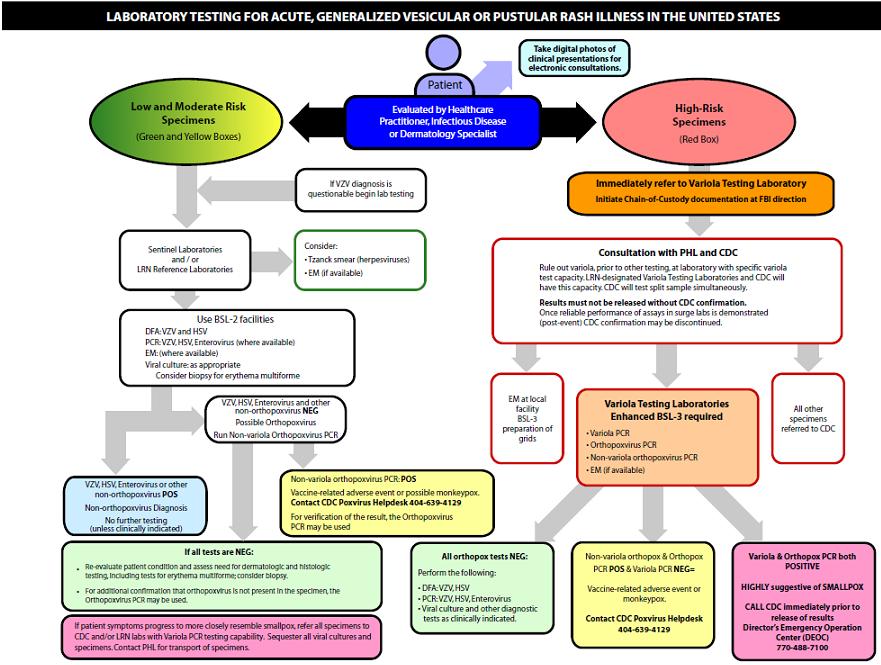
Smallpox laboratory tests
This chart describes the laboratory testing protocol for a patient that presents with generalized vesicular or pustular rash illness. It is also based upon the risk level the patient has of developing acquiring smallpox.
Laboratory confirmation
Laboratory criteria for confirmation
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) identification of variola DNA in a clinical specimen, OR
- Isolation of smallpox (variola) virus from a clinical specimen (WHO Smallpox Reference laboratory or laboratory with appropriate reference capabilities) with variola PCR confirmation.
Laboratory diagnostic testing for variola virus should be conducted in a CDC Laboratory Response Network (LRN) laboratory utilizing LRN-approved PCR tests and protocols for variola virus. Initial confirmation of a smallpox outbreak requires additional testing at CDC.
Note: Generic orthopox PCR and negative stain electron microscopy (EM) identification of a pox virus in a clinical specimen are suggestive of an 'orthopox ' virus infection but not diagnostic for smallpox.
The importance of case confirmation using laboratory diagnostic tests differs depending on the epidemiological situation. Because of the low predictive value of a positive lab test result in the absence of a known smallpox outbreak, in the pre-outbreak (pre-event) setting, laboratory testing should be reserved for cases that meet the clinical case definition and are thus classified as being a potential high risk for smallpox.
Vaccine
The chart below describes a patient that appears to show an adverse reaction to the smallpox vaccine and the protocol involved with it.