Pericardial effusion electrocardiogram
|
Pericardial effusion Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pericardial effusion electrocardiogram On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pericardial effusion electrocardiogram |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pericardial effusion electrocardiogram |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Overview
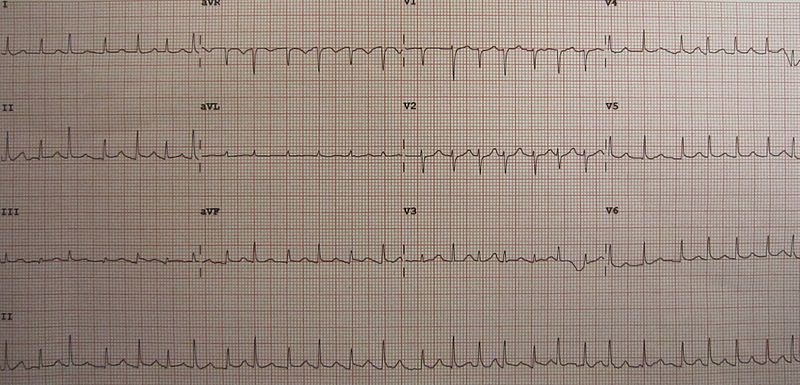
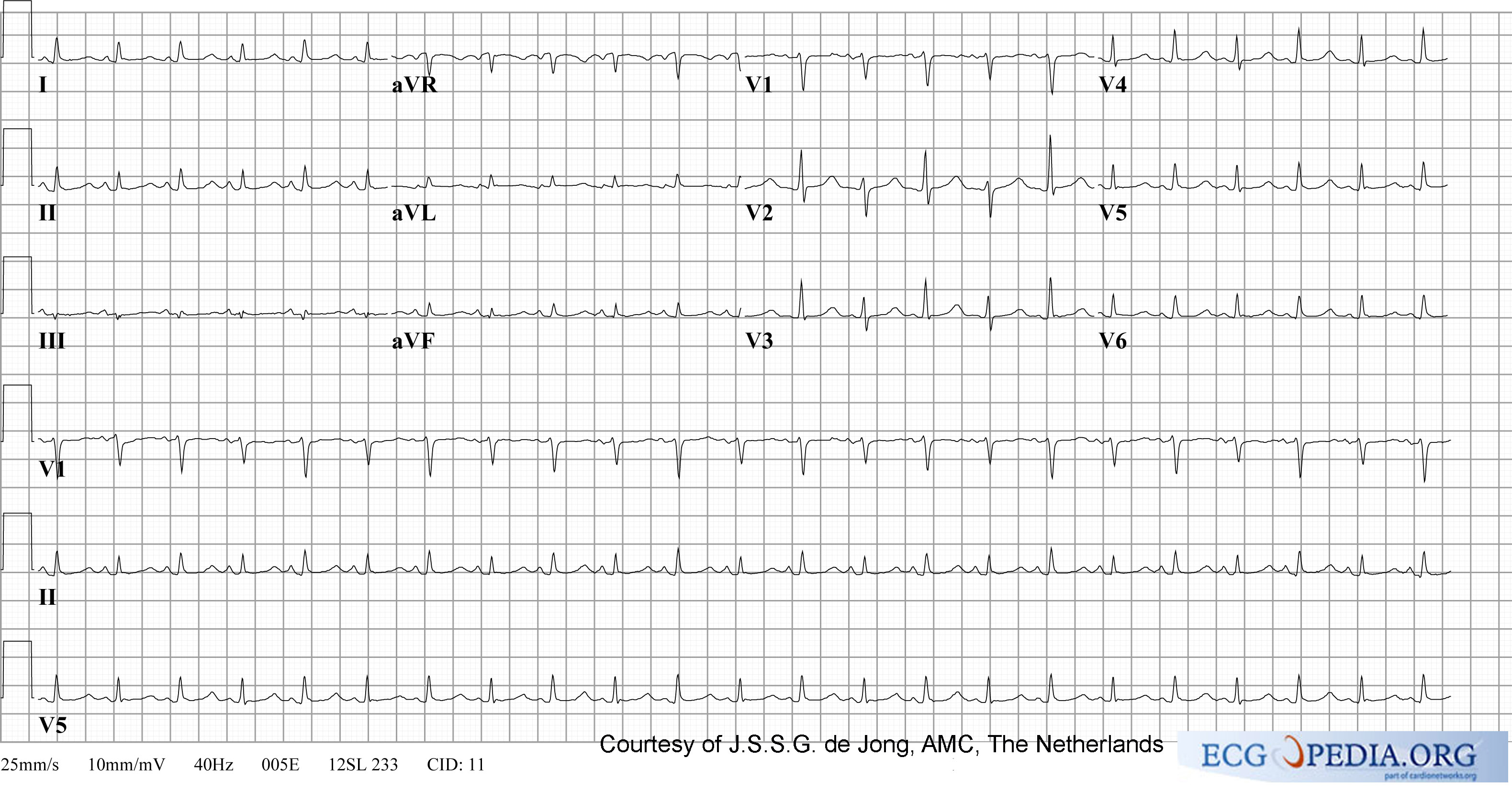
The EKG in patients with pericardial effusion may demonstrate low voltages (micro-voltages or short QRS complexes) and electrical alternans.
Electrocardiogram
Electrical alternans is an electrocardiographic phenomenon of alternation of QRS complex amplitude or axis between beats. It is seen in cardiac tamponade and pericardial effusion and is thought to be related to changes in the ventricular electrical axis due to fluid in the pericardium.
Electrocardiographic Examples