Pulmonary hypertension chest x ray
|
Pulmonary Hypertension Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Pulmonary hypertension chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Pulmonary hypertension chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Pulmonary hypertension chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1], Richard Channick, M.D.; Assistant Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ralph Matar.
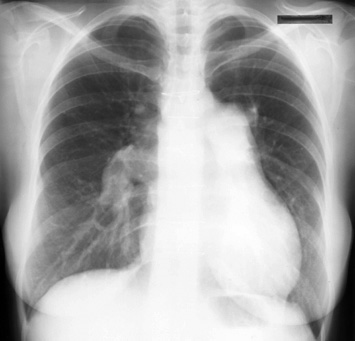
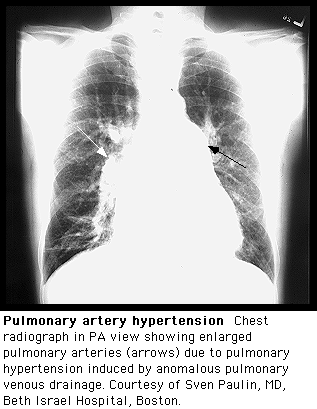
Chest x-ray in a patient with pulmonary hypertension:
- Chest x-ray is abnormal in 90% of patients with pulmonary hypertension at the time of diagnosis. However, no correlation have been found between the degree of severity of pulmonary hypertension and the findings on chest x-rays.
- It allows exclusion of moderate to severe lung diseases and pulmonary venous hypertension due to left heart disease.
Findings on Chest x-ray:
- Hilar pulmonary arterial dilation.
- Loss of peripheral blood vessel markings.
- Enlarged right atrium and right ventricle in advanced diseases.
Typical chest x-rays:
This is a posteroanterior radiograph revealing enlarged pulmonary arteries in a patient with Atrial septal defect.