Plerixafor: Difference between revisions
Gloria Picoy (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 20:00, 6 February 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Gloria Picoy [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Plerixafor is an hematopoietic that is FDA approved for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Common adverse reactions include diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, injection site reactions, headache, arthralgia, dizziness, and vomiting.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Plerixafor is indicated in combination with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) to the peripheral blood for collection and subsequent autologous transplantation in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) and multiple myeloma (MM).
- Dosage: 0.24 mg/kg body weight by subcutaneous (SC) injection
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Plerixafor in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Plerixafor in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Safety and efficacy not established in pediatric patients
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Plerixafor in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Plerixafor in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
History of hypersensitivity to Mozobil. Anaphylactic shock has occurred with use of Mozobil.
Warnings
Anaphylactic shock and Hypersensitivity reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening with clinically significant hypotension and shock have occurred in patients receiving Mozobil. Observe patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after Mozobil administration for at least 30 minutes and until clinically stable following completion of each administration. Only administer Mozobil when personnel and therapies are immediately available for the treatment of anaphylaxis and other hypersensitivity reactions.
In clinical studies, mild or moderate allergic reactions occurred within approximately 30 minutes after Mozobil administration in less than 1% of patients.
Tumor Cell Mobilization in Leukemia Patients
For the purpose of HSC mobilization, Mozobil may cause mobilization of leukemic cells and subsequent contamination of the apheresis product. Therefore, Mozobil is not intended for HSC mobilization and harvest in patients with leukemia.
Hematologic Effects
Leukocytosis
Administration of Mozobil in conjunction with G-CSF increases circulating leukocytes as well as HSC populations. Monitor white blood cell counts during Mozobil use.
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia has been observed in patients receiving Mozobil. Monitor platelet counts in all patients who receive Mozobil and then undergo apheresis.
Potential for Tumor Cell Mobilization
When Mozobil is used in combination with G-CSF for HSC mobilization‚ tumor cells may be released from the marrow and subsequently collected in the leukapheresis product. The effect of potential reinfusion of tumor cells has not been well-studied.
Splenic Enlargement and Potential for Rupture
Higher absolute and relative spleen weights associated with extramedullary hematopoiesis were observed following prolonged (2 to 4 weeks) daily plerixafor SC administration in rats at doses approximately 4-fold higher than the recommended human dose based on body surface area. The effect of Mozobil on spleen size in patients was not specifically evaluated in clinical studies. Evaluate individuals receiving Mozobil in combination with G-CSF who report left upper abdominal pain and/or scapular or shoulder pain for splenic integrity.
Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Mozobil may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Plerixafor is teratogenic in animals. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women using Mozobil. Advise women of childbearing potential to avoid becoming pregnant while receiving treatment with Mozobil. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) reported in patients who received Mozobil in conjunction with G-CSF regardless of causality and more frequent with Mozobil than placebo during HSC mobilization and apheresis were diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, injection site reactions, headache, arthralgia, dizziness, and vomiting.
Safety data for Mozobil in combination with G-CSF were obtained from two randomized placebo-controlled studies (301 patients) and 10 uncontrolled studies (242 patients). Patients were primarily treated with Mozobil at daily doses of 0.24 mg/kg SC. Median exposure to Mozobil in these studies was 2 days (range 1 to 7 days).
In the two randomized studies in patients with NHL and MM, a total of 301 patients were treated in the Mozobil and G-CSF group and 292 patients were treated in the placebo and G-CSF group. Patients received daily morning doses of G-CSF 10 micrograms/kg for 4 days prior to the first dose of Mozobil 0.24 mg/kg SC or placebo and on each morning prior to apheresis. The adverse reactions that occurred in ≥ 5% of the patients who received Mozobil regardless of causality and were more frequent with Mozobil than placebo during HSC mobilization and apheresis are shown in Table 2.
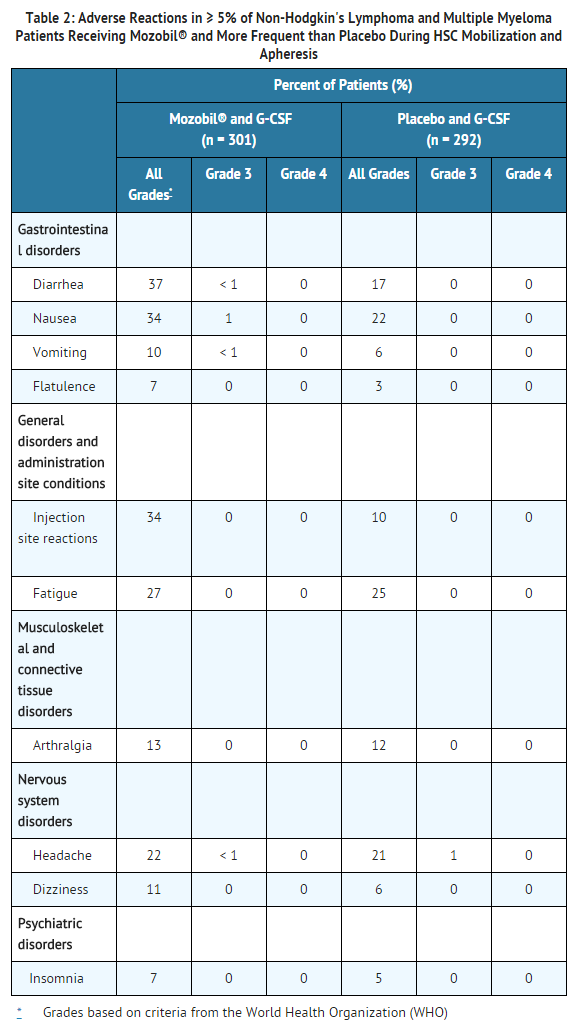
In the randomized studies, 34% of patients with NHL or MM had mild to moderate injection site reactions at the site of subcutaneous administration of Mozobil. These included erythema, hematoma, hemorrhage, induration, inflammation, irritation, pain, paresthesia, pruritus, rash, swelling, and urticaria.
Mild to moderate allergic reactions were observed in less than 1% of patients within approximately 30 min after Mozobil administration, including one or more of the following: urticaria (n = 2), periorbital swelling (n = 2), dyspnea (n = 1) or hypoxia (n = 1). Symptoms generally responded to treatments (e.g., antihistamines, corticosteroids, hydration or supplemental oxygen) or resolved spontaneously.
Vasovagal reactions, orthostatic hypotension, and/or syncope can occur following subcutaneous injections. In Mozobil oncology and healthy volunteer clinical studies, less than 1% of subjects experienced vasovagal reactions following subcutaneous administration of Mozobil doses ≤ 0.24 mg/kg. The majority of these events occurred within 1 hour of Mozobil administration. Because of the potential for these reactions, appropriate precautions should be taken.
Other adverse reactions in the randomized studies that occurred in < 5% of patients but were reported as related to Mozobil during HSC mobilization and apheresis included abdominal pain, hyperhidrosis, abdominal distention, dry mouth, erythema, stomach discomfort, malaise, hypoesthesia oral, constipation, dyspepsia, and musculoskeletal pain.
Hyperleukocytosis: In clinical trials, white blood cell counts of 100,000/mcL or greater were observed, on the day prior to or any day of apheresis, in 7% of patients receiving Mozobil and in 1% of patients receiving placebo. No complications or clinical symptoms of leukostasis were observed.
Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following adverse reactions have been reported from post-marketing experience with Mozobil. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactic reactions, including anaphylactic shock
- Psychiatric disorders: Abnormal dreams and nightmares
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Plerixafor in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Plerixafor in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Plerixafor during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Plerixafor in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Plerixafor in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Subcutaneous
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Plerixafor and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Plerixafor |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Plerixafor |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Plerixafor interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Plerixafor Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
Template:Chembox new Plerixafor (rINN and USAN, also known as MOZOBIL, JM 3100 and AMD3100) is a macrocyclic compound and potential fusion inhibitor. It is an antagonist (or perhaps more accurately a partial agonist) of the alpha-chemokine receptor CXCR4.
Research
HIV
It was initially developed for potential use in the treatment of HIV, for its role in the blocking of CXCR4, a chemokine receptor which acts as a co-receptor for certain strains of HIV (along with the virus's main cellular receptor, CD4). However, clinical trials in patients with HIV-AIDS have to date shown relatively little useful anti-viral activity.
Mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells
However, the CXCR4 alpha-chemokine receptor and its ligand SDF-1 are also important in hematopoietic stem cell homing to the bone marrow and in hematopoietic stem cell quiescence. Plerixafor has been found to be a strong inducer of "mobilization" of hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow to the bloodstream as peripheral blood stem cells.[1]
Peripheral blood stem cell mobilization, which has become extremely important as a source of hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation over the past 10 to 15 years, is generally performed using the cytokine drug G-CSF, but is ineffective in around 15 to 20% of patients. AMD3100 offers clinical promise as a drug for peripheral blood stem cell mobilization, and has recently completed Phase 3 clinical trials.[2] It is not yet in routine clinical use.
Small molecule cancer therapy
AMD3100 was seen to decrease metastasis in mice in several studies.[3]
References
- ↑ Cashen A, Nervi B, DiPersio J (2007). "AMD3100: CXCR4 antagonist and rapid stem cell-mobilizing agent". Future Oncol. 3 (1): 19–27. PMID 17280498.
- ↑ "Plerixafor: AMD 3100, AMD3100, JM 3100, SDZ SID 791". Drugs R D. 8 (2): 113–9. 2007. PMID 17324009.
- ↑ "CXCR4 regulates growth of both primary and metastatic breast cancer". Cancer Research. 64 (23): 8604–8612. 2004. PMID 15574767.