Fluorouracil Topical
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Fluorouracil Topical is a that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of multiple actinic or solar keratoses. Common adverse reactions include application site reaction, and eye irritation.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Multiple actinic or solar keratoses
- Dosing Information
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fluorouracil Topical in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fluorouracil Topical in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Fluorouracil Topical in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Fluorouracil Topical in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Fluorouracil Topical in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Fluorouracil may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Fluorouracil is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
- No adequate and well-controlled studies have been conducted in pregnant women with either topical or parenteral forms of fluorouracil. One birth defect (ventricular septal defect) and cases of miscarriage have been reported when fluorouracil was applied to mucous membrane areas. Multiple birth defects have been reported in the fetus of a patient treated with intravenous fluorouracil.
- Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Carac. Fluorouracil, the active ingredient, has been shown to be teratogenic in mice, rats, and hamsters when administered parenterally at doses greater than or equal to 10, 15 and 33 mg/kg/day, respectively, [4X, 11X and 20X, respectively, the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) based on body surface area (BSA)]. Fluorouracil was administered during the period of organogenesis for each species. Embryolethal effects occurred in monkeys at parenteral doses greater than 40 mg/kg/day (65X the MRHD based on BSA) administered during the period of organogenesis.
- Carac should not be used in patients with dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) enzyme deficiency. A large percentage of fluorouracil is catabolized by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD). DPD enzyme deficiency can result in shunting of fluorouracil to the anabolic pathway, leading to cytotoxic activity and potential toxicities.
- Carac is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to any of its components.
Warnings
- The potential for a delayed hypersensitivity reaction to fluorouracil exists. Patch testing to prove hypersensitivity may be inconclusive.
- Patients should discontinue therapy with Carac if symptoms of DPD enzyme deficiency develop.
- Rarely, unexpected, systemic toxicity (e.g. stomatitis, diarrhea, neutropenia, and neurotoxicity) associated with parenteral administration of fluorouracil has been attributed to deficiency of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase "DPD" activity. One case of life threatening systemic toxicity has been reported with the topical use of 5% fluorouracil in a patient with a complete absence of DPD enzyme activity. Symptoms included severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and chills. Physical examination revealed stomatitis, erythematous skin rash, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, inflammation of the esophagus, stomach, and small bowel. Although this case was observed with 5% fluorouracil cream, it is unknown whether patients with profound DPD enzyme deficiency would develop systemic toxicity with lower concentrations of topically applied fluorouracil.
- Applications to mucous membranes should be avoided due to the possibility of local inflammation and ulceration.
Precautions
- General
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- The following were adverse events considered to be drug-related and occurring with a frequency of ≥1% with Carac: application site reaction (94.6%), and eye irritation (5.4%). The signs and symptoms of facial irritation (application site reaction) are presented below.
- During clinical trials, irritation generally began on day 4 and persisted for the remainder of treatment. Severity of facial irritation at the last treatment visit was slightly below baseline for the vehicle group, mild to moderate for the 1 week active treatment group, and moderate for the 2 and 4 week active treatment groups. Mean severity declined rapidly for each active group after completion of treatment and was below baseline for each group at the week 2 post-treatment follow-up visit.
- Thirty-one patients (12% of those treated with Carac in the Phase 3 clinical studies) discontinued study treatment early due to facial irritation. Except for three patients, discontinuation of treatment occurred on or after day 11 of treatment.
- Eye irritation adverse events, described as mild to moderate in intensity, were characterized as burning, watering, sensitivity, stinging and itching. These adverse events occurred across all treatment arms in one of the two Phase 3 studies.
Adverse Experiences Reported by Body System
- In the Phase 3 studies, no serious adverse event was considered related to study drug. A total of five patients, three in the active treatment groups and two in the vehicle group, experienced at least one serious adverse event. Three patients died as a result of adverse event(s) considered unrelated to study drug (stomach cancer, myocardial infarction and cardiac failure).
- Post-treatment clinical laboratory tests other than pregnancy tests were not performed during the Phase 3 clinical studies. Clinical laboratory tests were performed during conduct of a Phase 2 study of 104 patients and 21 patients in a Phase 1 study. No abnormal serum chemistry, hematology, or urinalysis results in these studies were considered clinically significant.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Fluorouracil Topical in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Fluorouracil Topical Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category X
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Fluorouracil Topical in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Fluorouracil Topical during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether fluorouracil is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from fluorouracil, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
- Actinic keratosis is not a condition seen within the pediatric population, except in association with rare genetic diseases. Carac should not be used in children. The safety and effectiveness of Carac have not been established in patients less than 18 years old.
Geriatic Use
- No significant differences in safety and efficacy measures were demonstrated in patients age 65 and older compared to all other patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fluorouracil Topical with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fluorouracil Topical with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fluorouracil Topical in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fluorouracil Topical in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Fluorouracil Topical in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Fluorouracil Topical in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Topical
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Fluorouracil Topical in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Fluorouracil Topical in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- Ordinarily, topical overdosage will not cause acute problems.
Management
- If Carac is accidentally ingested, induce emesis and gastric lavage. Administer symptomatic and supportive care as needed. If contact is made with the eye, flush with copious amounts of water.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Fluorouracil Topical in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- There is evidence that the metabolism of fluorouracil in the anabolic pathway blocks the methylation reaction of deoxyuridylic acid to thymidylic acid. In this manner, fluorouracil interferes with the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and to a lesser extent inhibits the formation of ribonucleic acid (RNA). Since DNA and RNA are essential for cell division and growth, the effect of fluorouracil may be to create a thymine deficiency that provokes unbalanced growth and death of the cell. The effects of DNA and RNA deprivation are most marked on those cells that grow more rapidly and take up fluorouracil at a more rapid rate. The contribution to efficacy or safety of individual components of the vehicle has not been established.
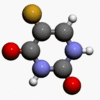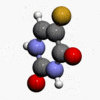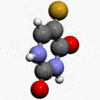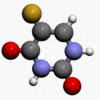
Structure
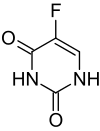
- Carac® (fluorouracil cream) Cream, 0.5%, contains fluorouracil for topical dermatologic use. Chemically, fluorouracil is 5-fluoro-2,4(1H, 3H)-pyrimidinedione. The molecular formula is C4H3FN2O2. Fluorouracil has a molecular weight of 130.08.
- Carac Cream contains 0.5% fluorouracil, with 0.35% being incorporated into a patented porous microsphere (Microsponge®)1 composed of methyl methacrylate / glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer and dimethicone. The cream formulation contains the following other inactive ingredients: Carbomer Homopolymer Type C, dimethicone, glycerin, methyl gluceth-20, methyl methacrylate / glycol dimethacrylate crosspolymer, methylparaben, octyl hydroxy stearate, polyethylene glycol 400, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sorbitan monooleate, stearic acid, and trolamine.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Fluorouracil Topical in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
- A multiple-dose, randomized, open-label, parallel study was performed in 21 patients with actinic keratoses. Twenty patients had pharmacokinetic samples collected: 10 patients treated with Carac and 10 treated with Efudex®2 5% Cream. Patients were treated for a maximum of 28 days with Carac, 1 g once daily in the morning; or Efudex® 5% Cream, 1 g twice daily, in the morning and evening. Steady-state plasma concentrations and the amounts of fluorouracil in urine resulting from the topical application of either product were measured.
- Three patients who received Carac and nine patients who received Efudex® 5% Cream had measurable plasma fluorouracil levels; however, only one patient receiving Carac and six patients receiving Efudex® 5% Cream had a sufficient number of data points to calculate mean pharmacokinetic parameters.
- Five of 10 patients receiving Carac and nine of 10 patients receiving Efudex® 5% Cream had measurable urine fluorouracil levels.
- Both Carac and Efudex® 5% Cream demonstrated low measurable plasma concentrations for fluorouracil when administered under steady-state conditions. Cumulative urinary excretion of fluorouracil was low for Carac and for Efudex®, corresponding to 0.055% and 0.24% of the applied doses, respectively.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Adequate long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted with fluorouracil. Studies with the active ingredient of Carac, fluorouracil, have shown positive effects in in vitro and in vivo tests for mutagenicity and on impairment of fertility in in vivo animal studies.
- Fluorouracil produced morphological transformation of cells in in vitro cell transformation assays. Morphological transformation was also produced in an in vitro assay by a metabolite of fluorouracil, and the transformed cells produced malignant tumors when injected into immunosuppressed syngeneic mice. Fluorouracil has been shown to exert mutagenic activity in yeast cells, Bacillus subtilis, and Drosophila assays. In addition, fluorouracil has produced chromosome damage at concentrations of 1.0 and 2.0 mcg/mL in an in vitro hamster fibroblast assay, was positive in a microwell mouse lymphoma assay, and was positive in in vivo micronucleus assays in rats and mice following intraperitoneal administration. Some patients receiving cumulative doses of 0.24 to 1.0 g of fluorouracil parenterally have shown an increase in numerical and structural chromosome aberrations in peripheral blood lymphocytes.
- Fluorouracil has been shown to impair fertility after parenteral administration in rats. Fluorouracil administered at intraperitoneal doses of 125 and 250 mg/kg has been shown to induce chromosomal aberrations and changes in chromosome organization of spermatogonia in rats. In mice, single-dose intravenous and intraperitoneal injections of fluorouracil have been reported to kill differentiated spermatogonia and spermatocytes at a dose of 500 mg/kg and produce abnormalities in spermatids at 50 mg/kg.
Clinical Studies
- Under the experimental conditions of the topical safety studies, Carac was not observed to cause contact sensitization. However, approximately 95% of subjects in the active arms of the Phase 3 clinical studies experienced facial irritation. Irritation is likely and sensitization is unlikely based on the results of the topical safety and Phase 3 studies.
- Two Phase 3 identically designed, multi-center, vehicle-controlled, double-blind studies were conducted to evaluate the clinical safety and efficacy of Carac. Patients with 5 or more actinic keratoses (AKs) on the face or anterior bald scalp were randomly allocated to active or vehicle treatment in a 2:1 ratio. Patients were randomly allocated to treatment durations of 1, 2, or 4 weeks in a 1:1:1 ratio. They applied the study cream once daily to the entire face/anterior bald scalp. Each patient's clinical response was evaluated 4 weeks after the patient's last scheduled application of study cream. No additional post-treatment follow-up efficacy or safety assessments were performed beyond 4 weeks after the last scheduled application. The following graphs show the percentage of patients in whom 100% of treated lesions cleared, and the percentage of patients in whom 75% or more of treated lesions cleared. Treatment with Carac cream for 1, 2, or 4 weeks is compared to treatment with vehicle cream. Outcomes from 1, 2, and 4 weeks of treatment with vehicle cream are pooled because duration of treatment with vehicle had no substantive effect on clearance. Results from the two Phase 3 studies are shown separately. Although all treatment regimens of Carac studied demonstrated efficacy over vehicle for the treatment of actinic keratosis, continuing treatment up to 4 weeks as tolerated results in further lesion reduction and clearing.
- Clinical efficacy and safety in the treatment of AKs on the ears and other sun-exposed areas were not evaluated in the studies.
How Supplied
- Cream - 30 gram tube NDC 0066-7150-30
- Store at Controlled Room Temperature 20 to 25° C.
- Prescribing Information as of August 2009.
- Keep out of the reach of children.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Fluorouracil Topical Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Fluorouracil Topical |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Fluorouracil Topical |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Patients using Carac should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- It is for external use only.
- Avoid contact with the eyes, eyelids, nostrils, and mouth.
- Cleanse affected area and wait 10 minutes before applying Carac.
- Wash hands immediately after applying Carac.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight or other forms of ultraviolet irradiation during treatment, as the intensity of the reaction may be increased.
- Most patients using Carac get skin reactions where the medicine is used. These reactions include redness, dryness, burning, pain, erosion (loss of the upper layer of skin), and swelling. Irritation at the application site may persist for two or more weeks after therapy is discontinued. Treated areas may be unsightly during and after therapy.
- If you develop abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, vomiting, fever, or chills while on Carac therapy, stop the medication and contact your physician and/or pharmacist.
- Report any side effects to the physician and/or pharmacist.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Fluorouracil Topical interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Carac®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- Carac® — Kuric®[2]
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "CARAC- fluorouracil cream".
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Fluorouracil Topical |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Fluorouracil Topical |Label Name=Fluorouracil Topical08.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Fluorouracil Topical |Label Name=Fluorouracil Topical09.png
}}