Pyelonephritis x ray: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) (→X Ray) |
Usama Talib (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==X Ray== | ==X Ray== | ||
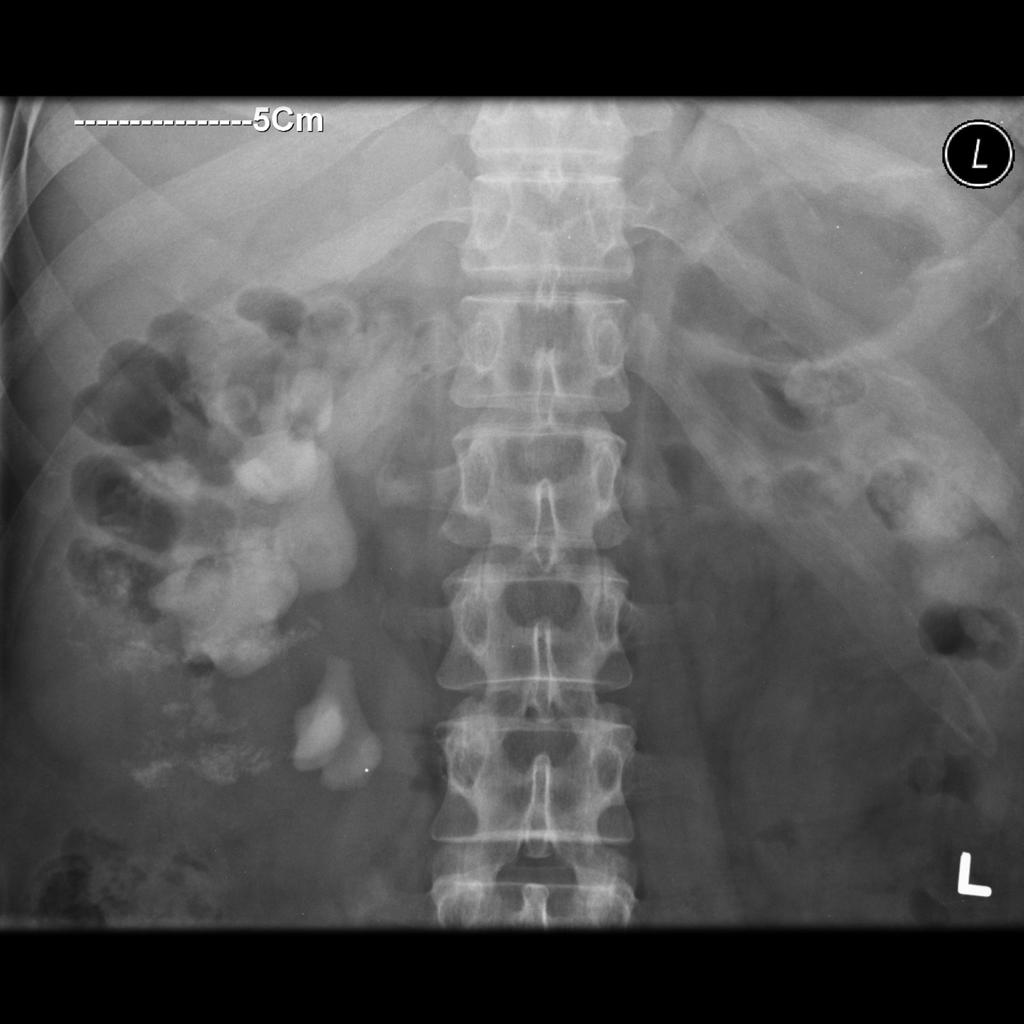
In the case of a suspicion of [[kidney stone]] due to classic [[Renal colic|colicky pain]]and variable amount of blood in the urine), x-rays of the kidneys, [[ureter]]s and [[Urinary bladder|bladder]] (KUB) may be helpful in finding radio opaque stones.<ref name="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9931">rID: 9931</ref> | |||
* Emphysematous pyelonephritis: In this case a radiograph may depict the presence of gas bubbles. | * Emphysematous pyelonephritis: In this case a radiograph may depict the presence of gas bubbles. | ||
*Xanthogranulomatous pyelonehritis: an Xray may show presence of a calculus which is most commonly involved in the pathophysiology of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis | |||
[[Image:Xanthogranulomatous-pyelonephritis.jpg|Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis|500px]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 15:07, 27 January 2017
|
Pyelonephritis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pyelonephritis x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pyelonephritis x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
PMID: 2724423 and 3052346 and 1571421 and http://www.guideline.gov/summary/summary.aspx?doc_id=13683&nbr=007017&string=pyelonephritis
Overview
Xray can be very helpful in diagnosing pyelonephritis. Kidney, ureter and bladder should be covered (KUB) in the Xray done to diagnose pyelonephritis. [1][2]
X Ray
In the case of a suspicion of kidney stone due to classic colicky painand variable amount of blood in the urine), x-rays of the kidneys, ureters and bladder (KUB) may be helpful in finding radio opaque stones.[3]
- Emphysematous pyelonephritis: In this case a radiograph may depict the presence of gas bubbles.
- Xanthogranulomatous pyelonehritis: an Xray may show presence of a calculus which is most commonly involved in the pathophysiology of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis
References
- ↑ Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG; et al. (2011). "International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases". Clin Infect Dis. 52 (5): e103–20. doi:10.1093/cid/ciq257. PMID 21292654.
- ↑ Ramakrishnan K, Scheid DC (2005). "Diagnosis and management of acute pyelonephritis in adults". Am Fam Physician. 71 (5): 933–42. PMID 15768623.
- ↑ Radiopaedia.org. Case courtesy of A.Prof Frank Gaillard, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/9931">rID: 9931