Blepharoplasty
|
WikiDoc Resources for Blepharoplasty |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Blepharoplasty Most cited articles on Blepharoplasty |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Blepharoplasty |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Blepharoplasty at Clinical Trials.gov Trial results on Blepharoplasty Clinical Trials on Blepharoplasty at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Blepharoplasty NICE Guidance on Blepharoplasty
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Blepharoplasty Discussion groups on Blepharoplasty Patient Handouts on Blepharoplasty Directions to Hospitals Treating Blepharoplasty Risk calculators and risk factors for Blepharoplasty
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Blepharoplasty |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editors-In-Chief: Michel C. Samson, M.D., FRCSC, FACS [1] and David Malitz, M.D. [2]
Overview
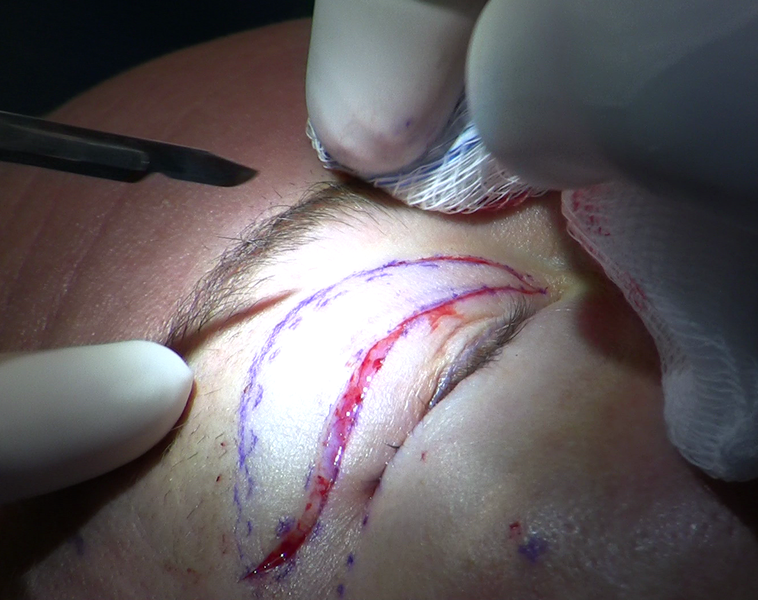
Blepharoplasty can be both a functional or cosmetic surgical procedure intended to reshape the upper eyelid or lower eyelid by the removal and/or repositioning of excess tissue as well as by reinforcement of surrounding muscles and tendons. When an advanced amount of upper eyelid skin is present, the skin may hang over the eyelashes and cause a loss of peripheral vision. The outer and upper parts of the visual field are most commonly affected and the condition may cause difficulty with activities such as driving or reading. In this circumstance, upper eyelid blepharoplasty is performed to improve peripheral vision. Patients with a less severe amount of excess skin may have a similar procedure performed for cosmetic reasons. Lower eyelid blepharoplasty is almost always done for cosmetic reasons, to improve puffy lower eyelid "bags" and reduce the wrinkling of skin.
Blepharoplasty is performed through external incisions made along the natural skin lines of the eyelids, such as the creases of the upper lids and below the lashes of the lower lids, or from the inside surface of the lower eyelid. Initial swelling and bruising take one to two weeks to resolve but at least several months are needed until the final result becomes stable. Depending upon the scope of the procedure, the operation takes one to three hours to complete.
The anatomy of the upper/lower eyelids, patients' skin quality, patients' age, and the adjacent bony and soft tissue all affect the cosmetic and functional outcomes after blepharoplasty. Factors which are known to cause complications after surgery include failure to recognize factors such as
- preexisting dry eyes - which may become exacerbated by disrupting the natural tear film
- laxity (loosness) of the lower lid margin (edge) - which predisposes to lower lid malposition
- prominence of the eye in relation to the malar (cheek) complex - which predisposes to lower lid malposition
The American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgeryestimates the average physician/surgeon fee for blepharoplasty for 2006 to be around $2,882. These fees are for the physician/surgeon fees only and do not include fees for the surgical facility, anesthesia, medical tests, prescriptions, surgical garments or any other miscellaneous costs related to the surgery. Physicians most qualified to perform blepharoplasties are plastic surgeons, ophthalmologists, oral and maxillofacial surgeons, and otolaryngologists.
The manner in which blepharoplasty surgery can alter a person's appearance is best appreciated by comparing before and after photos of surgical patients. Photos are available on a number of surgeon websites including: Dr. Frank Meronk based in Southern California , Dr. Paul S. Nassif based in Beverly Hills, California and Dr. Mitesh Kapadia based in Boston, Massachusetts.
An upper blepharoplasy in someone who is Asian is termed Asian blepharoplasty or double eyelid surgery.[1] It is the most popular form of cosmetic surgery among those of east and southeast Asian background. Due to anatomic differences between the asian and occidental eyelid, about half of this population are born without a supratarsal eyelid crease and are called single-lidded. Surgery can be used to artificially create a crease above the eye.
Transconjunctival blepharoplasty involves removing lower eyelid fat through an incision on the back of the eyelid, eliminating the need for an external incision. Because there is no external incision, excess skin can not be removed during the surgery, but skin resurfacing with a chemical peel or carbon dioxide laser may be performed simultaneously. [2] This allows for a faster recovery process.
History
Karl Ferdinand von Gräfe coined the phrase blepharoplasty in 1818 when the technique was used for repairing deformities caused by cancer in the eyelids.
The roots of the present cosmetic advancements began around 3000 years ago with the ancient Egyptians. Documents “written on papyrus text detail how surgeons, even in that primitive age performed reconstructions on lips, noses, and ears using skin grafts cut from folds from the forehead or cheek”. [3] As techniques began developing the ancient Greeks and Romans began writing down and collecting everything they knew involving these procedures. Aulus Cornelius Cellus, a first century Roman, described making an excision in the skin to relax the eyelids in his book De Medicine.[4] Knowledge of blood circulation and tissue health were discovered and spread throughout the ancient world allowing techniques to improve. However, during the middle ages, plastic surgery was prohibited because it was viewed as something that was spiritual and unethical. This ban was also due to poor hygiene. Luckily, during the Renaissance, modern intellectuals from ancient Greece and Rome developed text illustrating the rediscovery of surgical procedures and techniques.
As the 19th century approached developments were being made that would eventually be the foundation to modern cosmetic surgery. The First World War was the first major event that really relied on the dedication of surgeons and advancements in cosmetic surgery. This gave doctors a chance to practice and perfect reconstructive surgical procedures. It also prepared medical personnel for the tragedies of World War II and other subsequent catastrophes. As with any medical advancements, the development of surgical techniques goes through a period of trial and error as reconstructive surgery did during World War I. Each improvement eventually becomes the root of future advancements allowing physicians to combine procedures such as a basic lid fat resection and chemical peels insuring a speedy recovery.
References
- ↑ McCurdy JA Jr. "Upper blepharoplasty in the Asian patient: the 'double eyelid' operation." Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2005 Feb;13(1):47-64. Review. PMID 15519927.
- ↑ John Kitzmiller, “Blepharoplasty, Lower Lid Subciliary” 2006. eMedicine. Ed. 25 September 2006, http://www.emedicine.com/plastic/topic4.htm
- ↑ “History of Cosmetic Surgery”. Wise Medical & Health, 26 September 2006, http://www.resources4cosmeticsurgery.com/topics/history.html
- ↑ Cecilia Tran,“Preoperative Considerations in Blepharoplasty,” Baylor College of Medicine, 25 September 2006, http://www.bmc.edu/oto/grand/04_22_04.htm
External links
- Eyelid surgery patients from the American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery
- Blepharoplasty Flash animation
- Blepharoplasty images