Talimogene laherparepvec
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vishal Devarkonda, M.B.B.S[2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Talimogene laherparepvec is a live, attenuated Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 that is FDA approved for the treatment of local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with melanoma recurrent after initial surgery. Talimogene Laherparepvec has not been shown to improve overall survival or have an effect on visceral metastases.. Common adverse reactions include fatigue, chills, pyrexia, nausea, influenza-like illness, and injection site pain.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is a genetically modified oncolytic viral therapy indicated for the local treatment of unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, and nodal lesions in patients with melanoma recurrent after initial surgery.
Dosage and administration
- For intralesional injection only. Do not administer intravenously.
Dose
- Administer Talimogene Laherparepvec by injection into cutaneous, subcutaneous, and/or nodal lesions that are visible, palpable, or detectable by ultrasound guidance.
Talimogene Laherparepvec is provided in single-use vials of 1 mL each in two different dose strengths:
- 1 million plaque-forming units (PFU) per mL (light green cap) – for initial dose only
- 100 million PFU per mL (royal blue cap) – for all subsequent doses
Recommended Dose and Schedule
The total injection volume for each treatment visit should not exceed 4 mL for all injected lesions combined. It may not be possible to inject all lesions at each treatment visit or over the full course of treatment. Previously injected and/or uninjected lesion(s) may be injected at subsequent treatment visits. The initial recommended dose is up to 4 mL of Talimogene Laherparepvec at a concentration of 106 (1 million) PFU per mL. The recommended dose for subsequent administrations is up to 4 mL of Talimogene Laherparepvec at a concentration of 108 (100 million) PFU per mL. The recommended dosing schedule for Talimogene Laherparepvec is shown in Table 1.
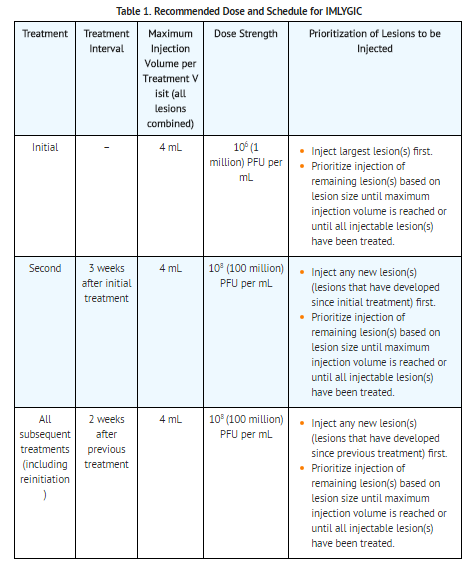
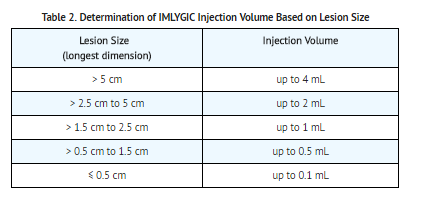
- When lesions are clustered together, inject them as a single lesion according to Table 2.
- Continue Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment for at least 6 months unless other treatment is required or until there are no injectable lesions to treat.
- Reinitiate Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment if new unresectable cutaneous, subcutaneous, or nodal lesions appear after a complete response.
Preparation and Handling
- Healthcare providers who are immunocompromised or pregnant should not prepare or administer Talimogene Laherparepvec and should not come into direct contact with the Talimogene Laherparepvec injection sites, dressings, or body fluids of treated patients.
Avoid accidental exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec and follow universal biohazard precautions for preparation, administration, and handling of Talimogene Laherparepvec:
- Wear personal protective equipment (protective gown or laboratory coat, safety glasses or face shield, and gloves) while preparing or administering Talimogene Laherparepvec.
- Avoid accidental exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec, especially contact with skin, eyes, and mucous membranes.
- Cover any exposed wounds before handling.
- In the event of an accidental occupational exposure (e.g., through a splash to the eyes or mucous membranes), flush with clean water for at least 15 minutes.
- In the event of exposure to broken skin or needle stick, clean the affected area thoroughly with soap and water and/or a disinfectant.
- Treat all Talimogene Laherparepvec spills with a virucidal agent such as 1% sodium hypochlorite and blot using absorbent materials.
- Dispose of all materials that may have come in contact with Talimogene Laherparepvec (e.g., vial, syringe, needle, cotton gauze, gloves, masks, or dressings) in accordance with universal biohazard precautions.
- Advise patients to place used dressings and cleaning materials into a sealed plastic bag and dispose in household waste.
Thawing Talimogene Laherparepvec Vials
- Determine the total volume required for injection, up to 4 ml.
- Thaw frozen Talimogene Laherparepvec vials at room temperature [20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF)] until Talimogene Laherparepvec is liquid (approximately 30 minutes). Do not expose the vial to higher temperatures. Keep the vial in original carton during thawing.
- Swirl gently. Do NOT shake.
- After thawing, administer Talimogene Laherparepvec immediately or store in its original vial and carton, protected from light in a refrigerator [2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F)] for no longer than the specified duration in Table 3. Do not refreeze Talimogene Laherparepvec after thawing. Discard any Talimogene Laherparepvec vial left in the refrigerator longer than the specified times in Table 3.
- Prepare sterile syringes and needles. A detachable needle of 18–26G may be used for Talimogene Laherparepvec withdrawal and a detachable needle of 22–26G may be used for injection. Small unit syringes (e.g., 0.5 mL insulin syringes) are recommended for better injection control.
- Using aseptic technique, remove the vial cap and withdraw the product from the vial into the syringe(s), noting the total volume. Avoid generating aerosols when loading syringes with product, and use a biologic safety cabinet if available.
Administration
- Follow the steps below to administer Talimogene Laherparepvec to patients:
Pre-Injection
- Clean the lesion and surrounding areas with an alcohol swab and let dry.
- Treat the injection site with a topical or local anesthetic agent, if necessary. Do not inject anesthetic agent directly into the lesion. Inject anesthetic agent around the periphery of the lesion.
Injection
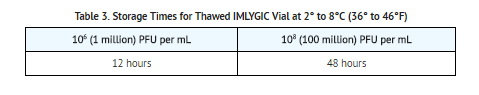
- Inject Talimogene Laherparepvec intralesionally into cutaneous, subcutaneous, and/or nodal lesions that are visible, palpable, or detectable by ultrasound guidance. Using a single insertion point, inject Talimogene Laherparepvec along multiple tracks as far as the radial reach of the needle allows within the lesion to achieve even and complete dispersion. Multiple insertion points may be used if a lesion is larger than the radial reach of the needle.
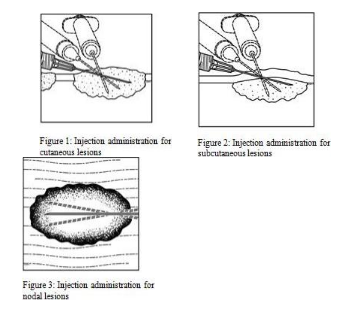
- Inject Talimogene Laherparepvec evenly and completely within the lesion by pulling the needle back without exiting the lesion. Redirect the needle as many times as necessary while injecting the remainder of the dose of Talimogene Laherparepvec. Continue until the full dose is evenly and completely dispersed.
- When removing the needle, withdraw it from the lesion slowly to avoid leakage of Talimogene Laherparepvec at the insertion point.
- Repeat steps 1-2 under pre-injection and steps 1-3 under injection for other lesions to be injected.
- Use a new needle any time the needle is completely removed from a lesion and each time a different lesion is injected.
Post-Injection
- Apply pressure to the injection site(s) with sterile gauze for at least 30 seconds.
- Swab the injection site(s) and surrounding area with alcohol.
- Change gloves and cover the injected lesion(s) with an absorbent pad and dry occlusive dressing.
- Wipe the exterior of occlusive dressing with alcohol.
- Advise patients to:
- Keep the injection site(s) covered for at least the first week after each treatment visit or longer if the injection site is weeping or oozing.
- Replace the dressing if it falls off.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Contraindications
Immunocompromised Patients
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is a live, attenuated herpes simplex virus and may cause life-threatening disseminated herpetic infection in patients who are immunocompromised. Do not administer Talimogene Laherparepvec to immunocompromised patients, including those with a history of primary or acquired immunodeficient states, leukemia, lymphoma, AIDS or other clinical manifestations of infection with human immunodeficiency viruses, and those on immunosuppressive therapy.
Pregnant Patients
- Do not administer Talimogene Laherparepvec to pregnant patients.
Warnings
Accidental Exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec
- Accidental exposure may lead to transmission of Talimogene Laherparepvec and herpetic infection. Accidental needle stick and splashback to the eyes have been reported in healthcare providers during preparation and administration of Talimogene Laherparepvec.
- Healthcare providers, close contacts (household members, caregivers, sex partners, or persons sharing the same bed), pregnant women, and newborns should avoid direct contact with injected lesions, dressings, or body fluids of treated patients. Healthcare providers who are immunocompromised or pregnant should not prepare or administer Talimogene Laherparepvec.
- Caregivers should wear protective gloves when assisting patients in applying or changing occlusive dressings and observe safety precautions for disposal of used dressings, gloves, and cleaning materials.
- In the event of an accidental exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec, exposed individuals should clean the affected area thoroughly with soap and water and/or a disinfectant. If signs or symptoms of herpetic infection develop, the exposed individuals should contact their healthcare provider for appropriate treatment.
- Patients should avoid touching or scratching injection sites or their occlusive dressings, as doing so could lead to inadvertent transfer of Talimogene Laherparepvec to other areas of the body.
Herpetic Infection
- In clinical studies, herpetic infections (including cold sores and herpetic keratitis) have been reported in patients treated with Talimogene Laherparepvec. Disseminated herpetic infection may also occur in immunocompromised patients.
- Patients who develop suspicious herpes-like lesions should follow standard hygienic practices to prevent viral transmission. Patients or close contacts with suspected herpetic infections should also contact their healthcare provider to evaluate the lesions. Suspected herpetic lesions should be reported to Amgen at 1-855-IMLYGIC (1-855-465-9442); patients or close contacts have the option of follow-up testing for further characterization of the infection.
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is sensitive to acyclovir. Acyclovir or other antiviral agents may interfere with the effectiveness of Talimogene Laherparepvec. Therefore, consider the risks and benefits of Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment before administering antiviral agents to manage herpetic infection.
Injection Site Complications
- Necrosis or ulceration of tumor tissue may occur during Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment. Cellulitis and systemic bacterial infection have been reported in clinical studies. Careful wound care and infection precautions are recommended, particularly if tissue necrosis results in open wounds.
- In clinical studies, impaired healing at the injection site has been reported. Talimogene Laherparepvec may increase the risk of impaired healing in patients with underlying risk factors (e.g., previous radiation at the injection site or lesions in poorly vascularized areas). One patient had an amputation of a lower extremity 6 months after Talimogene Laherparepvec injection due to an infected non-healing wound. This wound area had been treated with surgery and radiation prior to Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment and had previous wound complications.
- If there is persistent infection or delayed healing of the injection site(s), consider the risks and benefits of Talimogene Laherparepvec before continuing treatment with Talimogene Laherparepvec.
Immune-Mediated Events
- Talimogene Laherparepvec may result in immune-mediated events. In clinical studies, immune-mediated events, including glomerulonephritis, vasculitis, pneumonitis, worsening psoriasis, and vitiligo have been reported in patients treated with Talimogene Laherparepvec.
- Consider the risks and benefits of Talimogene Laherparepvec before initiating treatment in patients who have underlying autoimmune disease or before continuing treatment in patients who develop immune-mediated events.
Plasmacytoma at Injection Site
- In a clinical study, a plasmacytoma has been reported in proximity to the injection site after administration of Talimogene Laherparepvec in a patient with smoldering multiple myeloma.
- Consider the risks and benefits of Talimogene Laherparepvec in patients with multiple myeloma or in whom plasmacytoma develops during treatment.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
The most commonly reported adverse drug reactions (≥ 25%) in Talimogene Laherparepvec-treated patients were fatigue, chills, pyrexia, nausea, influenza-like illness, and injection site pain.
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in another section of the label:
- Herpetic Infection
- Injection Site Complications
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- The safety of Talimogene Laherparepvec was evaluated in 419 patients who received at least 1 dose of either Talimogene Laherparepvec (n = 292) or subcutaneously administered granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (n = 127) in an open-label, randomized clinical study of patients with stage IIIB, IIIC, and IV melanoma that was not considered to be surgically resectable. The median duration of exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec was 23 weeks (5.3 months). Twenty-six patients were exposed to Talimogene Laherparepvec for at least 1 year.
- Most adverse reactions reported were mild or moderate in severity and generally resolved within 72 hours. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse reaction was cellulitis.
- Pyrexia, chills, and influenza-like illness can occur any time during Talimogene Laherparepvec treatment but were more frequent during the first 3 months of treatment.
Table 4 below lists adverse reactions with a 5% or greater incidence in the Talimogene Laherparepvec arm compared to the GM-CSF arm in the clinical study.
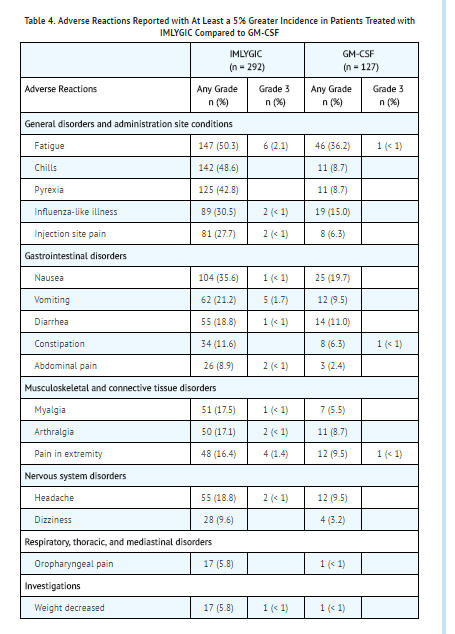
- Other adverse reactions associated with Talimogene Laherparepvec in the open-label, randomized study include glomerulonephritis, vitiligo, cellulitis, and oral herpes.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is sensitive to acyclovir. Acyclovir or other antiherpetic viral agents may interfere with the effectiveness of Talimogene Laherparepvec. No drug interaction studies have been conducted with Talimogene Laherparepvec.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA): Risk Summary
- Adequate and well-controlled studies with Talimogene Laherparepvec have not been conducted in pregnant women. No effects on embryo-fetal development have been observed in a study conducted in pregnant mice. The design of the study limits application of the animal data to humans.
- In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
- If the patient becomes pregnant while taking Talimogene Laherparepvec, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazards to the fetus and neonate. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to use an effective method of contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Talimogene Laherparepvec.
- If a pregnant woman has an infection with wild-type Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1) (primary or reactivation), there is potential for the virus to cross the placental barrier and also a risk of transmission during birth due to viral shedding. Infections with wild-type HSV-1 have been associated with serious adverse effects, including multi-organ failure and death, if a fetus or neonate contracts the wild-type herpes infection. While there are no clinical data to date on Talimogene Laherparepvec infections in pregnant women, there could be a risk to the fetus or neonate if Talimogene Laherparepvec were to act in the same manner.
Data
Animal Data
- No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed when Talimogene Laherparepvec was intravenously administered during organogenesis to immunocompetent pregnant mice at doses up to 4 x 108 (400 million) PFU per kg (60-fold higher, on a PFU per kg basis, compared to the maximum clinical dose). Levels of Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA in pooled fetal blood were at or below the assay detection level. Study design limitations included: 1) administration of Talimogene Laherparepvec expressing human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (huGM-CSF), which is not biologically active in mice; 2) unknown transplacental kinetics of Talimogene Laherparepvec following intravenous administration in pregnant mice; and 3) unknown significance of Talimogene Laherparepvec dose extrapolation from animal to human based on body weight.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Talimogene laherparepvec in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Talimogene laherparepvec during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Talimogene laherparepvec in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of Talimogene Laherparepvec have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
- In clinical studies, no overall differences in safety or efficacy were observed between geriatric patients (≥ 65 years old) and younger patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Talimogene laherparepvec with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Talimogene laherparepvec with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- No clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Talimogene Laherparepvec.
Hepatic Impairment
- No clinical studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Talimogene Laherparepvec.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
- No nonclinical or clinical studies were performed to evaluate the effect of Talimogene Laherparepvec on fertility.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Talimogene laherparepvec in patients who are immunocompromised.
Lactation
Risk Summary
- There is no information regarding the presence of Talimogene Laherparepvec in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Talimogene Laherparepvec and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Talimogene Laherparepvec or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
- Because medicinal products can be found in human milk, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue Talimogene Laherparepvec while nursing.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Talimogene laherparepvec and IV administrations.
Overdosage
/There is no clinical experience with an overdose with Talimogene Laherparepvec. Doses up to 4 mL at dose strength of 108 (100 million) PFU per mL every 2 weeks (maximum cumulative dose of 222.5 x 108 PFU) have been administered in clinical studies, with no evidence of dose-limiting toxicity. The maximum dose of Talimogene Laherparepvec that can be safely administered has not been determined. In the event of a suspected overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures instituted as required.
Pharmacology
Talimogene laherparepvec
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | L01 |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
TBD |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Injection |
Mechanism of Action
- Talimogene Laherparepvechas been genetically modified to replicate within tumors and to produce the immune stimulatory protein GM-CSF. Talimogene Laherparepvec causes lysis of tumors, followed by release of tumor-derived antigens, which together with virally derived GM-CSF may promote an antitumor immune response. However, the exact mechanism of action is unknown.
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
Biodistribution (within the body) and Viral Shedding (excretion/secretion)
- Talimogene Laherparepvec viral DNA levels in various tissues and secretions were determined using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assay. Infectious Talimogene Laherparepvec at the injection sites and at some potential herpetic lesions was also quantified using viral infectivity assays.
Nonclinical data
- Following repeat intratumoral administration in mice, Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA was primarily detected in the tumor, blood, spleen, lymph node, liver, heart, and kidney. Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA was not detected in bone marrow, eyes, lachrymal glands, nasal mucosa, or feces. The highest level of Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA was found in the injected tumor. Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA was found in the injected tumor through 84 days and in blood samples through 14 days after the last administration of Talimogene Laherparepvec.
Clinical data
- The biodistribution and shedding of intralesionally administered Talimogene Laherparepvec are being investigated in an ongoing study measuring Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA and virus in blood, oral mucosa, urine, injection site, and occlusive dressings. In the initial 20 patients with melanoma who received Talimogene Laherparepvec intralesional injection at a dose and schedule similar to that of the clinical study, available data indicate that Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA was present in the blood in 17 (85%) patients and in urine of 4 (20%) patients during the study. The peak levels of Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA in the urine were detected on the day of treatment. Infectious Talimogene Laherparepvec virus was detected at the site of injection in 3 (15%) patients at a single time point each, and all within the first week after the initial injection. The exterior of the occlusive dressings was positive for Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA in 14 (70%) patients during the study; however, no infectious virus was detected on the exterior of the occlusive dressing. The number of patients with measurable levels of Talimogene Laherparepvec DNA on the exterior of occlusive dressings declined over time with no measurable DNA by the third treatment in 13 patients tested.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
- Repeated intratumoral administration at 2 x 108 (200 million) PFU per kg (30-fold maximum proposed clinical dose, extrapolated based on body weight) did not demonstrate any adverse effects in immunocompetent mice. Severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice administered repeat intratumoral injections of Talimogene Laherparepvec at a dose of 30-fold maximum proposed clinical dose developed systemic viral infection (viral inclusion bodies or necrosis in enteric neurons in the gastrointestinal tract, adrenal gland, skin, pancreatic islet cells, eye, pineal gland, and brain).
Clinical Studies
- The safety and efficacy of intralesional injections of Talimogene Laherparepvec compared with subcutaneously administered GM-CSF was evaluated in a multicenter, open-label, randomized clinical study in patients with stage IIIB, IIIC, and IV melanoma that was considered to be not surgically resectable. Talimogene Laherparepvec was injected into cutaneous, subcutaneous, or nodal melanoma lesions and was not injected into visceral lesions. Previous systemic treatment for melanoma was allowed. Patients with active cerebral metastases, bony metastases, extensive visceral disease, primary ocular or mucosal melanoma, evidence of immunosuppression, or receiving treatment with a systemic antiherpetic agent were excluded from the study.
- The study included 250 (57%) men and 186 (43%) women. The mean age was 63 (range: 22 to 94) years. Most patients (98%) were white. Seventy percent (70%) of patients had baseline Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status of zero. Seventy percent (70%) of patients had stage IV disease (27% M1a; 21% M1b; and 22% M1c), and 30% had stage III disease. Fifty-three percent (53%) of patients had received prior therapy for melanoma (other than or in addition to surgery, adjuvant therapy, or radiation), and 58% were seropositive for wild-type HSV-1 at baseline.
- A total of 436 patients were randomized to receive either Talimogene Laherparepvec (n = 295) or GM-CSF (n = 141). Talimogene Laherparepvec was administered by intralesional injection at an initial concentration of 106 (1 million) PFU per mL on Day 1, followed by a concentration of 108 (100 million) PFU per mL on Day 21 and every 2 weeks thereafter, at a dose of up to 4 mL per visit. GM-CSF was administered subcutaneously in 28-day cycles, i.e., 125 µg/m2 daily for 14 days followed by 14 days without GM-CSF administration.
- Patients were to be treated for at least 6 months or until there were no injectable lesions. During this period, treatment could continue despite an increase in size in existing lesion(s) and/or development of new lesion(s), unless the patient developed intolerable toxicity or the investigator believed that it was in the best interest of the patient to stop treatment or to be given other therapy for melanoma. After 6 months of treatment, patients were to continue treatment until clinically relevant disease progression (i.e., disease progression associated with a decline in performance status and/or alternative therapy was required in the opinion of the investigator), up to 12 months. Patients experiencing a response at 12 months after the start of treatment could continue treatment for up to an additional 6 months, unless there were no remaining injectable lesions or disease progression. All patients were to be followed for survival status for at least 36 months.
- The major efficacy outcome was durable response rate (DRR), defined as the percent of patients with complete response (CR) or partial response (PR) maintained continuously for a minimum of 6 months. Tumor responses were determined according to World Health Organization (WHO) response criteria modified to allow patients who developed new lesions or disease progression of existing lesions to continue the treatment and be evaluated later for tumor response.
- The DRR was 16.3% in the Talimogene Laherparepvec arm and 2.1% in the GM-CSF arm in the overall study population. The unadjusted relative risk was 7.6 (95% CI: 2.4, 24.1), with a p-value < 0.0001. The median time to response was 4.1 (range: 1.2 to 16.7) months in the Talimogene Laherparepvec arm.
- There was no statistically significant difference in overall survival (OS) between the Talimogene Laherparepvec and the GM-CSF arms. The median OS in the overall study population was 22.9 months in the Talimogene Laherparepvec arm and 19.0 months in the GM-CSF arm (p = 0.116).
How Supplied
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is a sterile suspension for intralesional injection. Talimogene Laherparepvec is a live, attenuated HSV-1 that has been genetically modified to express huGM-CSF. The parental virus for Talimogene Laherparepvec was a primary isolate, which was subsequently altered using recombinant methods to result in gene deletions and insertions.
- Each vial contains 1 mL deliverable volume of Talimogene Laherparepvec at either 1 million PFU per mL or 100 million PFU per mL concentrations and the following excipients: di-sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate (15.4 mg), sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate (2.44 mg), sodium chloride (8.5 mg), myo-inositol (40 mg), sorbitol (20 mg), and water for injection.
- The 1 million PFU per mL vial of Talimogene Laherparepvec contains a clear to semi-translucent liquid following thaw from its frozen state. The 100 million PFU per mL vial of Talimogene Laherparepvec contains a semi-translucent to opaque liquid following thaw from its frozen state. The liquid in each vial may contain white, visible, variously shaped, virus-containing particles.
- Each vial of Talimogene Laherparepvec may also contain residual components of VERO cells including DNA and protein and trace quantities of fetal bovine serum.
- The product contains no preservative.
- Initial dose only: 1 million PFU per mL solution in 1 mL single-use vial (light green cap)
- Subsequent doses: 100 million PFU per mL solution in 1 mL single-use vial (royal blue cap)
- Talimogene Laherparepvec is provided as a sterile frozen suspension in a single-use, cyclic olefin polymer (COP) plastic resin vial with a chlorobutyl elastomer stopper, aluminum seal, and polypropylene cap. Each vial contains a retrievable minimal volume of 1 mL.
- The vial cap is color coded:
- 1 million PFU per mL is light green (NDC 55513-078-01).
- 100 million PFU per mL is royal blue (NDC 55513-079-01).
Storage
- Store and transport Talimogene Laherparepvec at −90°C to −70°C (−130°F to −94°F).
- Protect Talimogene Laherparepvec from light.
- Store Talimogene Laherparepvec in the carton until use.
- Thaw Talimogene Laherparepvec immediately prior to administration.
- Do not draw Talimogene Laherparepvec into a syringe until immediately prior to administration.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Talimogene laherparepvec |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel


{{#ask: Label Page::Talimogene laherparepvec |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients and/or close contacts to:
- Read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
- Follow instructions below to prevent viral transmission
- Avoid direct contact with injection sites, dressings, or body fluids of patients.
- Wear gloves when changing dressing.
- Avoid touching or scratching injection sites.
- Keep injection sites covered for at least the first week after each treatment visit or longer if the injection site is weeping or oozing. Replace dressing if it falls off.
- Dispose of used dressings and cleaning materials in household waste in a sealed plastic bag.
- Female patients of childbearing potential should use an effective method of contraception to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Talimogene Laherparepvec
- Close contacts who are pregnant or immunocompromised should not change dressings or clean injection sites
- In case of accidental exposure to Talimogene Laherparepvec, clean the exposed area with soap and water and/or a disinfectant. Patients or close contacts with suspected herpetic infections should contact their healthcare provider to evaluate the lesions. Suspected herpetic lesions should be reported to Amgen at 1-855-IMLYGIC (1-855-465-9442); patients or close contacts have the option of follow-up testing for further characterization of the infection.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Talimogene laherparepvec interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
IMLYGIC TM
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Talimogene laherparepvec Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.