Portal vein thrombosis overview: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Infobox Disease | Name = Portal vein thrombosis | Image = Pfortaderthrombose001.png | Caption = Portal vein thrombosis in computert...") |
Irfan Dotani (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{Portal vein thrombosis}} | |||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} | |||
{{PleaseHelp}} | |||
==Overview== | |||
'''Portal vein thrombosis''' is a form of [[venous thrombosis]] affecting the [[hepatic portal vein]], which can lead to [[portal hypertension]] and reduction in the blood supply to the [[liver]]. | |||
{{Infobox Disease | | {{Infobox Disease | | ||
Name = Portal vein thrombosis | | Name = Portal vein thrombosis | | ||
| Line 11: | Line 20: | ||
MeshID = | | MeshID = | | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Historical Perspective== | |||
==Classification== | |||
==Pathophysiology== | |||
==Causes== | ==Causes== | ||
Causes can include [[pancreatitis]], [[cirrhosis]], [[diverticulitis]], and [[cholangiocarcinoma]]. It is also a known [[Complication (medicine)|complication]] of [[splenectomy]].<ref>Ali Cadili, Chris de Gara, "Complications of Splenectomy", ''The American Journal of Medicine'', 2008, pp 371-375.</ref> Drugs such as [[Romiplostim]]. | Causes can include [[pancreatitis]], [[cirrhosis]], [[diverticulitis]], and [[cholangiocarcinoma]]. It is also a known [[Complication (medicine)|complication]] of [[splenectomy]].<ref>Ali Cadili, Chris de Gara, "Complications of Splenectomy", ''The American Journal of Medicine'', 2008, pp 371-375.</ref> Drugs such as [[Romiplostim]]. | ||
==Differentiating {{PAGENAME}} from Other Diseases== | |||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | |||
==Risk Factors== | |||
==Screening== | |||
==Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis== | |||
===Natural History=== | |||
===Complications=== | |||
===Prognosis=== | |||
==Diagnosis== | ==Diagnosis== | ||
The diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis is usually made by [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography]] with contrast or [[magnetic resonance imaging]]. [[D-dimer]] levels in the blood blood may be elevated as a result of fibrin degradation. | The diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis is usually made by [[ultrasound]], [[computed tomography]] with contrast or [[magnetic resonance imaging]]. [[D-dimer]] levels in the blood blood may be elevated as a result of fibrin degradation. | ||
===Diagnostic Criteria=== | |||
===History and Symptoms=== | |||
===Physical Examination=== | |||
===Laboratory Findings=== | |||
===Imaging Findings=== | |||
===Other Diagnostic Studies=== | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 64: | ||
Image:Kavernoese Transformation nach Pfortaderthrombose 001.png|Portal vein thrombosis on computed tomography (left) and cavernous transformation of the portal vein after 1 year (right)</gallery> | Image:Kavernoese Transformation nach Pfortaderthrombose 001.png|Portal vein thrombosis on computed tomography (left) and cavernous transformation of the portal vein after 1 year (right)</gallery> | ||
Treatments include [[anticoagulant]]s, [[Shunt (medical)|shunt]]s, [[Coronary artery bypass surgery|bypass surgery]], and [[Organ transplant|transplant]]s. | Treatments include [[anticoagulant]]s, [[Shunt (medical)|shunt]]s, [[Coronary artery bypass surgery|bypass surgery]], and [[Organ transplant|transplant]]s. | ||
===Medical Therapy=== | |||
===Surgery=== | |||
===Prevention=== | |||
==Related Chapters== | ==Related Chapters== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 74: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{ | {{reflist|2}} | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 40: | Line 82: | ||
[[Category:Hepatology]] | [[Category:Hepatology]] | ||
{{WS}} | |||
{{WH}} | |||
Revision as of 17:01, 18 July 2016
|
Portal vein thrombosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Portal vein thrombosis overview On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Portal vein thrombosis overview |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Portal vein thrombosis overview |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Please help WikiDoc by adding content here. It's easy! Click here to learn about editing.
Overview
Portal vein thrombosis is a form of venous thrombosis affecting the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to portal hypertension and reduction in the blood supply to the liver.
| Portal vein thrombosis | |
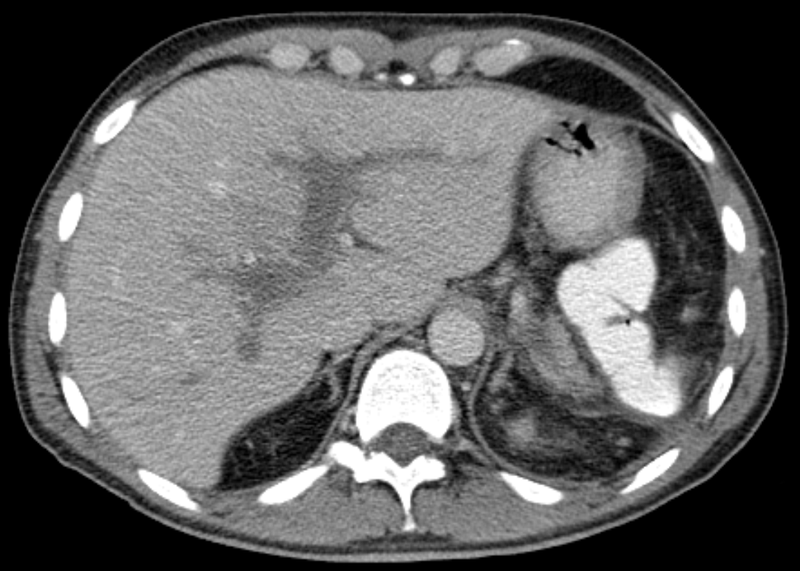 | |
|---|---|
| Portal vein thrombosis in computertomography. | |
| ICD-10 | I81 |
| ICD-9 | 452 |
Historical Perspective
Classification
Pathophysiology
Causes
Causes can include pancreatitis, cirrhosis, diverticulitis, and cholangiocarcinoma. It is also a known complication of splenectomy.[1] Drugs such as Romiplostim.
Differentiating Portal vein thrombosis overview from Other Diseases
Epidemiology and Demographics
Risk Factors
Screening
Natural History, Complications, and Prognosis
Natural History
Complications
Prognosis
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of portal vein thrombosis is usually made by ultrasound, computed tomography with contrast or magnetic resonance imaging. D-dimer levels in the blood blood may be elevated as a result of fibrin degradation.
Diagnostic Criteria
History and Symptoms
Physical Examination
Laboratory Findings
Imaging Findings
Other Diagnostic Studies
Treatment
-
Portal vein thrombosis on computed tomography (left) and cavernous transformation of the portal vein after 1 year (right)
Treatments include anticoagulants, shunts, bypass surgery, and transplants.
Medical Therapy
Surgery
Prevention
Related Chapters
References
- ↑ Ali Cadili, Chris de Gara, "Complications of Splenectomy", The American Journal of Medicine, 2008, pp 371-375.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Portal vein thrombosis. |
