Blau syndrome: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
'''Blau syndrome''' is characterized by familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin granulomas, comprising an [[autosomal dominant|autosomal dominantly]] inherited syndrome that overlaps both sarcoidosis and granuloma annulare.<ref name="Fitz2">Freedberg, et. al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071380760.</ref>{{rp|983}}<ref name="Andrews">James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0721629210.</ref>{{rp|149}} Restated, Blau syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by granulomatous polyarthritis, panuveitis, cranial neuropathies and exanthema.<ref name="pmid17223962">{{cite journal |author=Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE |title=Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation |journal=Clin. Exp. Immunol. |volume=147 |issue=2 |pages=227–35 |year=2007 |month=February |pmid=17223962 |pmc=1810472 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03261.x |url=}}</ref>{{rp|232}} | '''Blau syndrome''' is characterized by familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin granulomas, comprising an [[autosomal dominant|autosomal dominantly]] inherited syndrome that overlaps both sarcoidosis and granuloma annulare.<ref name="Fitz2">Freedberg, et. al. (2003). ''Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine''. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071380760.</ref>{{rp|983}}<ref name="Andrews">James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0721629210.</ref>{{rp|149}} Restated, Blau syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by granulomatous polyarthritis, panuveitis, cranial neuropathies and exanthema.<ref name="pmid17223962">{{cite journal |author=Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE |title=Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation |journal=Clin. Exp. Immunol. |volume=147 |issue=2 |pages=227–35 |year=2007 |month=February |pmid=17223962 |pmc=1810472 |doi=10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03261.x |url=}}</ref>{{rp|232}} | ||
==Historical Perspective== | ==Historical Perspective== | ||
*Blau syndrome was first discovered by Dr. Edward B. Blau, in 1985 following observation of a four-generation family with a variety of symptoms including granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin rash.<ref name="Blau1985">{{cite journal|last1=Blau|first1=Edward B.|title=Familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and rash|journal=The Journal of Pediatrics|volume=107|issue=5|year=1985|pages=689–693|issn=00223476|doi=10.1016/S0022-3476(85)80394-2}}</ref> | *Blau syndrome was first discovered by Dr. Edward B. Blau, in 1985 following observation of a four-generation family with a variety of [[symptoms]] including [[granulomatous]] [[arthritis]], [[iritis]], and [[skin rash]].<ref name="Blau1985">{{cite journal|last1=Blau|first1=Edward B.|title=Familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and rash|journal=The Journal of Pediatrics|volume=107|issue=5|year=1985|pages=689–693|issn=00223476|doi=10.1016/S0022-3476(85)80394-2}}</ref> | ||
*Jabs Syndrome was introduced in the same year (1985) by Dr. A. Douglas Jabs following visiting patients with polyarthritis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathy.<ref name="JabsHouk1985">{{cite journal|last1=Jabs|first1=Douglas A.|last2=Houk|first2=J.Lawrence|last3=Bias|first3=Wilma B.|last4=Arnett|first4=Frank C.|title=Familial granulomatous synovitis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathies|journal=The American Journal of Medicine|volume=78|issue=5|year=1985|pages=801–804|issn=00029343|doi=10.1016/0002-9343(85)90286-4}}</ref> | *Jabs Syndrome was introduced in the same year (1985) by Dr. A. Douglas Jabs following visiting patients with [[polyarthritis]], [[uveitis]], and [[cranial neuropathy]].<ref name="JabsHouk1985">{{cite journal|last1=Jabs|first1=Douglas A.|last2=Houk|first2=J.Lawrence|last3=Bias|first3=Wilma B.|last4=Arnett|first4=Frank C.|title=Familial granulomatous synovitis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathies|journal=The American Journal of Medicine|volume=78|issue=5|year=1985|pages=801–804|issn=00029343|doi=10.1016/0002-9343(85)90286-4}}</ref> | ||
*In 19??, NOD2 mutations were first implicated in the pathogenesis of Blau syndrome. | *In 19??, NOD2 mutations were first implicated in the [[pathogenesis]] of Blau syndrome. | ||
==Classification== | ==Classification== | ||
*There is no established system for the classification of Blau syndrome. | *There is no established system for the [[classification]] of Blau syndrome. | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
*The exact pathogenesis of Blau syndrome is not fully understood. However, it is caused by a mutation in the NOD2 gene. | *The exact [[pathogenesis]] of Blau syndrome is not fully understood. However, it is caused by a [[mutation]] in the [[NOD2]] [[gene]]. | ||
*The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant mode. | *The [[disease]] is inherited in an [[autosomal dominant]] mode. | ||
*This gene encodes a protein called xxxx, involving in the .... | *This gene encodes a protein called xxxx, involving in the .... | ||
*NOD2 mutation leads to overactivation of xxxxx which may trigger an exaggerated inflammatory response. | *NOD2 mutation leads to overactivation of xxxxx which may trigger an exaggerated inflammatory response. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
*Blau syndrome may be caused by a mutation in the NOD2 gene. | *Blau syndrome may be caused by a mutation in the NOD2 gene. | ||
==Differentiating Blau syndrome from Other Diseases== | ==Differentiating Blau syndrome from Other Diseases== | ||
*Blau syndrome must be differentiated from other diseases that cause arthritis, skin rash, and | *Blau syndrome must be differentiated from other [[diseases]] that cause [[arthritis]], [[skin rash]], and [[ophthalmological]] involvement, such as Neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID), [[cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome]] ([[CAPS]]), and [[familial mediterranean fever]]. | ||
*For more information please click here. | *For more information please click here. | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
*There is no available data on the prevalence and incidence of Blau syndrome. | *There is no available data on the [[prevalence]] and [[incidence]] of Blau syndrome. | ||
*Blau syndrome commonly affects individuals younger than 4 years of age. | *Blau syndrome commonly affects individuals younger than 4 years of age. | ||
*There is no racial predilection to Blau syndrome. | *There is no [[racial]] predilection to Blau syndrome. | ||
*Blau syndrome affects men and women equally. | *Blau syndrome affects men and women equally. | ||
==Risk Factors== | ==Risk Factors== | ||
*There are no established risk factors for Blau syndrome. | *There are no established [[risk factors]] for Blau syndrome. | ||
==Screening== | ==Screening== | ||
There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for Blau syndrome. | There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine [[screening]] for Blau syndrome. | ||
==Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis== | ==Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis== | ||
*If left untreated, patients with Blau syndrome may progress to develop blindness, vasculitis, and joint deformities. | *If left untreated, patients with Blau syndrome may progress to develop [[blindness]], [[vasculitis]], and [[joint]] [[deformities]]. | ||
*Other possible complications include: | *Other possible [[complications]] include: | ||
**Arterial hypertension | **[[Arterial hypertension]] | ||
**Pulmonary embolism | **[[Pulmonary embolism]] | ||
** | ** | ||
*Prognosis is generally excellent/good/poor, and the 1/5/10-year mortality/survival rate of patients with [disease name] is approximately [#]%. | *Prognosis is generally excellent/good/poor, and the 1/5/10-year mortality/survival rate of patients with [disease name] is approximately [#]%. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
There are no established criteria for the diagnosis of Blau syndrome. | There are no established criteria for the diagnosis of Blau syndrome. | ||
===History and Symptoms=== | ===History and Symptoms=== | ||
*Blau syndrome first presents with a scaly rash often by 4 months of age. Fever, arthritis, abdominal pain, and other symptoms may present later by 4 years of age.<ref name="RoséAróstegui2009">{{cite journal|last1=Rosé|first1=Carlos D.|last2=Aróstegui|first2=Juan I.|last3=Martin|first3=Tammy M.|last4=Espada|first4=Graciela|last5=Scalzi|first5=Lisabeth|last6=Yagüe|first6=Jordi|last7=Rosenbaum|first7=James T.|last8=Modesto|first8=Consuelo|last9=Cristina Arnal|first9=Maria|last10=Merino|first10=Rosa|last11=García-Consuegra|first11=Julia|last12=Carballo Silva|first12=María Antonia|last13=Wouters|first13=Carine H.|title=NOD2-Associated pediatric granulomatous arthritis, an expanding phenotype: Study of an international registry and a national cohort in spain|journal=Arthritis & Rheumatism|volume=60|issue=6|year=2009|pages=1797–1803|issn=00043591|doi=10.1002/art.24533}}</ref> | *Blau syndrome first presents with a scaly [[rash]] often by 4 months of age. [[Fever]], [[arthritis]], [[abdominal pain]], and other [[Symptom|symptoms]] may present later by 4 years of age.<ref name="RoséAróstegui2009">{{cite journal|last1=Rosé|first1=Carlos D.|last2=Aróstegui|first2=Juan I.|last3=Martin|first3=Tammy M.|last4=Espada|first4=Graciela|last5=Scalzi|first5=Lisabeth|last6=Yagüe|first6=Jordi|last7=Rosenbaum|first7=James T.|last8=Modesto|first8=Consuelo|last9=Cristina Arnal|first9=Maria|last10=Merino|first10=Rosa|last11=García-Consuegra|first11=Julia|last12=Carballo Silva|first12=María Antonia|last13=Wouters|first13=Carine H.|title=NOD2-Associated pediatric granulomatous arthritis, an expanding phenotype: Study of an international registry and a national cohort in spain|journal=Arthritis & Rheumatism|volume=60|issue=6|year=2009|pages=1797–1803|issn=00043591|doi=10.1002/art.24533}}</ref> | ||
*Rash spread follows a cephalocaudal order. It first appears on the face and then affects the trunk. | *[[Rash]] spread follows a cephalocaudal order. It first appears on the face and then affects the [[trunk]]. | ||
*Arthritis usually affects wrists, knees, and ankles and tends to be symmetrical and chronic. | *[[Arthritis]] usually affects [[Wrist|wrists]], [[knees]], and [[Ankle|ankles]] and tends to be symmetrical and [[chronic]]. | ||
===Physical Examination=== | ===Physical Examination=== | ||
{| align="right" | {| align="right" | ||
|[[File:Blau syndrome.jpg|thumb|none|300px|Multiple, reddish-brown papules coalescing over the right arm in a boy with Blau syndrome, Image courtesy of Donald A Glass II MD, PhD, Jennifer Maender MD, Denise Metry M]] | |[[File:Blau syndrome.jpg|thumb|none|300px|Multiple, reddish-brown papules coalescing over the right arm in a boy with Blau syndrome, Image courtesy of Donald A Glass II MD, PhD, Jennifer Maender MD, Denise Metry M]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
*Common physical examination findings of Blau syndrome include fever, scaly rash, and arthritis. | *Common physical examination findings of Blau syndrome include [[fever]], scaly [[rash]], and [[arthritis]]. | ||
*Other possible findings include: | *Other possible findings include: | ||
**Cranial nerve involvement | **[[Cranial nerve]] involvement | ||
**Lymphadenopathy | **[[Lymphadenopathy]] | ||
**Hepatosplenomegaly | **[[Hepatosplenomegaly]] | ||
**Uveitis | **[[Uveitis]] | ||
**Conjunctivitis | **[[Conjunctivitis]] | ||
===Laboratory Findings=== | ===Laboratory Findings=== | ||
*An elevated concentration of serum acute phase reactants is diagnostic of Blau syndrome. | *An elevated [[concentration]] of serum [[Acute phase reactant|acute phase reactants]] is [[diagnostic]] of Blau syndrome. | ||
===Electrocardiogram=== | ===Electrocardiogram=== | ||
*There are no ECG findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no [[ECG]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===X-ray=== | ===X-ray=== | ||
*There are no x-ray findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no [[x-ray]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===Echocardiography or Ultrasound=== | ===Echocardiography or Ultrasound=== | ||
*There are no echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no [[echocardiography]]/[[ultrasound]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===CT scan=== | ===CT scan=== | ||
*There are no CT scan findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no [[CT scan]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===MRI=== | ===MRI=== | ||
*There are no MRI findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no [[MRI]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===Other Imaging Findings=== | ===Other Imaging Findings=== | ||
*There are no other imaging findings associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no other [[imaging]] findings associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
===Other Diagnostic Studies=== | ===Other Diagnostic Studies=== | ||
*There are no other diagnostic studies associated with Blau syndrome. | *There are no other [[diagnostic]] studies associated with Blau syndrome. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
===Medical Therapy=== | ===Medical Therapy=== | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 22 July 2019
|
WikiDoc Resources for Blau syndrome |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Blau syndrome Most cited articles on Blau syndrome |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Blau syndrome |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Blau syndrome at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Blau syndrome Clinical Trials on Blau syndrome at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Blau syndrome NICE Guidance on Blau syndrome
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Blau syndrome Discussion groups on Blau syndrome Patient Handouts on Blau syndrome Directions to Hospitals Treating Blau syndrome Risk calculators and risk factors for Blau syndrome
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Blau syndrome |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[2]
Synonyms and keywords: Pediatric Granulomatous Arthritis (PGA), Juvenile Systemic Granulomatosis, Early Onset Sarcoidosis, Jabs Syndrome, NOD2-associated disease-Blau
 |
Overview
Blau syndrome is characterized by familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin granulomas, comprising an autosomal dominantly inherited syndrome that overlaps both sarcoidosis and granuloma annulare.[1]:983[2]:149 Restated, Blau syndrome is a rare autosomal dominant disorder characterized by granulomatous polyarthritis, panuveitis, cranial neuropathies and exanthema.[3]:232
Historical Perspective
- Blau syndrome was first discovered by Dr. Edward B. Blau, in 1985 following observation of a four-generation family with a variety of symptoms including granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and skin rash.[4]
- Jabs Syndrome was introduced in the same year (1985) by Dr. A. Douglas Jabs following visiting patients with polyarthritis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathy.[5]
- In 19??, NOD2 mutations were first implicated in the pathogenesis of Blau syndrome.
Classification
- There is no established system for the classification of Blau syndrome.
Pathophysiology
- The exact pathogenesis of Blau syndrome is not fully understood. However, it is caused by a mutation in the NOD2 gene.
- The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant mode.
- This gene encodes a protein called xxxx, involving in the ....
- NOD2 mutation leads to overactivation of xxxxx which may trigger an exaggerated inflammatory response.
Causes
- Blau syndrome may be caused by a mutation in the NOD2 gene.
Differentiating Blau syndrome from Other Diseases
- Blau syndrome must be differentiated from other diseases that cause arthritis, skin rash, and ophthalmological involvement, such as Neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID), cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS), and familial mediterranean fever.
- For more information please click here.
Epidemiology and Demographics
- There is no available data on the prevalence and incidence of Blau syndrome.
- Blau syndrome commonly affects individuals younger than 4 years of age.
- There is no racial predilection to Blau syndrome.
- Blau syndrome affects men and women equally.
Risk Factors
- There are no established risk factors for Blau syndrome.
Screening
There is insufficient evidence to recommend routine screening for Blau syndrome.
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
- If left untreated, patients with Blau syndrome may progress to develop blindness, vasculitis, and joint deformities.
- Other possible complications include:
- Prognosis is generally excellent/good/poor, and the 1/5/10-year mortality/survival rate of patients with [disease name] is approximately [#]%.
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
The diagnosis of Blau syndrome is made when at least [number] of the following [number] diagnostic criteria are met: [criterion 1], [criterion 2], [criterion 3], and [criterion 4].
OR
The diagnosis of [disease name] is based on the [criteria name] criteria, which include [criterion 1], [criterion 2], and [criterion 3].
OR
The diagnosis of [disease name] is based on the [definition name] definition, which includes [criterion 1], [criterion 2], and [criterion 3].
OR
There are no established criteria for the diagnosis of Blau syndrome.
History and Symptoms
- Blau syndrome first presents with a scaly rash often by 4 months of age. Fever, arthritis, abdominal pain, and other symptoms may present later by 4 years of age.[6]
- Rash spread follows a cephalocaudal order. It first appears on the face and then affects the trunk.
- Arthritis usually affects wrists, knees, and ankles and tends to be symmetrical and chronic.
Physical Examination
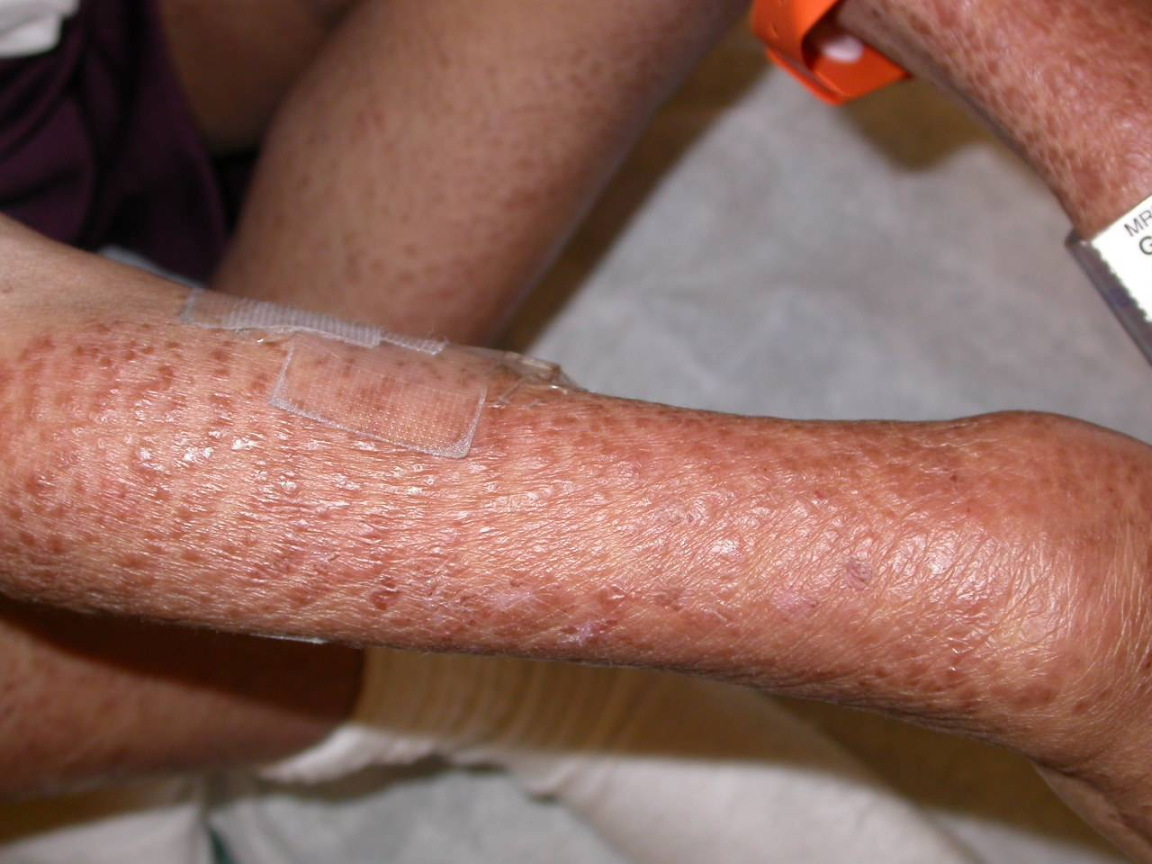 |
- Common physical examination findings of Blau syndrome include fever, scaly rash, and arthritis.
- Other possible findings include:
Laboratory Findings
- An elevated concentration of serum acute phase reactants is diagnostic of Blau syndrome.
Electrocardiogram
- There are no ECG findings associated with Blau syndrome.
X-ray
- There are no x-ray findings associated with Blau syndrome.
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
- There are no echocardiography/ultrasound findings associated with Blau syndrome.
CT scan
- There are no CT scan findings associated with Blau syndrome.
MRI
- There are no MRI findings associated with Blau syndrome.
Other Imaging Findings
- There are no other imaging findings associated with Blau syndrome.
Other Diagnostic Studies
- There are no other diagnostic studies associated with Blau syndrome.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- There is no treatment for Blau syndrome; the mainstay of therapy is supportive care.
Surgery
- Surgical intervention is not recommended for the management of Blau syndrome.
Primary Prevention
- There are no established measures for the primary prevention of Blau syndrome.
Secondary Prevention
- There are no established measures for the secondary prevention of Blau syndrome.
References
- ↑ Freedberg, et. al. (2003). Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. (6th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071380760.
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN 0721629210.
- ↑ Ferrero-Miliani L, Nielsen OH, Andersen PS, Girardin SE (2007). "Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1beta generation". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 147 (2): 227–35. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03261.x. PMC 1810472. PMID 17223962. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Blau, Edward B. (1985). "Familial granulomatous arthritis, iritis, and rash". The Journal of Pediatrics. 107 (5): 689–693. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(85)80394-2. ISSN 0022-3476.
- ↑ Jabs, Douglas A.; Houk, J.Lawrence; Bias, Wilma B.; Arnett, Frank C. (1985). "Familial granulomatous synovitis, uveitis, and cranial neuropathies". The American Journal of Medicine. 78 (5): 801–804. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(85)90286-4. ISSN 0002-9343.
- ↑ Rosé, Carlos D.; Aróstegui, Juan I.; Martin, Tammy M.; Espada, Graciela; Scalzi, Lisabeth; Yagüe, Jordi; Rosenbaum, James T.; Modesto, Consuelo; Cristina Arnal, Maria; Merino, Rosa; García-Consuegra, Julia; Carballo Silva, María Antonia; Wouters, Carine H. (2009). "NOD2-Associated pediatric granulomatous arthritis, an expanding phenotype: Study of an international registry and a national cohort in spain". Arthritis & Rheumatism. 60 (6): 1797–1803. doi:10.1002/art.24533. ISSN 0004-3591.