Portal vein thrombosis MRI
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
Portal vein thrombosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Portal vein thrombosis MRI On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Portal vein thrombosis MRI |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Portal vein thrombosis MRI |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Farima Kahe M.D. [2]
Overview
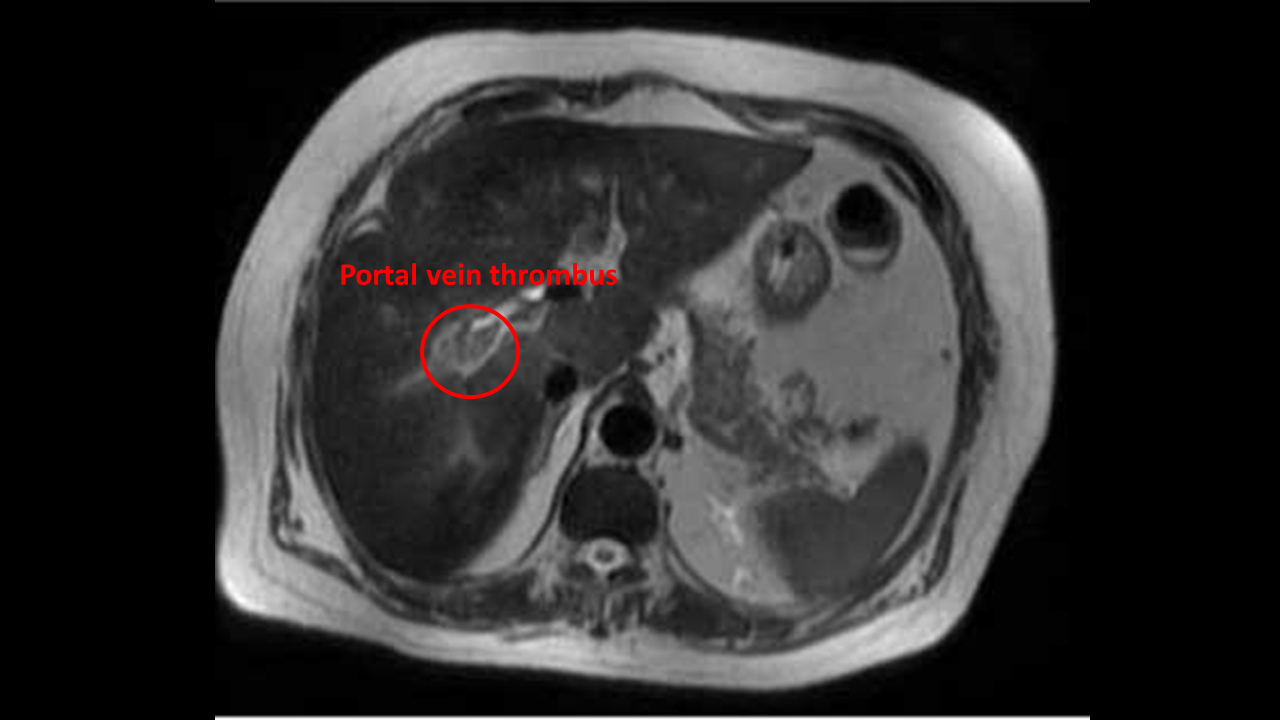
Abdominal MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis. Findings on MRI diagnostic of portal vein thrombosis include filling defect that partially or completely occludes the vessel lumen in the portal venous phase, clot appears isointense on T1- weighted images, and usually has a more intense signal on T2 images, and presence of varices.
MRI
- Abdominal MRI may be helpful in the diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis. Findings on MRI diagnostic of portal vein thrombosis include:[1][2][3]
- Filling defect that partially or completely occludes the vessel lumen in the portal venous phase
- Clot appears isointense on T1- weighted images, or hyperintense if recent, and usually has a more intense signal on T2 images
- Presence of varices
- Verify the correct function of surgical shunts
References
- ↑ Chawla YK, Bodh V (2015). "Portal vein thrombosis". J Clin Exp Hepatol. 5 (1): 22–40. doi:10.1016/j.jceh.2014.12.008. PMC 4415192. PMID 25941431.
- ↑ Catalano OA, Choy G, Zhu A, Hahn PF, Sahani DV (2010). "Differentiation of malignant thrombus from bland thrombus of the portal vein in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: application of diffusion-weighted MR imaging". Radiology. 254 (1): 154–62. doi:10.1148/radiol.09090304. PMID 20032150.
- ↑ Ponziani FR, Zocco MA, Campanale C, Rinninella E, Tortora A, Di Maurizio L, Bombardieri G, De Cristofaro R, De Gaetano AM, Landolfi R, Gasbarrini A (2010). "Portal vein thrombosis: insight into physiopathology, diagnosis, and treatment". World J. Gastroenterol. 16 (2): 143–55. PMC 2806552. PMID 20066733.