physical examination of endocarditis include fever, presence of a new or changing heart murmur, rigors, Osler's nodes, Janeway lesions and evidence of embolization. Aortic insufficiency with a wide pulse pressure, mitral regurgitation or tricuspid regurgitation may be present depending upon the valve that is infected.[1][2]
Physical Examination
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with endocarditis usually appear ill.
Vital Signs
- A fever will likely be present.
- Rigors may be present.
- Some patients may have a wide pulse pressure due to aortic insufficiency. If the pulse pressure narrows, this may be a sign of left ventricular failure due to earlier closure of the mitral valve and a more rapid rise in the left ventricular end diastolic pressure which will in turn raise the diastolic pressure.
Skin
- Petechiae are present in 10% to 40% of patients
- Splinter hemorrhages are present in 5% to 15% of patients
- Osler's nodes which are tender subcutaneous nodules in pulp of digits are present in 7% to 10% of patients
- Janeway lesions which are erythematous, nontender lesions on palm or sole are present in 6% to 10% of patients
| Petechiae | 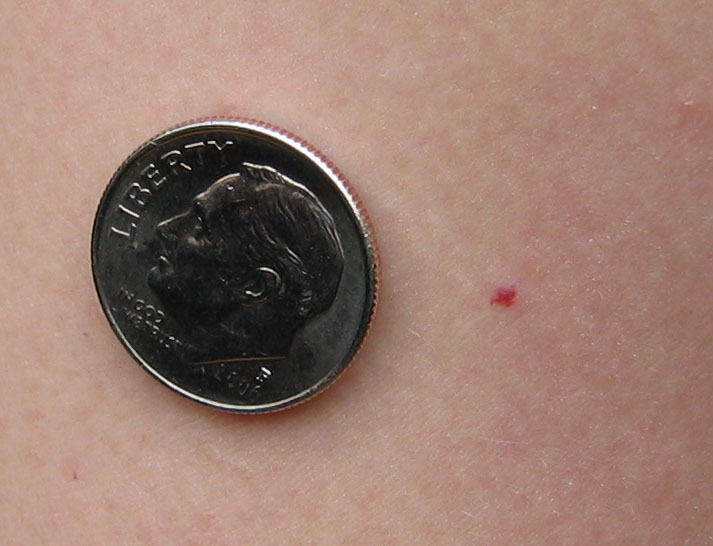
|
| Splinter hemorrhages | 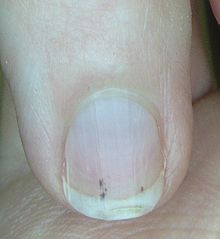
|
| Osler's nodes | 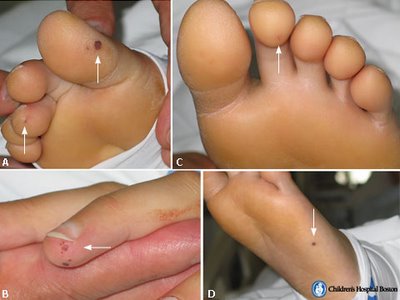
|
| Janeway lesions | 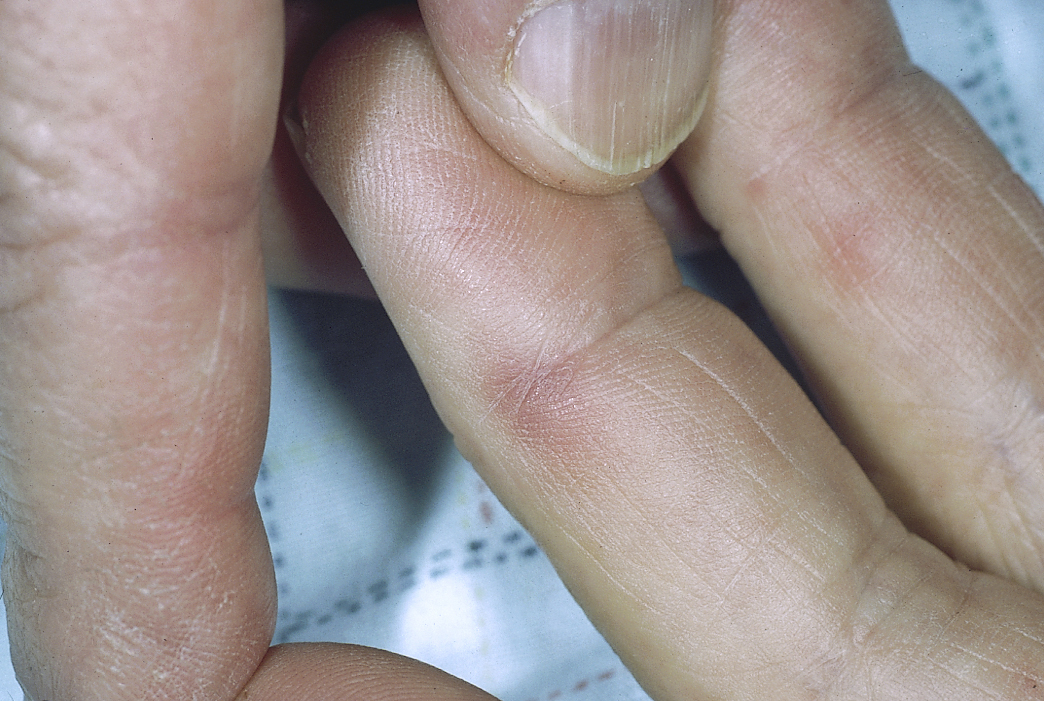
|
Oral Cavity
Examine the oral cavity:
- Poor oral hygiene[3]
- Teeth looking for periodontitis, plaque and calculus[3]
- Gingiva looking for gingivitis[3]
- Recent dental procedure
HEENT
- Conjunctival hemorrhage
- Roth's spots in the retina
- Bobbing of the uvula may be present among patients with new onset aortic regurgitation.
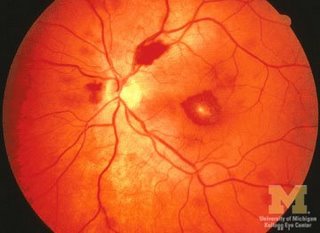
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with endocarditis is usually normal.
Lungs
- Signs of heart failure such as rales may present
Heart
- Heart murmurs are present in 80% to 85% of patients including that of aortic insufficiency, tricuspid regurgitation and mitral regurgitation.
Abdomen
- Abdominal pain may be present due to mesenteric embolization or ileus both of which may manifest as reduced bowel sounds.
- Splenomegaly may be present in 15% to 30% patients.
- Left upper quadrant pain (LUQ pain) may be present as a result of a splenic infarct from embolization.
- Flank pain may be present as a result of an embolus to the kidney.
Back
- Back examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Point tenderness over __ vertebrae (e.g. L3-L4)
- Sacral edema
- Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally
- Buffalo hump
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- A pelvic/adnexal mass may be palpated
- Inflamed mucosa
- Clear/(color), foul-smelling/odorless penile/vaginal discharge
Neurologic
- Septic emboli may result in stroke and focal neurologic findings
- Seizures may be present
- Intracranial hemorrhage may occur
- Signs of a brain abscess may be present
Extremities
- Janeway lesions (painless hemorrhagic cutaneous lesions on the palms and soles)
- Gangrene of fingers may occur
- The fingers may show splinter haemorrhages
- Osler's nodes (painful subcutaneous lesions in the distal fingers)
References
- ↑ Infective endocarditis. Wikipedia (2015). https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Infective_endocarditis Accessed on September 23, 2015
- ↑ Baddour, LM.; Wilson, WR.; Bayer, AS.; Fowler, VG.; Bolger, AF.; Levison, ME.; Ferrieri, P.; Gerber, MA.; Tani, LY. (2005). "Infective endocarditis: diagnosis, antimicrobial therapy, and management of complications: a statement for healthcare professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, and the Councils on Clinical Cardiology, Stroke, and Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia, American Heart Association: endorsed by the Infectious Diseases Society of America". Circulation. 111 (23): e394–434. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.165564. PMID 15956145. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Lockhart PB, Brennan MT, Thornhill M, Michalowicz BS, Noll J, Bahrani-Mougeot FK; et al. (2009). "Poor oral hygiene as a risk factor for infective endocarditis-related bacteremia". J Am Dent Assoc. 140 (10): 1238–44. PMC 2770162. PMID 19797553.