Mycosis fungoides differential diagnosis: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
* [[Eczema]] | * [[Eczema]] | ||
* [[Psoriasis]] | * [[Psoriasis]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Disease | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Rash Characteristics | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Signs and Symptoms | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Associated Conditions | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Rash Appearance | |||
|- | |||
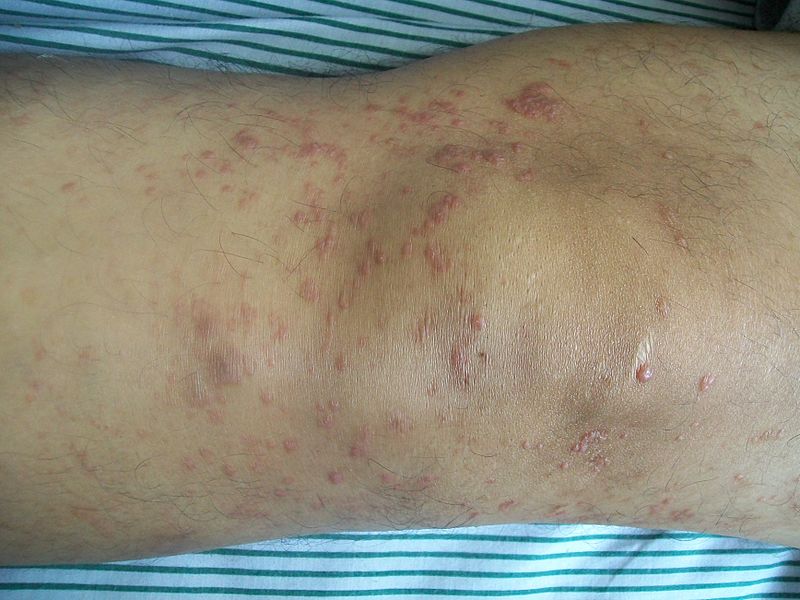
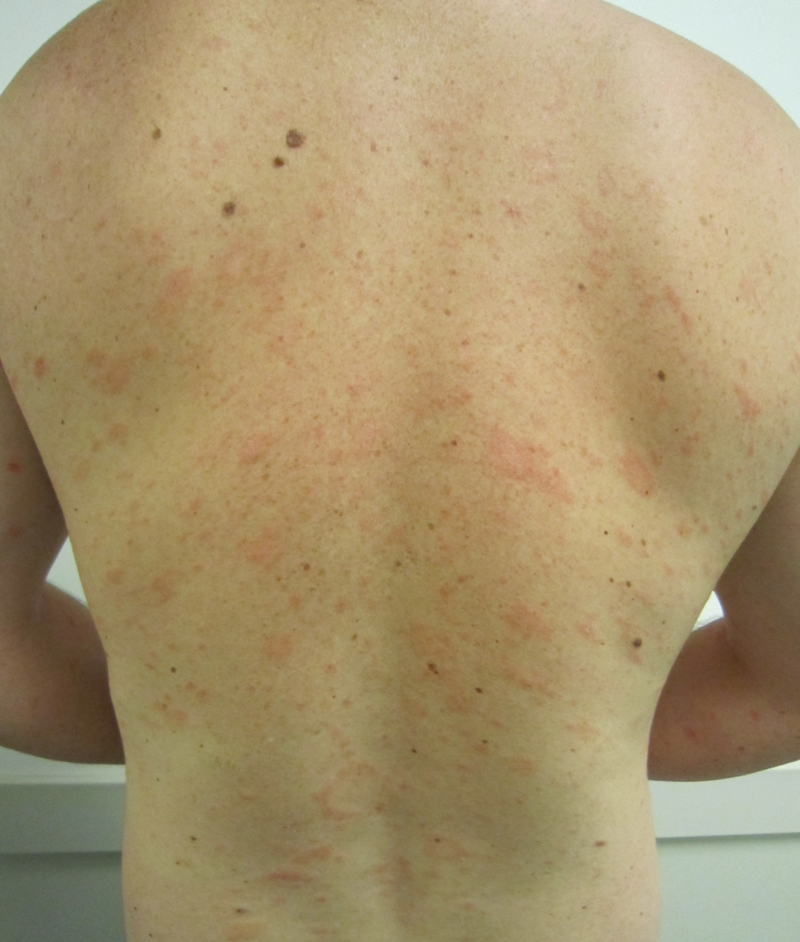
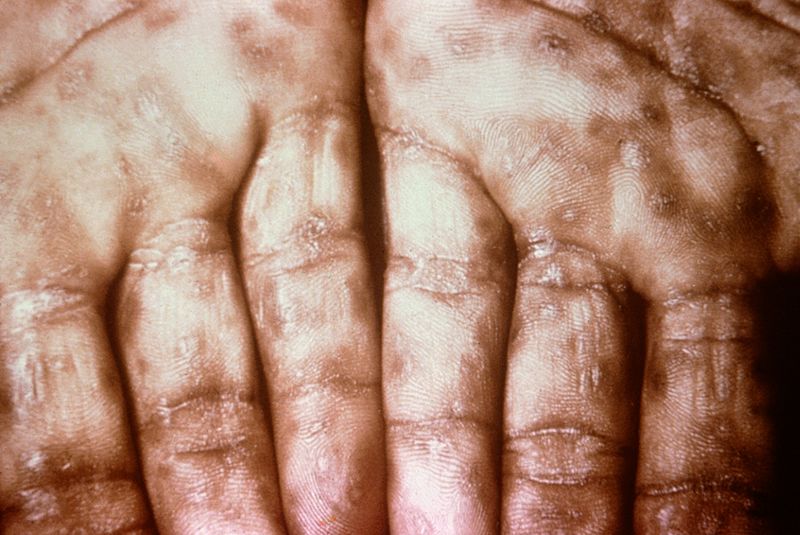
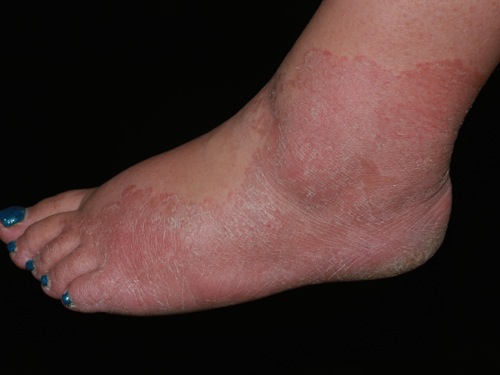
|[[Cutaneous T cell lymphoma]]/[[Mycosis fungoides]]<ref name="urlMycosis Fungoides and the Sézary Syndrome Treatment (PDQ®)—Patient Version - National Cancer Institute">{{cite web |url=https://www.cancer.gov/types/lymphoma/patient/mycosis-fungoides-treatment-pdq |title=Mycosis Fungoides and the Sézary Syndrome Treatment (PDQ®)—Patient Version - National Cancer Institute |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Premycotic phase: A scaly, red [[rash]] in areas of the [[body]] that usually are not exposed to the sun. This rash does not cause symptoms and may last for months or years. | |||
* Patch phase: Thin, reddened, [[eczema]] -like rash. | |||
* [[Plaque]] phase: Small raised [[Bumps on skin|bumps]] ([[Papule|papules]]) or hardened lesions on the skin, which may be reddened. | |||
* [[Tumor]] phase: Tumors form on the [[skin]]. These tumors may develop [[Ulcer|ulcers]]<nowiki/>and the skin may get infected. | |||
| | |||
* [[Epidermis (skin)|Epidermal]] [[atrophy]] or poikiloderma | |||
* Generalized [[itching]] ([[pruritus]]) | |||
* [[Pain]] in the affected area of the skin. | |||
* [[Insomnia]] | |||
* Red ([[erythematous]]) patches scattered over the [[skin]] of the [[trunk]] and the [[extremities]] | |||
* Tumor-like lobulated outgrowths form on the skin in the latter part of the disease | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Malaise]] and [[fatigue]] | |||
* [[Anemia]] | |||
* May progress to [[Sezary syndrome]] (Skin involvement plus hematogenous dissemination) | |||
| | |||
* [[Sezary syndrome]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Mycosis_fungoides.JPG|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Pityriasis rosea]]<ref name="pmid27512182">{{cite journal |vauthors=Mahajan K, Relhan V, Relhan AK, Garg VK |title=Pityriasis Rosea: An Update on Etiopathogenesis and Management of Difficult Aspects |journal=Indian J Dermatol |volume=61 |issue=4 |pages=375–84 |year=2016 |pmid=27512182 |pmc=4966395 |doi=10.4103/0019-5154.185699 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Pink or salmon in colour, which may be scaly, termed as "herald patch" | |||
* Oval in shape | |||
* Long axis oriented along the clevage lines | |||
* Distributed on the [[trunk]] and [[proximal extremities]] | |||
* Squamous marginal collarette and a “fir-tree” or “Christmas tree” distribution on the posterior trunk | |||
* Develops after [[viral infection]] | |||
* Resolves spontaneously after 6-8 weeks | |||
| | |||
* Preceded by a prodrome of: | |||
** [[Sore throat]] | |||
** [[Gastrointestinal tract|Gastrointestinal]] disturbance | |||
** [[Fever]] | |||
** [[Arthralgia]] | |||
| | |||
* Infection by any of the following:<ref name="pmid19997691">{{cite journal |vauthors=Prantsidis A, Rigopoulos D, Papatheodorou G, Menounos P, Gregoriou S, Alexiou-Mousatou I, Katsambas A |title=Detection of human herpesvirus 8 in the skin of patients with pityriasis rosea |journal=Acta Derm. Venereol. |volume=89 |issue=6 |pages=604–6 |year=2009 |pmid=19997691 |doi=10.2340/00015555-0703 |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Human herpesvirus 6|HHV-6]] | |||
** [[HHV-7]] | |||
** [[HHV-8]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Pityriasisrosea.png|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
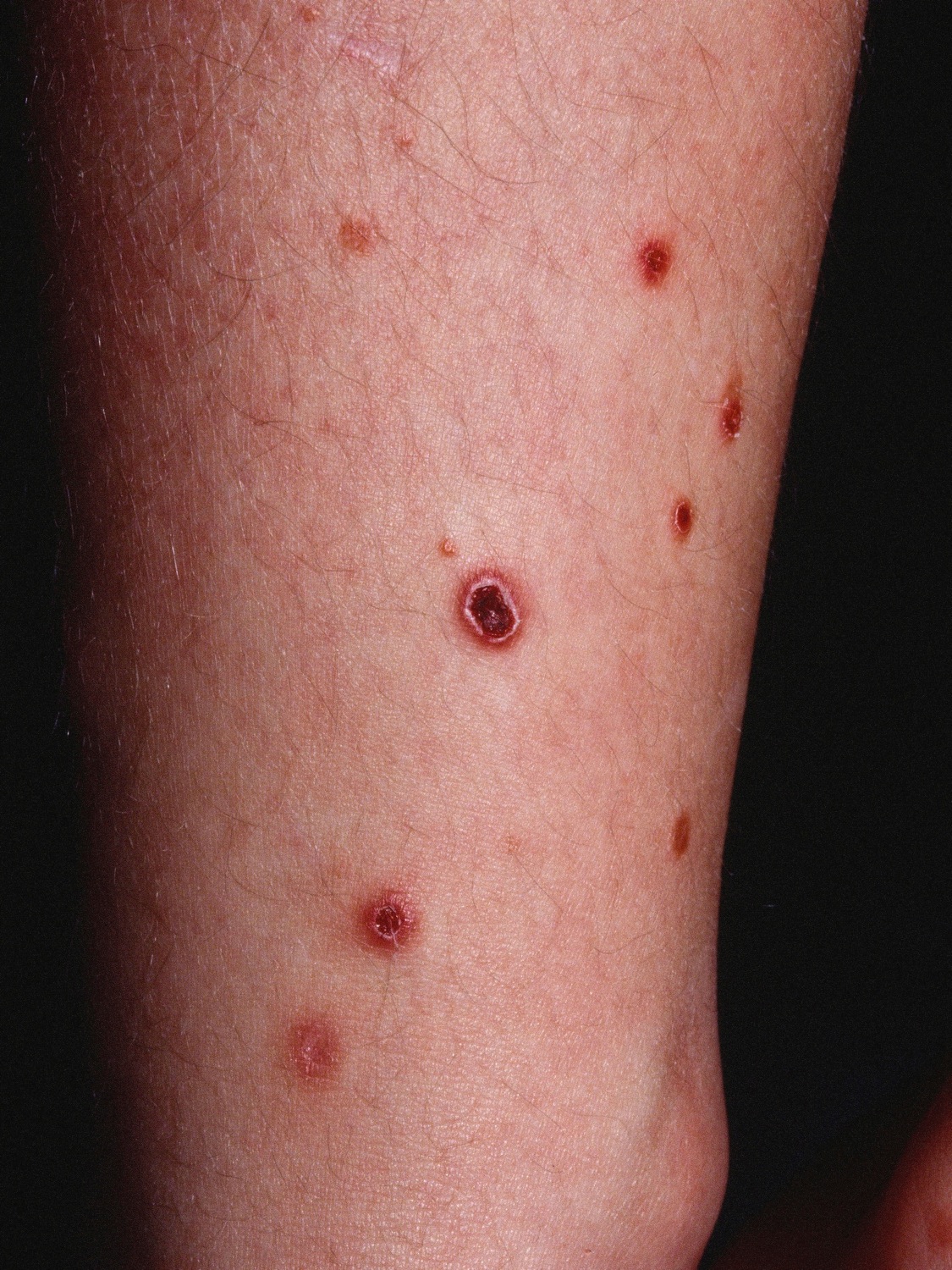
|[[Pityriasis lichenoides chronica]] | |||
| | |||
* Recurrent lesions are usually less evenly scattered than psoriasis | |||
* Brownish red or orange-brown color | |||
* Lesions are capped by a single detachable opaque mica-like scale | |||
* Often leave [[Hypopigmented area|hypopigmented]] [[Macule|macules]] | |||
| | |||
* High [[fever]] | |||
* [[Malaise]] | |||
* [[Myalgias]] | |||
* Skin burning | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
| | |||
* Infection by any of the following:<ref name="pmid9109005">{{cite journal |vauthors=Smith KJ, Nelson A, Skelton H, Yeager J, Wagner KF |title=Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta in HIV-1+ patients: a marker of early stage disease. The Military Medical Consortium for the Advancement of Retroviral Research (MMCARR) |journal=Int. J. Dermatol. |volume=36 |issue=2 |pages=104–9 |year=1997 |pmid=9109005 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Epstein Barr virus|Epstein-Barr virus]] (EBV) | |||
** ''[[Toxoplasma gondii]]'' | |||
** [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|Human immunodeficiency virus]] (HIV) | |||
| | |||
[[Image:PLEVA2.jpg|200px|courtesy http://www.regionalderm.com]] | |||
|- | |||
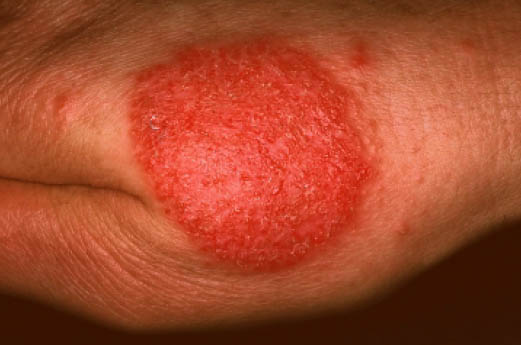
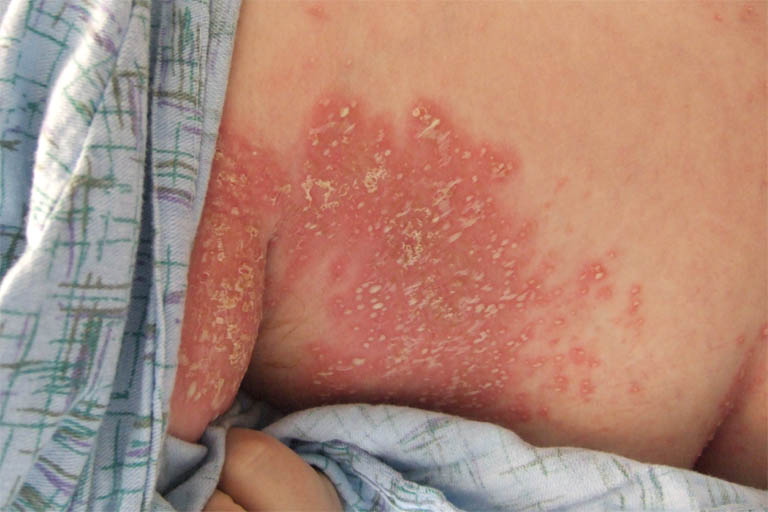
|[[Nummular dermatitis]]<ref name="pmid23517392">{{cite journal |vauthors=Jiamton S, Tangjaturonrusamee C, Kulthanan K |title=Clinical features and aggravating factors in nummular eczema in Thais |journal=Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. |volume=31 |issue=1 |pages=36–42 |year=2013 |pmid=23517392 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Multiple coinshaped [[Eczematous Scaling|eczematous]] lesions | |||
* Commonly affecting the [[extremities]] (lower>upper) and [[trunk]] | |||
* May ooze [[fluid]] and become dry and crusty | |||
| | |||
* Often appears after a skin injury, such as a [[burn]], [[abrasion]] (from friction), or [[insect bite]] | |||
* Lesions commonly relapse after occasional remission or may persist for long periods | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** Dry skin | |||
** Emotional stress | |||
** Allergens(rubber chemicals, [[formaldehyde]], [[neomycin]], chrome, [[Mercury (element)|mercury]] and [[nickel]]) | |||
** [[Staphylococcus]] infection | |||
** Seasonal variation | |||
** [[Alcohol]] | |||
** [[Drugs]] | |||
** [[Atopy]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Nummular_dermatitis_eczematous.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
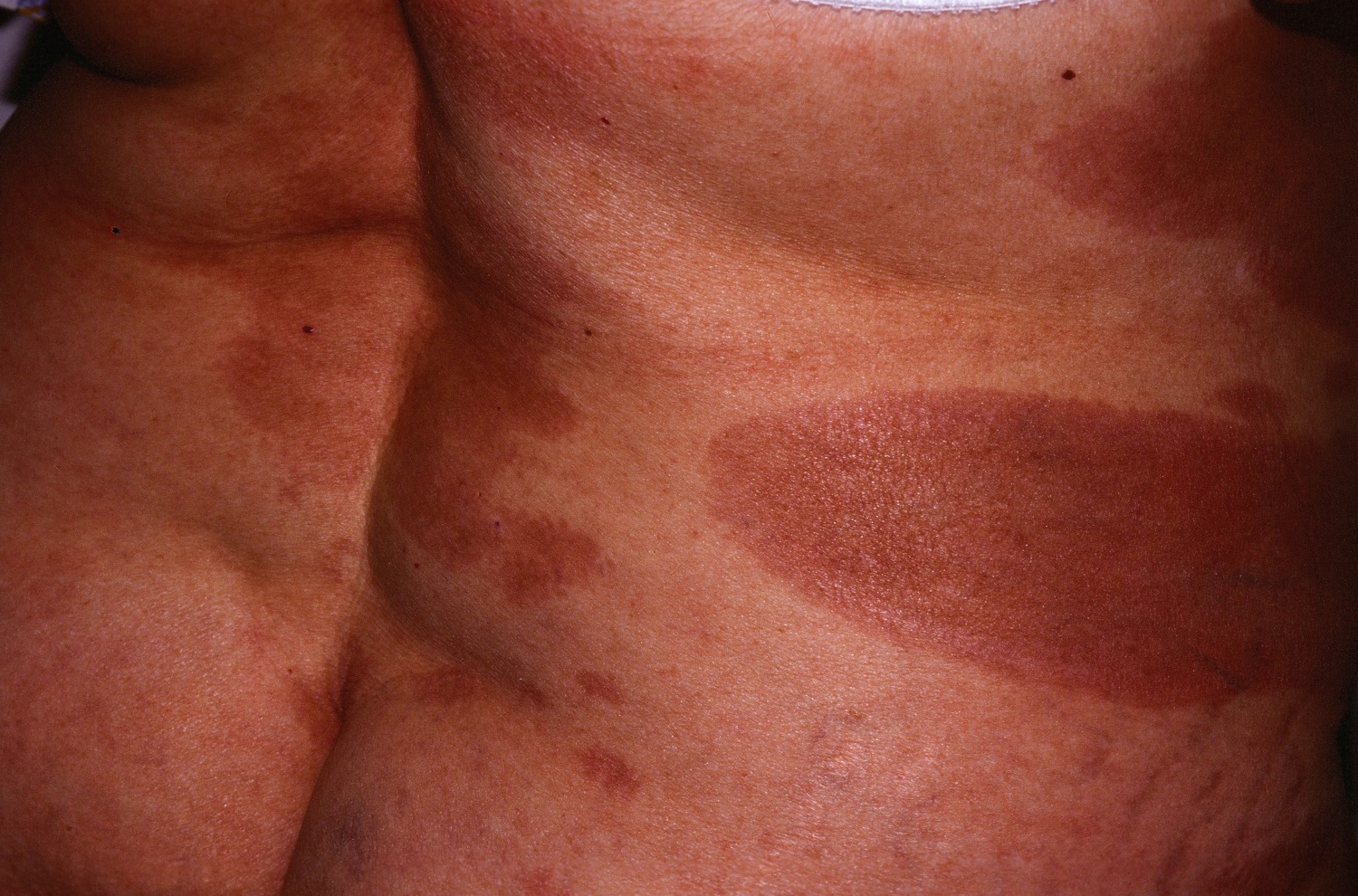
|[[Secondary syphilis]]<ref name="urlSTD Facts - Syphilis">{{cite web |url=https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm |title=STD Facts - Syphilis |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Round coppery red color lesions on palms and soles | |||
* [[Papule|Papules]] with collarette of scales | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy|Generalized lymphadenopathy]] | |||
* [[Sore throat]] | |||
* [[Hair loss|Patchy hair loss]] | |||
* [[Headaches]] | |||
* [[Weight loss]] | |||
* [[Myalgia]] | |||
* [[Fatigue]] | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** [[Condyloma latum|Condylomata lata]] | |||
** Corona verinata | |||
** Positive [[Venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test|VDRL]] test | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Secondary_Syphilis.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
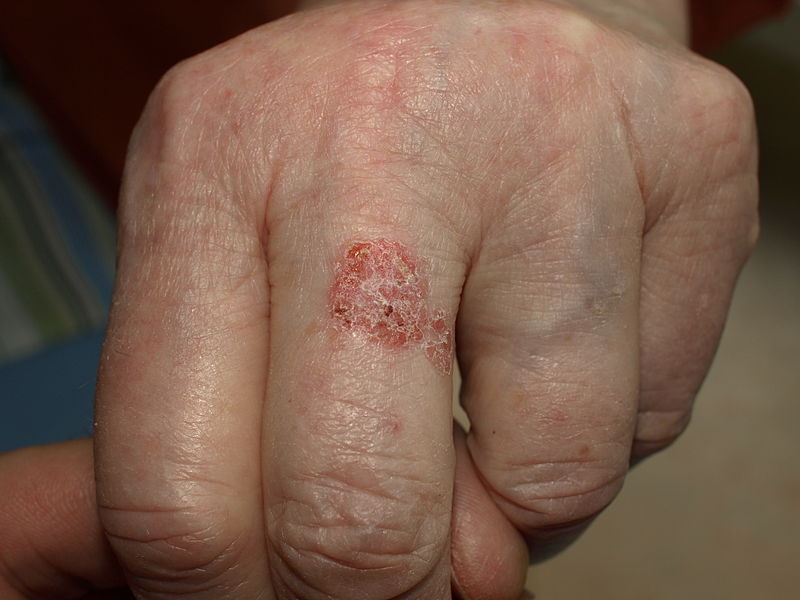
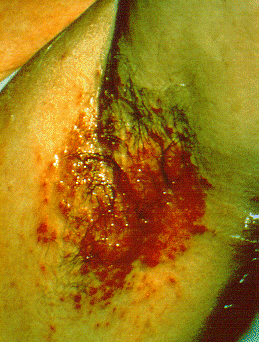
|[[Bowen’s disease]]<ref name="pmid28523295">{{cite journal |vauthors=Neagu TP, Ţigliş M, Botezatu D, Enache V, Cobilinschi CO, Vâlcea-Precup MS, GrinŢescu IM |title=Clinical, histological and therapeutic features of Bowen's disease |journal=Rom J Morphol Embryol |volume=58 |issue=1 |pages=33–40 |year=2017 |pmid=28523295 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* [[Erythematous]] little scaly plaque, which enlarges over time in an erratic manner | |||
* Scale is usually yellow or white and it is easily detachable without producing any [[bleeding]] | |||
* Well defined margins | |||
| | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
* [[Pain]] | |||
* Bleeding lesions | |||
| | |||
* Associated with:<ref name="pmid25201325">{{cite journal |vauthors=Murao K, Yoshioka R, Kubo Y |title=Human papillomavirus infection in Bowen disease: negative p53 expression, not p16(INK4a) overexpression, is correlated with human papillomavirus-associated Bowen disease |journal=J. Dermatol. |volume=41 |issue=10 |pages=878–84 |year=2014 |pmid=25201325 |doi=10.1111/1346-8138.12613 |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Erythroplasia of Queyrat]] ([[Bowen's disease]] of the [[penis]]) | |||
** [[Squamous cell carcinoma]] | |||
** Solar radiation and [[ultraviolet]] (UV) exposure | |||
** [[Radiation therapy|Radiotherapy]] | |||
** [[Immunosuppression]] | |||
** [[Arsenic]] exposure | |||
** [[Human papillomavirus|Human papilloma virus]] (HPV) type 16 | |||
** [[Polyomavirus|Merkel cell polyomavirus]] | |||
** [[Sjögren's syndrome|Sjögren’s syndrome]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Bowen.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
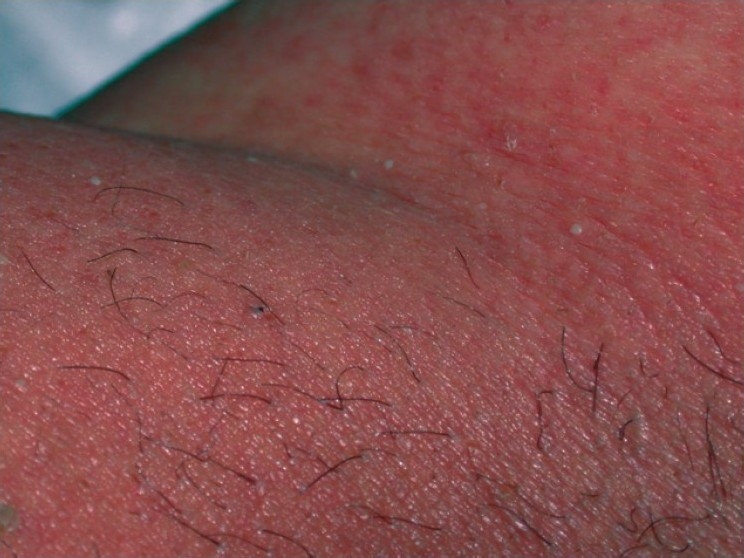
|[[Exanthematous pustulosis]]<ref name="pmid26354880">{{cite journal |vauthors=Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA |title=Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update |journal=J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. |volume=73 |issue=5 |pages=843–8 |year=2015 |pmid=26354880 |doi=10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Numerous small, primarily non-follicular, sterile [[pustules]], arising within large areas of [[Edema|edematous]] [[erythema]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Fever]] | |||
* [[Leukocytosis]] | |||
* Intracorneal, subcorneal, and/or intraepidermal [[pustules]] with [[papillary]] [[dermal]] [[edema]] containing [[neutrophils]] and [[eosinophils]] | |||
| | |||
* Associated with:<ref name="pmid12466124">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schmid S, Kuechler PC, Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Yawalkar N, Limat A, Baltensperger K, Braathen L, Pichler WJ |title=Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: role of cytotoxic T cells in pustule formation |journal=Am. J. Pathol. |volume=161 |issue=6 |pages=2079–86 |year=2002 |pmid=12466124 |pmc=1850901 |doi=10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64486-0 |url=}}</ref> | |||
** Antibiotics([[Penicillin|penicillins]], [[sulfonamides]], [[tetracyclines]]) | |||
** [[Carbamazepine]] | |||
** [[Calcium channel blocker|Calcium channel blockers]]([[Diltiazem]]) | |||
** [[Hydroxychloroquine]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Acute_generalized_exanthematous_pustulosis.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
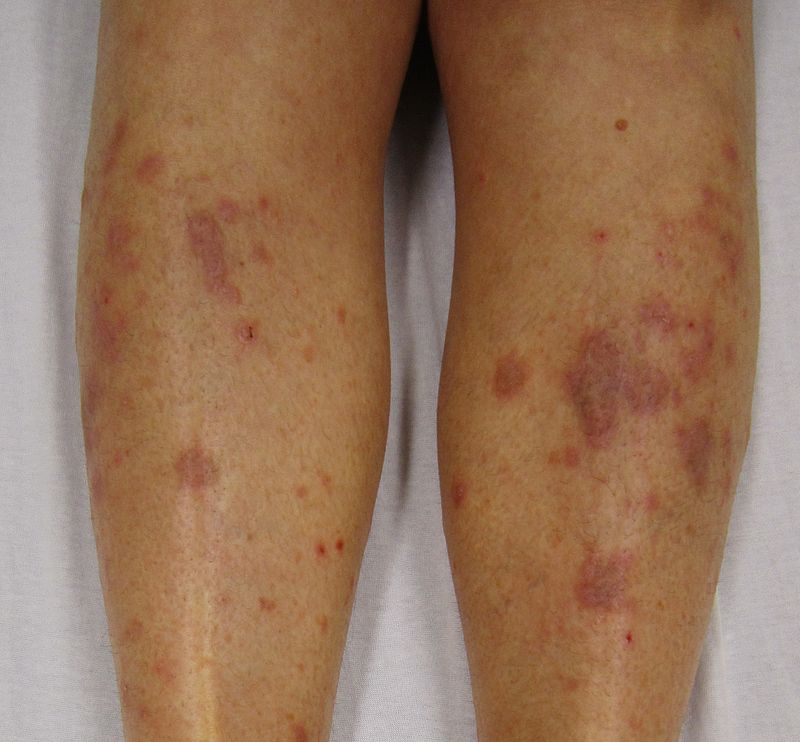
|[[Lichen planus|Hypertrophic lichen planus]]<ref name="pmid27222766">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ankad BS, Beergouder SL |title=Hypertrophic lichen planus versus prurigo nodularis: a dermoscopic perspective |journal=Dermatol Pract Concept |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=9–15 |year=2016 |pmid=27222766 |pmc=4866621 |doi=10.5826/dpc.0602a03 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Classically involves shin and ankles and is characterized by [[Hyperkeratosis|hyperkeratotic]] [[Plaque|plaques]] and [[Nodule (medicine)|nodules]] covered by a scale | |||
* Lesions may transform into [[Hyperkeratosis|hyperkeratotic]] thickened elevated purplish or reddish [[Plaque|plaques]] and [[nodules]] | |||
| | |||
* Chronic [[pruritis]] | |||
* Scaling | |||
* May be asymptomatic | |||
| | |||
* Associated with [[Hepatitis C virus]] infection<ref name="pmid19770446">{{cite journal |vauthors=Shengyuan L, Songpo Y, Wen W, Wenjing T, Haitao Z, Binyou W |title=Hepatitis C virus and lichen planus: a reciprocal association determined by a meta-analysis |journal=Arch Dermatol |volume=145 |issue=9 |pages=1040–7 |year=2009 |pmid=19770446 |doi=10.1001/archdermatol.2009.200 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Lichen_planus2.JPG|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
|Sneddon–Wilkinson disease<ref name="pmid9564592">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lutz ME, Daoud MS, McEvoy MT, Gibson LE |title=Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a clinical study of ten patients |journal=Cutis |volume=61 |issue=4 |pages=203–8 |year=1998 |pmid=9564592 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* [[Flaccid]] [[pustules]] that are often generalized and have a tendency to involve the flexural areas | |||
* Have an annular configuration | |||
| | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
* May be asymptomatic | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** [[Monoclonal gammopathy]], usually an IgA paraproteinemia<ref name="pmid3056995">{{cite journal |vauthors=Kasha EE, Epinette WW |title=Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) in association with a monoclonal IgA gammopathy: a report and review of the literature |journal=J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. |volume=19 |issue=5 Pt 1 |pages=854–8 |year=1988 |pmid=3056995 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Crohn's disease]]<ref name="pmid1357895">{{cite journal |vauthors=Delaporte E, Colombel JF, Nguyen-Mailfer C, Piette F, Cortot A, Bergoend H |title=Subcorneal pustular dermatosis in a patient with Crohn's disease |journal=Acta Derm. Venereol. |volume=72 |issue=4 |pages=301–2 |year=1992 |pmid=1357895 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Osteomyelitis]] | |||
** [[Adalimumab]]<ref name="pmid23489057">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sauder MB, Glassman SJ |title=Palmoplantar subcorneal pustular dermatosis following adalimumab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis |journal=Int. J. Dermatol. |volume=52 |issue=5 |pages=624–8 |year=2013 |pmid=23489057 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05707.x |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Snedden.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Parapsoriasis|Small plaque parapsoriasis]]<ref name="pmid7026622">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lambert WC, Everett MA |title=The nosology of parapsoriasis |journal=J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. |volume=5 |issue=4 |pages=373–95 |year=1981 |pmid=7026622 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* [[Erythematous]] [[plaques]] which are covered with fine scale. | |||
* May present with elongated, finger-like patches symmetrically distributed on the flanks, also known as digitate dermatosis | |||
| | |||
* Lesions may be asymptomatic | |||
* May be mildly [[Itch|pruritic]] | |||
* May fade or disappear after sun exposure during the summer season, but typically recur during the winter | |||
| | |||
* May progress to [[mycosis fungoides]]<ref name="pmid16191852">{{cite journal |vauthors=Väkevä L, Sarna S, Vaalasti A, Pukkala E, Kariniemi AL, Ranki A |title=A retrospective study of the probability of the evolution of parapsoriasis en plaques into mycosis fungoides |journal=Acta Derm. Venereol. |volume=85 |issue=4 |pages=318–23 |year=2005 |pmid=16191852 |doi=10.1080/00015550510030087 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Small_plaque_parapsoriasis.jpg|200px|courtesy http://www.regionalderm.com]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Intertrigo]]<ref name="pmid16156342">{{cite journal |vauthors=Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, Szepietowski JC, Reich A |title=Intertrigo and common secondary skin infections |journal=Am Fam Physician |volume=72 |issue=5 |pages=833–8 |year=2005 |pmid=16156342 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Red and fleshy looking lesion in [[skin]] folds | |||
* [[Itching]] | |||
* oozing | |||
* May be sore | |||
| | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
* Musty odor | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** [[Infections]] (Fungal, bacterial, viral) | |||
** [[Allergies]] | |||
** [[Diabetes Mellitus|Diabetes]] | |||
** [[Obesity]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Axillary_intertrigo.png|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
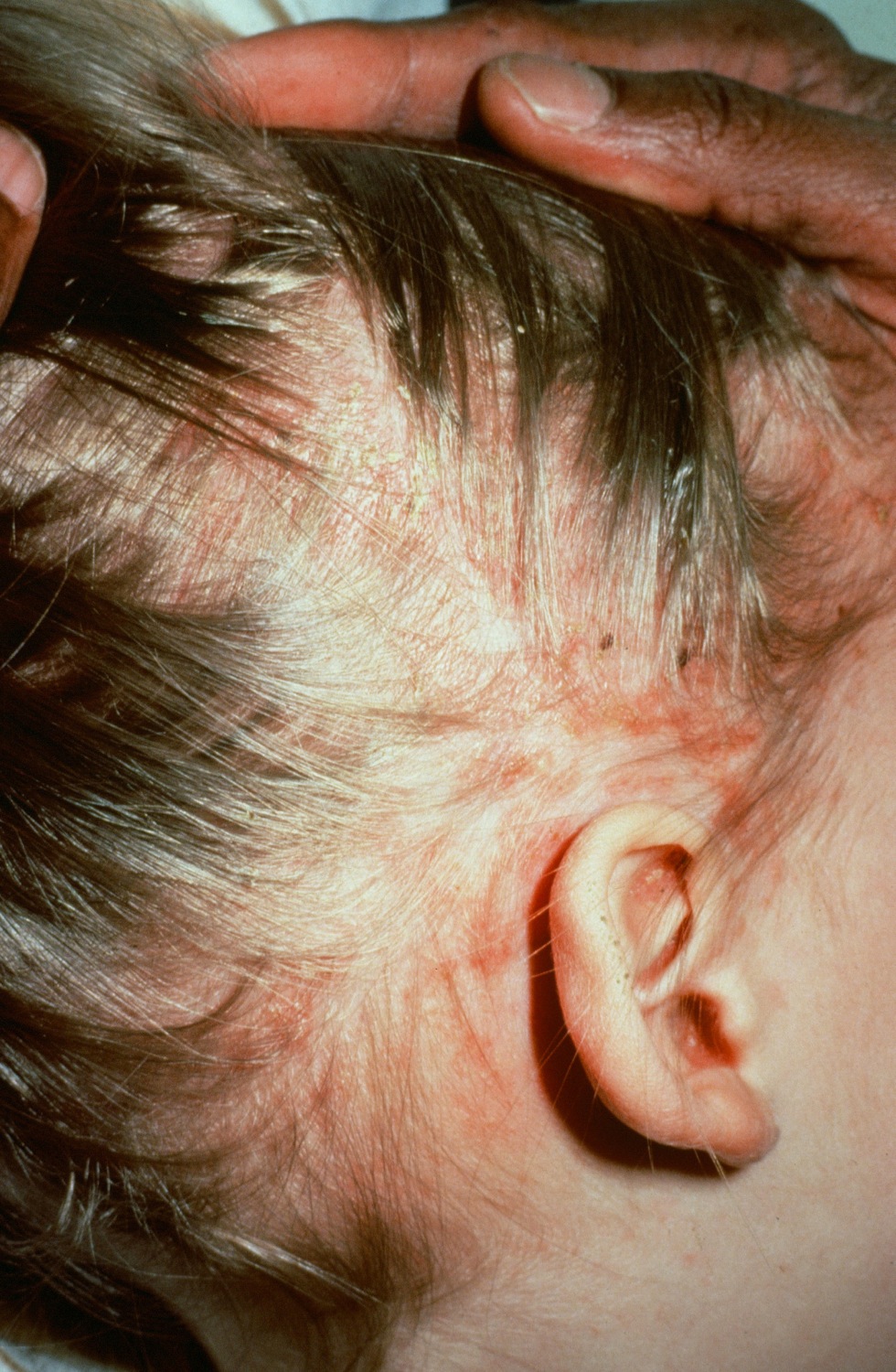
|[[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]<ref name="pmid18577030">{{cite journal |vauthors=Satter EK, High WA |title=Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a review of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society |journal=Pediatr Dermatol |volume=25 |issue=3 |pages=291–5 |year=2008 |pmid=18577030 |doi=10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00669.x |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* Scaling and crusting of the [[scalp]] | |||
| | |||
* Pathological fractures<ref name="pmid1636041">{{cite journal |vauthors=Stull MA, Kransdorf MJ, Devaney KO |title=Langerhans cell histiocytosis of bone |journal=Radiographics |volume=12 |issue=4 |pages=801–23 |year=1992 |pmid=1636041 |doi=10.1148/radiographics.12.4.1636041 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Visceromegaly ([[hepatomegaly]], [[spleenomegaly]]) | |||
* [[Chronic cough, severe cold|Chronic cough]] | |||
* [[Dyspnea]]<ref name="pmid17527085">{{cite journal |vauthors=Sholl LM, Hornick JL, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS, Padera RF |title=Immunohistochemical analysis of langerin in langerhans cell histiocytosis and pulmonary inflammatory and infectious diseases |journal=Am. J. Surg. Pathol. |volume=31 |issue=6 |pages=947–52 |year=2007 |pmid=17527085 |doi=10.1097/01.pas.0000249443.82971.bb |url=}}</ref> | |||
* [[Lymphadenopathy]] | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** [[Diabetes insipidus]]<ref name="pmid16047354">{{cite journal |vauthors=Grois N, Pötschger U, Prosch H, Minkov M, Arico M, Braier J, Henter JI, Janka-Schaub G, Ladisch S, Ritter J, Steiner M, Unger E, Gadner H |title=Risk factors for diabetes insipidus in langerhans cell histiocytosis |journal=Pediatr Blood Cancer |volume=46 |issue=2 |pages=228–33 |year=2006 |pmid=16047354 |doi=10.1002/pbc.20425 |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Pancytopenia]] | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Langerhan_cell_histiocytosis.jpg|200px|courtesy http://www.regionalderm.com ]] | |||
|- | |||
|[[Tinea manuum]]/pedum/capitis<ref name="pmid15050029">{{cite journal |vauthors=Al Hasan M, Fitzgerald SM, Saoudian M, Krishnaswamy G |title=Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its complications |journal=Clin Mol Allergy |volume=2 |issue=1 |pages=5 |year=2004 |pmid=15050029 |pmc=419368 |doi=10.1186/1476-7961-2-5 |url=}}</ref> | |||
| | |||
* scaling, flaking, and sometimes blistering of the affected areas | |||
* Hair loss with a black dot on scalp in case of [[tinea capitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Pruritis]] | |||
* KOH preparation of the lesions confirms [[fungal infection]] | |||
| | |||
* Associated with: | |||
** [[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetes]] | |||
** [[Immunosupression]] | |||
** Intimate contact with infected person | |||
** May lead to [[asthma]] exacerbation | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Tinea_pedis.jpg|200px]] | |||
|- | |||
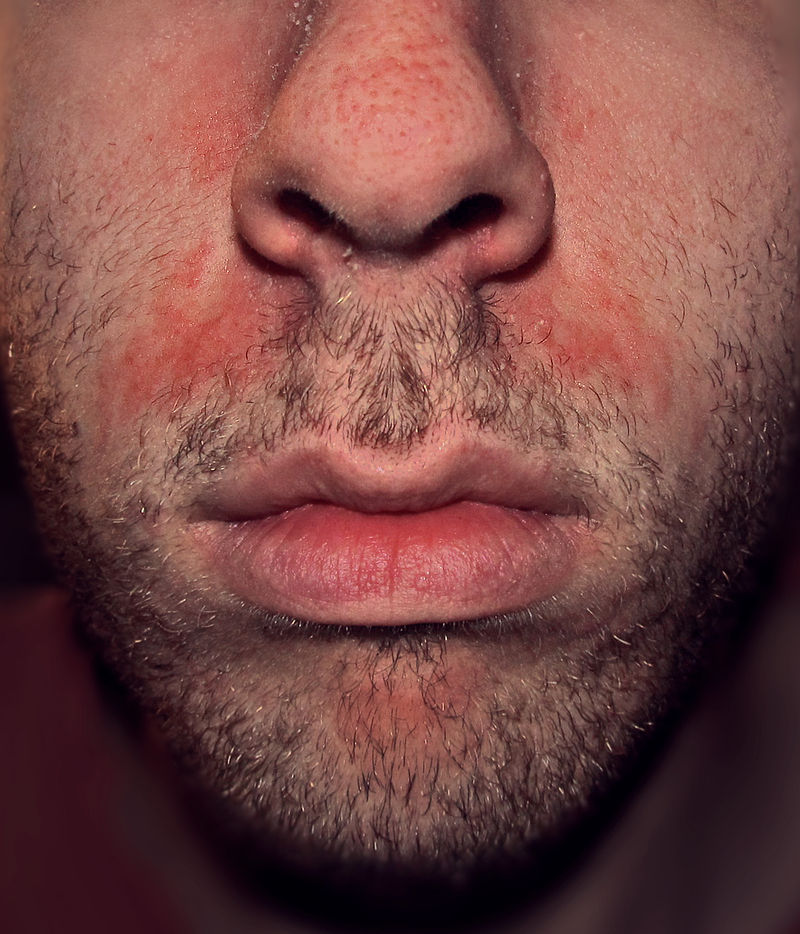
|[[Seborrheic dermatitis]] | |||
| | |||
* [[Papulosquamous]], scaly, flaky, [[itchy]], and red [[rash]] found particularly at [[sebaceous gland]]-rich areas of the body | |||
| | |||
| | |||
* Associated with:<ref name="pmid16848386">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schwartz RA, Janusz CA, Janniger CK |title=Seborrheic dermatitis: an overview |journal=Am Fam Physician |volume=74 |issue=1 |pages=125–30 |year=2006 |pmid=16848386 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[AIDS]] | |||
** [[Stress]]<ref name="pmid18033062">{{cite journal |vauthors=Misery L, Touboul S, Vinçot C, Dutray S, Rolland-Jacob G, Consoli SG, Farcet Y, Feton-Danou N, Cardinaud F, Callot V, De La Chapelle C, Pomey-Rey D, Consoli SM |title=[Stress and seborrheic dermatitis] |language=French |journal=Ann Dermatol Venereol |volume=134 |issue=11 |pages=833–7 |year=2007 |pmid=18033062 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
** [[Fungal infection]] | |||
** [[Fatigue]] | |||
** [[Sleep deprivation]] | |||
** Change of season | |||
** [[Parkinson's disease|Parkinson's]] disease | |||
** [[Biotin]] deficiency | |||
| | |||
[[Image:Seborrhoeic_dermatitisnew.jpg|200px]] | |||
|} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 25 July 2017
|
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma Microchapters |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sowminya Arikapudi, M.B,B.S. [2]
Overview
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as eczema and psoriasis.
Differentiating Cutaneous T cell lymphoma from other Diseases
Cutaneous T cell lymphoma must be differentiated from other diseases such as:
| Disease | Rash Characteristics | Signs and Symptoms | Associated Conditions | Rash Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutaneous T cell lymphoma/Mycosis fungoides[1] |
|
|
||
| Pityriasis rosea[2] |
|
|
||
| Pityriasis lichenoides chronica |
|
|
||
| Nummular dermatitis[5] |
|
|
|
|
| Secondary syphilis[6] |
|
|
||
| Bowen’s disease[7] |
|
|
||
| Exanthematous pustulosis[9] |
|
|
||
| Hypertrophic lichen planus[11] |
|
|
|
|
| Sneddon–Wilkinson disease[13] |
|
|
||
| Small plaque parapsoriasis[17] |
|
|
|
|
| Intertrigo[19] |
|
|
||
| Langerhans cell histiocytosis[20] |
|
|
|
|
| Tinea manuum/pedum/capitis[24] |
|
|
|
|
| Seborrheic dermatitis |
|
|
References
- ↑ "Mycosis Fungoides and the Sézary Syndrome Treatment (PDQ®)—Patient Version - National Cancer Institute".
- ↑ Mahajan K, Relhan V, Relhan AK, Garg VK (2016). "Pityriasis Rosea: An Update on Etiopathogenesis and Management of Difficult Aspects". Indian J Dermatol. 61 (4): 375–84. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.185699. PMC 4966395. PMID 27512182.
- ↑ Prantsidis A, Rigopoulos D, Papatheodorou G, Menounos P, Gregoriou S, Alexiou-Mousatou I, Katsambas A (2009). "Detection of human herpesvirus 8 in the skin of patients with pityriasis rosea". Acta Derm. Venereol. 89 (6): 604–6. doi:10.2340/00015555-0703. PMID 19997691.
- ↑ Smith KJ, Nelson A, Skelton H, Yeager J, Wagner KF (1997). "Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta in HIV-1+ patients: a marker of early stage disease. The Military Medical Consortium for the Advancement of Retroviral Research (MMCARR)". Int. J. Dermatol. 36 (2): 104–9. PMID 9109005.
- ↑ Jiamton S, Tangjaturonrusamee C, Kulthanan K (2013). "Clinical features and aggravating factors in nummular eczema in Thais". Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 31 (1): 36–42. PMID 23517392.
- ↑ "STD Facts - Syphilis".
- ↑ Neagu TP, Ţigliş M, Botezatu D, Enache V, Cobilinschi CO, Vâlcea-Precup MS, GrinŢescu IM (2017). "Clinical, histological and therapeutic features of Bowen's disease". Rom J Morphol Embryol. 58 (1): 33–40. PMID 28523295.
- ↑ Murao K, Yoshioka R, Kubo Y (2014). "Human papillomavirus infection in Bowen disease: negative p53 expression, not p16(INK4a) overexpression, is correlated with human papillomavirus-associated Bowen disease". J. Dermatol. 41 (10): 878–84. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.12613. PMID 25201325.
- ↑ Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA (2015). "Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 73 (5): 843–8. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.07.017. PMID 26354880.
- ↑ Schmid S, Kuechler PC, Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Yawalkar N, Limat A, Baltensperger K, Braathen L, Pichler WJ (2002). "Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: role of cytotoxic T cells in pustule formation". Am. J. Pathol. 161 (6): 2079–86. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64486-0. PMC 1850901. PMID 12466124.
- ↑ Ankad BS, Beergouder SL (2016). "Hypertrophic lichen planus versus prurigo nodularis: a dermoscopic perspective". Dermatol Pract Concept. 6 (2): 9–15. doi:10.5826/dpc.0602a03. PMC 4866621. PMID 27222766.
- ↑ Shengyuan L, Songpo Y, Wen W, Wenjing T, Haitao Z, Binyou W (2009). "Hepatitis C virus and lichen planus: a reciprocal association determined by a meta-analysis". Arch Dermatol. 145 (9): 1040–7. doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2009.200. PMID 19770446.
- ↑ Lutz ME, Daoud MS, McEvoy MT, Gibson LE (1998). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis: a clinical study of ten patients". Cutis. 61 (4): 203–8. PMID 9564592.
- ↑ Kasha EE, Epinette WW (1988). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis (Sneddon-Wilkinson disease) in association with a monoclonal IgA gammopathy: a report and review of the literature". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 19 (5 Pt 1): 854–8. PMID 3056995.
- ↑ Delaporte E, Colombel JF, Nguyen-Mailfer C, Piette F, Cortot A, Bergoend H (1992). "Subcorneal pustular dermatosis in a patient with Crohn's disease". Acta Derm. Venereol. 72 (4): 301–2. PMID 1357895.
- ↑ Sauder MB, Glassman SJ (2013). "Palmoplantar subcorneal pustular dermatosis following adalimumab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis". Int. J. Dermatol. 52 (5): 624–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05707.x. PMID 23489057.
- ↑ Lambert WC, Everett MA (1981). "The nosology of parapsoriasis". J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 5 (4): 373–95. PMID 7026622.
- ↑ Väkevä L, Sarna S, Vaalasti A, Pukkala E, Kariniemi AL, Ranki A (2005). "A retrospective study of the probability of the evolution of parapsoriasis en plaques into mycosis fungoides". Acta Derm. Venereol. 85 (4): 318–23. doi:10.1080/00015550510030087. PMID 16191852.
- ↑ Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, Szepietowski JC, Reich A (2005). "Intertrigo and common secondary skin infections". Am Fam Physician. 72 (5): 833–8. PMID 16156342.
- ↑ Satter EK, High WA (2008). "Langerhans cell histiocytosis: a review of the current recommendations of the Histiocyte Society". Pediatr Dermatol. 25 (3): 291–5. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00669.x. PMID 18577030.
- ↑ Stull MA, Kransdorf MJ, Devaney KO (1992). "Langerhans cell histiocytosis of bone". Radiographics. 12 (4): 801–23. doi:10.1148/radiographics.12.4.1636041. PMID 1636041.
- ↑ Sholl LM, Hornick JL, Pinkus JL, Pinkus GS, Padera RF (2007). "Immunohistochemical analysis of langerin in langerhans cell histiocytosis and pulmonary inflammatory and infectious diseases". Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 31 (6): 947–52. doi:10.1097/01.pas.0000249443.82971.bb. PMID 17527085.
- ↑ Grois N, Pötschger U, Prosch H, Minkov M, Arico M, Braier J, Henter JI, Janka-Schaub G, Ladisch S, Ritter J, Steiner M, Unger E, Gadner H (2006). "Risk factors for diabetes insipidus in langerhans cell histiocytosis". Pediatr Blood Cancer. 46 (2): 228–33. doi:10.1002/pbc.20425. PMID 16047354.
- ↑ Al Hasan M, Fitzgerald SM, Saoudian M, Krishnaswamy G (2004). "Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its complications". Clin Mol Allergy. 2 (1): 5. doi:10.1186/1476-7961-2-5. PMC 419368. PMID 15050029.
- ↑ Schwartz RA, Janusz CA, Janniger CK (2006). "Seborrheic dermatitis: an overview". Am Fam Physician. 74 (1): 125–30. PMID 16848386.
- ↑ Misery L, Touboul S, Vinçot C, Dutray S, Rolland-Jacob G, Consoli SG, Farcet Y, Feton-Danou N, Cardinaud F, Callot V, De La Chapelle C, Pomey-Rey D, Consoli SM (2007). "[Stress and seborrheic dermatitis]". Ann Dermatol Venereol (in French). 134 (11): 833–7. PMID 18033062.