Radiation induced pericarditis: Difference between revisions
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
| Sudden [[pain]], that lasts for hours or sometimes days before a [[patient]] comes to the [[ER]] | | Sudden [[pain]], that lasts for hours or sometimes days before a [[patient]] comes to the [[ER]] | ||
| Sudden or [[Chronic (medicine)|chronically]] worsening pain that can come and go in [[paroxysm]]s or it can last for hours before the [[patient]] decides to come to the [[ER]] | | Sudden or [[Chronic (medicine)|chronically]] worsening pain that can come and go in [[paroxysm]]s or it can last for hours before the [[patient]] decides to come to the [[ER]] | ||
|} | |||
===Differentiating pericarditis from other diseases on the basis of chest pain, shortness of breath, and tachypnea=== | |||
The differentials include the following:<ref name="pmid24550636">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brenes-Salazar JA |title=Westermark's and Palla's signs in acute and chronic pulmonary embolism: Still valid in the current computed tomography era |journal=J Emerg Trauma Shock |volume=7 |issue=1 |pages=57–8 |year=2014 |pmid=24550636 |pmc=3912657 |doi=10.4103/0974-2700.125645 |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlCT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics">{{cite web |url=http://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/rg.245045008 |title=CT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23940438">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A |title=Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism |journal=Exp Clin Cardiol |volume=18 |issue=2 |pages=129–38 |year=2013 |pmid=23940438 |pmc=3718593 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="urlPulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health">{{cite web |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMHT0022657/ |title=Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20118395">{{cite journal |vauthors=Ramani GV, Uber PA, Mehra MR |title=Chronic heart failure: contemporary diagnosis and management |journal=Mayo Clin. Proc. |volume=85 |issue=2 |pages=180–95 |year=2010 |pmid=20118395 |pmc=2813829 |doi=10.4065/mcp.2009.0494 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18215495">{{cite journal |vauthors=Blinderman CD, Homel P, Billings JA, Portenoy RK, Tennstedt SL |title=Symptom distress and quality of life in patients with advanced congestive heart failure |journal=J Pain Symptom Manage |volume=35 |issue=6 |pages=594–603 |year=2008 |pmid=18215495 |pmc=2662445 |doi=10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.06.007 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid19168510">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hawkins NM, Petrie MC, Jhund PS, Chalmers GW, Dunn FG, McMurray JJ |title=Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: diagnostic pitfalls and epidemiology |journal=Eur. J. Heart Fail. |volume=11 |issue=2 |pages=130–9 |year=2009 |pmid=19168510 |pmc=2639415 |doi=10.1093/eurjhf/hfn013 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid9465867">{{cite journal |vauthors=Takasugi JE, Godwin JD |title=Radiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=Radiol. Clin. North Am. |volume=36 |issue=1 |pages=29–55 |year=1998 |pmid=9465867 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid14651761">{{cite journal |vauthors=Wedzicha JA, Donaldson GC |title=Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=Respir Care |volume=48 |issue=12 |pages=1204–13; discussion 1213–5 |year=2003 |pmid=14651761 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23833163">{{cite journal |vauthors=Nakawah MO, Hawkins C, Barbandi F |title=Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the overlap syndrome |journal=J Am Board Fam Med |volume=26 |issue=4 |pages=470–7 |year=2013 |pmid=23833163 |doi=10.3122/jabfm.2013.04.120256 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20511488">{{cite journal |vauthors=Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, Sinak LJ, Hayes SN, Melduni RM, Oh JK |title=Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management |journal=Mayo Clin. Proc. |volume=85 |issue=6 |pages=572–93 |year=2010 |pmid=20511488 |pmc=2878263 |doi=10.4065/mcp.2010.0046 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23610095">{{cite journal |vauthors=Bogaert J, Francone M |title=Pericardial disease: value of CT and MR imaging |journal=Radiology |volume=267 |issue=2 |pages=340–56 |year=2013 |pmid=23610095 |doi=10.1148/radiol.13121059 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11680112">{{cite journal |vauthors=Gharib AM, Stern EJ |title=Radiology of pneumonia |journal=Med. Clin. North Am. |volume=85 |issue=6 |pages=1461–91, x |year=2001 |pmid=11680112 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23507061">{{cite journal |vauthors=Schmidt WA |title=Imaging in vasculitis |journal=Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol |volume=27 |issue=1 |pages=107–18 |year=2013 |pmid=23507061 |doi=10.1016/j.berh.2013.01.001 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16891436">{{cite journal |vauthors=Suresh E |title=Diagnostic approach to patients with suspected vasculitis |journal=Postgrad Med J |volume=82 |issue=970 |pages=483–8 |year=2006 |pmid=16891436 |pmc=2585712 |doi=10.1136/pgmj.2005.042648 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid123074">{{cite journal |vauthors=Stein PD, Dalen JE, McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA, Wenger NK, Willis PW |title=The electrocardiogram in acute pulmonary embolism |journal=Prog Cardiovasc Dis |volume=17 |issue=4 |pages=247–57 |year=1975 |pmid=123074 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23413894">{{cite journal |vauthors=Warnier MJ, Rutten FH, Numans ME, Kors JA, Tan HL, de Boer A, Hoes AW, De Bruin ML |title=Electrocardiographic characteristics of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |journal=COPD |volume=10 |issue=1 |pages=62–71 |year=2013 |pmid=23413894 |doi=10.3109/15412555.2012.727918 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid23000104">{{cite journal |vauthors=Stein PD, Matta F, Ekkah M, Saleh T, Janjua M, Patel YR, Khadra H |title=Electrocardiogram in pneumonia |journal=Am. J. Cardiol. |volume=110 |issue=12 |pages=1836–40 |year=2012 |pmid=23000104 |doi=10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.019 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid26209947">{{cite journal |vauthors=Hazebroek MR, Kemna MJ, Schalla S, Sanders-van Wijk S, Gerretsen SC, Dennert R, Merken J, Kuznetsova T, Staessen JA, Brunner-La Rocca HP, van Paassen P, Cohen Tervaert JW, Heymans S |title=Prevalence and prognostic relevance of cardiac involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis |journal=Int. J. Cardiol. |volume=199 |issue= |pages=170–9 |year=2015 |pmid=26209947 |doi=10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.087 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid20112390">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dennert RM, van Paassen P, Schalla S, Kuznetsova T, Alzand BS, Staessen JA, Velthuis S, Crijns HJ, Tervaert JW, Heymans S |title=Cardiac involvement in Churg-Strauss syndrome |journal=Arthritis Rheum. |volume=62 |issue=2 |pages=627–34 |year=2010 |pmid=20112390 |doi=10.1002/art.27263 |url=}}</ref><small> | |||
{| | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
! rowspan="2" |<small>Diseases</small> | |||
! colspan="3" |<small>Diagnostic tests</small> | |||
! colspan="3" |<small>Physical Examination</small> | |||
| colspan="7" |<small>Symptoms | |||
! colspan="1" rowspan="2" |<small>Past medical history</small> | |||
! rowspan="2" |<small>Other Findings</small> | |||
|- style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | |||
!<small>CT scan and MRI</small> | |||
!<small>EKG</small> | |||
!<small>Chest X-ray</small> | |||
!<small>Tachypnea</small> | |||
!<small>Tachycardia</small> | |||
!<small>Fever</small> | |||
!<small>Chest Pain</small> | |||
!<small>Hemoptysis</small> | |||
!<small>Dyspnea on Exertion</small> | |||
!<small>Wheezing</small> | |||
!<small>Chest Tenderness</small> | |||
!<small>Nasalopharyngeal Ulceration</small> | |||
!<small>Carotid Bruit</small> | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Percarditis]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On contrast enhanced [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
**Enhancement of the [[pericardium]] (due to [[inflammation]]) | |||
**[[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
**[[Pericardial calcification]] | |||
*On [[gadolinium]]-enhanced fat-saturated [[Magnetic resonance imaging|T1-weighted MRI]]: | |||
**[[Pericardial]] enhancement (due to [[inflammation]]) | |||
**[[Pericardial effusion]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*ST elevation | |||
*PR depression | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Large collection of fluid inside the pericardial sac (pericardial effusion) | |||
*Calcification of pericardial sac | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Low grade) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Relieved by sitting up and leaning forward) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Infections: | |||
**[[Viral]] (Coxsackie virus, [[Herpes simplex virus|Herpes virus]], [[Mumps virus]], [[Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)|HIV]]) | |||
**[[Bacteria]] ([[Mycobacterium tuberculosis]]-common in developing countries) | |||
**[[Fungal]] ([[Histoplasmosis]]) | |||
*Idiopathic in a large number of cases | |||
*[[Autoimmune]] | |||
*[[Uremia]] | |||
*[[Malignancy]] | |||
*Previous [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*May be clinically classified into: | |||
**Acute (< 6 weeks) | |||
**Sub-acute (6 weeks - 6 months) | |||
**Chronic (> 6 months) | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pulmonary embolism]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[CT angiography]]: | |||
** Intra-luminal filling defect | |||
*On [[MRI]]: | |||
** Narrowing of involved [[Blood vessel|vessel]] | |||
** No contrast seen distal to [[obstruction]] | |||
** Polo-mint sign (partial filling defect surrounded by contrast) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Pulmonary embolism electrocardiogram|S1Q3T3]] pattern representing acute [[right heart]] strain | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Fleischner sign]] (enlarged pulmonary artery), [[Hampton's hump|Hampton hump]], [[Westermark's sign]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (Low grade) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ (In case of massive PE) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Hypercoagulating conditions ([[Factor V Leiden]], [[thrombophilia]], [[deep vein thrombosis]], immobilization, [[malignancy]], [[pregnancy]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
* May be associated with [[metabolic alkalosis]] and [[syncope]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Congestive heart failure]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
**[[Mediastinal lymphadenopathy]] | |||
** Hazy [[mediastinal]] fat | |||
*On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]]: | |||
** Abnormality of [[cardiac]] chambers ([[Hypertrophy (medical)|hypertrophy]], dilation) | |||
** Delayed enhancement [[MRI]] may help characterize the [[myocardial]] [[Tissue (biology)|tissue]] ([[fibrosis]]) | |||
** Late enhancement of contrast in conditions such as [[myocarditis]], [[sarcoidosis]], [[amyloidosis]], [[Anderson-Fabry disease|Anderson-Fabry]]'s disease, [[Chagas disease]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Goldberg's criteria may aid in diagnosis of left ventricular dysfunction: (High specificity) | |||
**[[S wave|S]]V1 or [[S wave|S]]V2 + [[R wave|R]]V5 or [[R wave|R]]V6 ≥3.5 mV | |||
**Total [[QRS complex|QRS]] amplitude in each of the limb leads ≤0.8 mV | |||
**[[R wave|R]]/[[S wave|S]] ratio <1 in lead V4 | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Cardiomegaly]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Previous [[myocardial infarction]] | |||
*[[Hypertension]] ([[Systemic hypertension|systemic]] and [[Pulmonary hypertension|pulmonary]]) | |||
*[[Cardiac arrhythmia|Cardiac arrythmias]] | |||
*[[Viral]] infections ([[myocarditis]]) | |||
*[[Congenital heart disease|Congenital heart defects]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Right heart failure]] associated with: | |||
**[[Hepatomegaly]] | |||
**Positive hepato-jugular reflex | |||
**Increased [[jugular venous pressure]] | |||
**[[Peripheral edema]] | |||
*[[Left heart failure]] associated with: | |||
**[[Pulmonary edema]] | |||
**Eventual [[right heart failure]] | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Pneumonia]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: (not generally indicated) | |||
**[[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] ([[alveolar]]/lobar pneumonia) | |||
**Peribronchial [[nodules]] ([[bronchopneumonia]]) | |||
**[[Ground glass opacification on CT|Ground-glass opacity]] (GGO) | |||
**[[Abscess]] | |||
**[[Pleural effusion]] | |||
**On [[MRI]]: | |||
*Not indicated | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Prolonged [[PR interval]] | |||
*Transient [[T wave]] inversions | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Consolidation (medicine)|Consolidation]] ([[alveolar]]/lobar [[pneumonia]]) | |||
*Peribronchial [[nodules]] (bronchopneumonia) | |||
*Ground-glass opacity (GGO) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Ill-contact | |||
*Travelling | |||
*[[Smoking]] | |||
*[[Diabetes mellitus|Diabetic]] | |||
*Recent hospitalization | |||
*[[Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Requires [[Sputum|sputum stain]] and culture for diagnosis | |||
*[[Empiric therapy|Empiric management]] usually started before [[Culture collection|culture]] results | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Vasculitis]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: ([[Takayasu's arteritis|Takayasu arteritis]]) | |||
**[[Blood vessel|Vessel]] wall thickening | |||
**Luminal narrowing of [[pulmonary artery]] | |||
**Masses or nodules ([[Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody|ANCA]]-associated granulomatous vasculitis) | |||
*On [[Magnetic resonance imaging|MRI]]: | |||
Homogeneous, circumferential [[Blood vessel|vessel]] wall [[swelling]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Bundle branch block|Right or left bundle-branch block]] ([[Churg-Strauss syndrome]]) | |||
*[[Atrial fibrillation]] ([[Churg-Strauss syndrome]]) | |||
*Non-specific [[ST interval|ST segment]] and [[T wave]] changes | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Nodule (medicine)|Nodules]] | |||
*[[Cavitation]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Takayasu's arteritis|Takayasu arteritis]] usually found in persons aged 4-60 years with a mean of 30 | |||
*[[Giant-cell arteritis]] usually occurrs in persons aged > 60 years | |||
*[[Churg-Strauss syndrome]] may present with [[asthma]], [[sinusitis]], transient [[pulmonary]] infiltrates and neuropathy alongwith [[cardiac]] involvement | |||
*Granulomatous vasculitides may present with [[nephritis]] and [[upper airway]] ([[nasopharyngeal]]) destruction | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
|- | |||
| style="background: #DCDCDC; padding: 5px; text-align: center;" |[[Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease]] (COPD) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*On [[Computed tomography|CT scan]]: | |||
**[[Chronic bronchitis]] may show [[bronchial]] wall thickening, scarring with bronchovascular irregularity, [[fibrosis]] | |||
**[[Emphysema]] may show [[alveolar]] septal destruction and airspace enlargement (Centrilobular- upper lobe, panlobular- lower lobe) | |||
**Giant bubbles | |||
*On [[MRI]]: | |||
**Increased diameter of [[pulmonary arteries]] | |||
**Peripheral [[pulmonary]] [[vasculature]] attentuation | |||
**Loss of retrosternal airspace due to right ventricular enlargement | |||
**Hyperpolarized Helium MRI may show progressively poor ventilation and destruction of lung | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Multifocal atrial tachycardia]] (atleast 3 distinct [[P waves|P wave]] morphologies) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*Enlarged [[lung]] shadows ([[emphysema]]) | |||
*Flattening of [[diaphragm]] ([[emphysema]]) | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" |✔ | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | - | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Smoking]] | |||
*[[Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency|Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency]] | |||
*Increased [[sputum]] production ([[chronic bronchitis]]) | |||
*[[Cough]] | |||
| style="background: #F5F5F5; padding: 5px;" | | |||
*[[Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency|Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency]] may be associated with [[hepatomegaly]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 15 April 2020
|
Pericarditis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Surgery |
|
Case Studies |
|
Radiation induced pericarditis On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Radiation induced pericarditis |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Radiation induced pericarditis |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]; Associate Editor(s)-In-Chief: Varun Kumar, M.B.B.S.; Lakshmi Gopalakrishnan, M.B.B.S.
Overview
The survival rate in Hodgkin lymphoma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and breast carcinomas has significantly improved with use of radiation therapy. However, radiation therapy to thoracic and mediastinal cancers have also led to the development of pericarditis, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, conduction abnormalities in heart and valvular heart diseases which account for significant morbidity and mortality. The incidence is higher with doses greater than 40 Gy (4000 rad).
Historical Perspective
Classification
Based on the presentation and onset of symptoms, the radiation-induced pericardial disease may be classified as:[1]
- Acute pericarditis
- Delayed pericarditis
- Pancarditis
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Pericardial effusion
Pathophysiology
Radiation therapy disrupts endothelial cells of the microvasculature of the pericardium and leads to repeated episodes of ischemia. The final result is the formation of fibrosis and fibrinous exudates that are ultimately replaced by fibroblasts and collagen fibers [2][3][4][5].
Radiation-induced pericarditis depends on:
- Total dose of radiation
- Amount of cardiac silhouette exposed
- Nature of the radiation source
- Duration and fractionation of therapy
In a retrospective study, 27.7% of the patients developed pericardial effusion after median time period of 5.3 months following radiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma with radiation dose ranging between 3 to 50Gy. It was concluded that high dose-volume of the irradiated pericardium and heart increased the risk of developing pericarditis[6].
Causes
Radiation-induced pericardial disease can occur in any cancer survivor who receive thoracic radiation therapy, including breast cancer, Hodgkin's lymphoma, esophageal cancer, and lung cancer. However, most data come from patients treated for breast cancer and Hodgkin's lymphoma, in which radiation therapy is a frequent component of management.
Differentiating Radiation-induced Pericarditis from other Diseases
- Pericarditis must be differentiated from diseases presenting with chest pain, shortness of breath and tachypnea.
- For a full discussion of the differential diagnosis of chest pain click here
- For an expert algorithm that aids in the diagnosis of the cause of chest pain click here
- Pericarditis must be differentiated from myocardial infarction as an important cause of chest pain.The differentiating features include:[7]
| Characteristic/Parameter | Pericarditis | Myocardial infarction |
|---|---|---|
| Pain description | Sharp, pleuritic, retro-sternal (under the sternum) or left precordial (left chest) pain. | Crushing, pressure-like, heavy pain. Described as "elephant on the chest". |
| Radiation | Pain radiates to the trapezius ridge (to the lowest portion of the scapula on the back) or no radiation. | Pain radiates to the jaw, or the left or arm, or does not radiate. |
| Exertion | Does not change the pain | Can increase the pain |
| Position | Pain is worse supine or upon inspiration (breathing in) | Not positional |
| Onset/duration | Sudden pain, that lasts for hours or sometimes days before a patient comes to the ER | Sudden or chronically worsening pain that can come and go in paroxysms or it can last for hours before the patient decides to come to the ER |
Differentiating pericarditis from other diseases on the basis of chest pain, shortness of breath, and tachypnea
The differentials include the following:[8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27]
| Diseases | Diagnostic tests | Physical Examination | Symptoms | Past medical history | Other Findings | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT scan and MRI | EKG | Chest X-ray | Tachypnea | Tachycardia | Fever | Chest Pain | Hemoptysis | Dyspnea on Exertion | Wheezing | Chest Tenderness | Nasalopharyngeal Ulceration | Carotid Bruit | |||
| Percarditis |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ (Low grade) | ✔ (Relieved by sitting up and leaning forward) | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
|
| Pulmonary embolism |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ (Low grade) | ✔ | ✔ (In case of massive PE) | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
|
| Congestive heart failure |
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
|
| ||
| Pneumonia |
|
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | - |
|
|
| Vasculitis |
|
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | - | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
|
||
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) |
|
|
✔ | ✔ | - | - | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | - |
|
| |
Epidemiology and Demographics
Pericardial changes are the most common cardiac complications of radiation therapy[3]. Incidence of radiation induced pericarditis has significantly decreased with the use of lower doses and newer radiotherapy techniques [28][29][30]. In a study, incidence decreased from 20% to 2.5% with the changes in methods of RT administration[28]
In as study among pediatric population with various cancers, radiation therapy with ≥15 GY increased the risk of developing pericarditis by two to six times[31]
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Diagnosis
Diagnostic Study of Choice
There are no established criteria for radiation induced pericarditis.
History and Symptoms
- Acute pericarditis: Acute pericarditis is a rare complication of radiation therapy. It presents with nonspecific pericarditis symptoms such as chest pain and fever shortly after radiation therapy[1][3].
- Delayed pericarditis: Delayed pericarditis occurs from months to years after exposure to radiation [32][33]. It usually presents with:
- Chest pain
- Dyspnea
- Orthopnea
- Pericardial effusion: Protein-rich exudate may accumulate in the pericardial sac leading to pericardial effusion. Rapid accumulation may result in the development of cardiac tamponade presenting with clinical signs and symptoms of tamponade[3][32].
- Constrictive pericarditis: Constrictive pericarditis is a late complication of radiation therapy. Patients typically present with signs and symptoms of heart failure, similar to other causes of constrictive pericarditis[3].
Physical Examination
Physical examination of patients with radiation-induced pericarditis depends on the presentation. In acute pericarditis, the physical examination may show fever and pericardial rub. In patients presenting with tamponade physical examination may show:
- Hypotension
- Tachycardia
- Jugular venous distention with a prominent Y descent
- Kussmaul's sign, and distant heart sounds
In constrictive pericarditis, signs of congestive heart failure may be present, including:
- Hepatomegaly
- Ascites
- Ankle edema [3]
Laboratory Findings
Laboratory findings consistent with the diagnosis of radiation-induced acute pericarditis include elevated inflammatory markers such as neutrophil count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)[3].
Electrocardiogram
In acute pericarditis, non-specific ST and T wave changes or ST segment elevation in all leads may be noted[1][3].
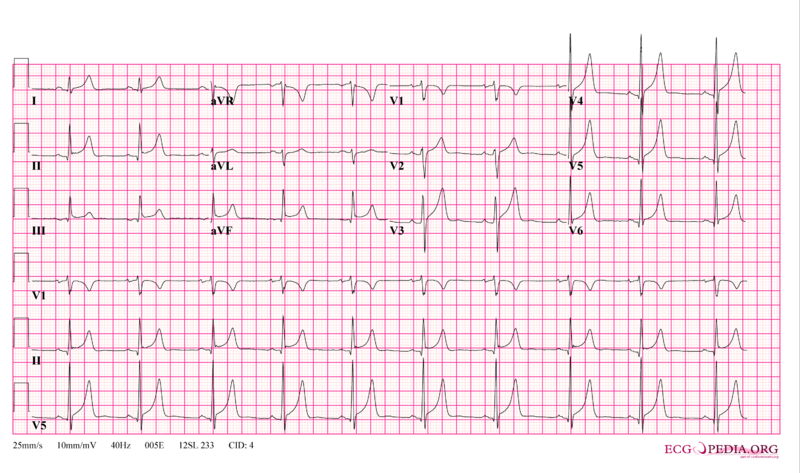
In patients presenting with constrictive pericarditis, electrocardiographic changes are similar to other causes of constrictive pericarditis. Electrocardiographic signs of constrictive chronic pericarditis is usually inconsistent and non specific[34]
- Left atrial enlargement
- Frequent atrial arrhythmias
- Right axis deflection
- Possible reduction in voltages
- Diffuse negative T-waves
- Typical (normal QRS axis, low voltage, and generalized T wave flattening or inversion)
- Right ventricular hypertrophy
- Right axis deviation
X-ray
Echocardiography or Ultrasound
CT scan
MRI
Other Imaging Findings
Other Diagnostic Studies
Pericardiocentesis
- Radiation induced pericardial effusion can be confused with malignant pericarditis and hypothyroidism (secondary to mediastinal irradiation) induced pericarditis.
- Pericardiocentesis can be used to differentiate them with fluid analysis for malignant cells and thyroid function tests.
- For more information on pericardiocentesis, click here.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
Surgery
- Pericarditis with large effusion can be drained either percutaneously or surgically
- Those with recurrent pericardial effusion can be treated with pericardiotomy(pericardial window) or by surgical stripping.
- Pericardiectomy is recommended for patients who develop constrictive pericarditis. However, the perioperative mortality rate is higher in postradiation constrictive pericarditis compared to that of idiopathic constrictive pericarditis[35].
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Yusuf SW, Sami S, Daher IN (2011). "Radiation-induced heart disease: a clinical update". Cardiol Res Pract. 2011: 317659. doi:10.4061/2011/317659. PMC 3051159. PMID 21403872.
- ↑ Fajardo LF (1989). "The unique physiology of endothelial cells and its implications in radiobiology". Front Radiat Ther Oncol. 23: 96–112. doi:10.1159/000416574. PMID 2697671.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Yusuf SW, Venkatesulu BP, Mahadevan LS, Krishnan S (2017). "Radiation-Induced Cardiovascular Disease: A Clinical Perspective". Front Cardiovasc Med. 4: 66. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2017.00066. PMC 5662579. PMID 29124057.
- ↑ Taunk NK, Haffty BG, Kostis JB, Goyal S (2015). "Radiation-induced heart disease: pathologic abnormalities and putative mechanisms". Front Oncol. 5: 39. doi:10.3389/fonc.2015.00039. PMC 4332338. PMID 25741474.
- ↑ Hooning MJ, Aleman BM, van Rosmalen AJ, Kuenen MA, Klijn JG, van Leeuwen FE (2006). "Cause-specific mortality in long-term survivors of breast cancer: A 25-year follow-up study". Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 64 (4): 1081–91. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2005.10.022. PMID 16446057.
- ↑ Wei X, Liu HH, Tucker SL, Wang S, Mohan R, Cox JD; et al. (2008). "Risk factors for pericardial effusion in inoperable esophageal cancer patients treated with definitive chemoradiation therapy". Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 70 (3): 707–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.10.056. PMID 18191334.
- ↑ American College of Physicians (ACP). Medical Knowledge Self-Assessment Program (MKSAP-15): Cardiovascular Medicine. "Pericardial disease." p. 64. ISBN 978-934465-28-8 [1]
- ↑ Brenes-Salazar JA (2014). "Westermark's and Palla's signs in acute and chronic pulmonary embolism: Still valid in the current computed tomography era". J Emerg Trauma Shock. 7 (1): 57–8. doi:10.4103/0974-2700.125645. PMC 3912657. PMID 24550636.
- ↑ "CT Angiography of Pulmonary Embolism: Diagnostic Criteria and Causes of Misdiagnosis | RadioGraphics".
- ↑ Bĕlohlávek J, Dytrych V, Linhart A (2013). "Pulmonary embolism, part I: Epidemiology, risk factors and risk stratification, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism". Exp Clin Cardiol. 18 (2): 129–38. PMC 3718593. PMID 23940438.
- ↑ "Pulmonary Embolism: Symptoms - National Library of Medicine - PubMed Health".
- ↑ Ramani GV, Uber PA, Mehra MR (2010). "Chronic heart failure: contemporary diagnosis and management". Mayo Clin. Proc. 85 (2): 180–95. doi:10.4065/mcp.2009.0494. PMC 2813829. PMID 20118395.
- ↑ Blinderman CD, Homel P, Billings JA, Portenoy RK, Tennstedt SL (2008). "Symptom distress and quality of life in patients with advanced congestive heart failure". J Pain Symptom Manage. 35 (6): 594–603. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2007.06.007. PMC 2662445. PMID 18215495.
- ↑ Hawkins NM, Petrie MC, Jhund PS, Chalmers GW, Dunn FG, McMurray JJ (2009). "Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: diagnostic pitfalls and epidemiology". Eur. J. Heart Fail. 11 (2): 130–9. doi:10.1093/eurjhf/hfn013. PMC 2639415. PMID 19168510.
- ↑ Takasugi JE, Godwin JD (1998). "Radiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Radiol. Clin. North Am. 36 (1): 29–55. PMID 9465867.
- ↑ Wedzicha JA, Donaldson GC (2003). "Exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Respir Care. 48 (12): 1204–13, discussion 1213–5. PMID 14651761.
- ↑ Nakawah MO, Hawkins C, Barbandi F (2013). "Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and the overlap syndrome". J Am Board Fam Med. 26 (4): 470–7. doi:10.3122/jabfm.2013.04.120256. PMID 23833163.
- ↑ Khandaker MH, Espinosa RE, Nishimura RA, Sinak LJ, Hayes SN, Melduni RM, Oh JK (2010). "Pericardial disease: diagnosis and management". Mayo Clin. Proc. 85 (6): 572–93. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0046. PMC 2878263. PMID 20511488.
- ↑ Bogaert J, Francone M (2013). "Pericardial disease: value of CT and MR imaging". Radiology. 267 (2): 340–56. doi:10.1148/radiol.13121059. PMID 23610095.
- ↑ Gharib AM, Stern EJ (2001). "Radiology of pneumonia". Med. Clin. North Am. 85 (6): 1461–91, x. PMID 11680112.
- ↑ Schmidt WA (2013). "Imaging in vasculitis". Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 27 (1): 107–18. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2013.01.001. PMID 23507061.
- ↑ Suresh E (2006). "Diagnostic approach to patients with suspected vasculitis". Postgrad Med J. 82 (970): 483–8. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2005.042648. PMC 2585712. PMID 16891436.
- ↑ Stein PD, Dalen JE, McIntyre KM, Sasahara AA, Wenger NK, Willis PW (1975). "The electrocardiogram in acute pulmonary embolism". Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 17 (4): 247–57. PMID 123074.
- ↑ Warnier MJ, Rutten FH, Numans ME, Kors JA, Tan HL, de Boer A, Hoes AW, De Bruin ML (2013). "Electrocardiographic characteristics of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". COPD. 10 (1): 62–71. doi:10.3109/15412555.2012.727918. PMID 23413894.
- ↑ Stein PD, Matta F, Ekkah M, Saleh T, Janjua M, Patel YR, Khadra H (2012). "Electrocardiogram in pneumonia". Am. J. Cardiol. 110 (12): 1836–40. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.019. PMID 23000104.
- ↑ Hazebroek MR, Kemna MJ, Schalla S, Sanders-van Wijk S, Gerretsen SC, Dennert R, Merken J, Kuznetsova T, Staessen JA, Brunner-La Rocca HP, van Paassen P, Cohen Tervaert JW, Heymans S (2015). "Prevalence and prognostic relevance of cardiac involvement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis". Int. J. Cardiol. 199: 170–9. doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.06.087. PMID 26209947.
- ↑ Dennert RM, van Paassen P, Schalla S, Kuznetsova T, Alzand BS, Staessen JA, Velthuis S, Crijns HJ, Tervaert JW, Heymans S (2010). "Cardiac involvement in Churg-Strauss syndrome". Arthritis Rheum. 62 (2): 627–34. doi:10.1002/art.27263. PMID 20112390.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 Carmel RJ, Kaplan HS (1976). "Mantle irradiation in Hodgkin's disease. An analysis of technique, tumor eradication, and complications". Cancer. 37 (6): 2813–25. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(197606)37:6<2813::aid-cncr2820370637>3.0.co;2-s. PMID 949701.
- ↑ Maisch B, Ristić AD (2003). "Practical aspects of the management of pericardial disease". Heart. 89 (9): 1096–103. PMC 1767862. PMID 12923044.
- ↑ Maisch B, Seferović PM, Ristić AD, Erbel R, Rienmüller R, Adler Y; et al. (2004). "Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases executive summary; The Task force on the diagnosis and management of pericardial diseases of the European society of cardiology". Eur Heart J. 25 (7): 587–610. doi:10.1016/j.ehj.2004.02.002. PMID 15120056.
- ↑ Mulrooney DA, Yeazel MW, Kawashima T, Mertens AC, Mitby P, Stovall M; et al. (2009). "Cardiac outcomes in a cohort of adult survivors of childhood and adolescent cancer: retrospective analysis of the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study cohort". BMJ. 339: b4606. doi:10.1136/bmj.b4606. PMID 19996459.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Morton DL, Glancy DL, Joseph WL, Adkins PC (1973). "Management of patients with radiation-induced pericarditis with effusion: a note on the development of aortic regurgitation in two of them". Chest. 64 (3): 291–7. doi:10.1378/chest.64.3.291. PMID 4127171.
- ↑ Applefeld MM, Cole JF, Pollock SH, Sutton FJ, Slawson RG, Singleton RT; et al. (1981). "The late appearance of chronic pericardial disease in patients treated by radiotherapy for Hodgkin's disease". Ann Intern Med. 94 (3): 338–41. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-94-3-338. PMID 7224379.
- ↑ Chesler E, Mitha AS, Matisonn RE (1976). "The ECG of constrictive pericarditis--pattern resembling right ventricular hypertrophy". Am Heart J. 91 (4): 420–4. doi:10.1016/s0002-8703(76)80321-3. PMID 1258748.
- ↑ Bertog SC, Thambidorai SK, Parakh K, Schoenhagen P, Ozduran V, Houghtaling PL; et al. (2004). "Constrictive pericarditis: etiology and cause-specific survival after pericardiectomy". J Am Coll Cardiol. 43 (8): 1445–52. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.11.048. PMID 15093882.