Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound: Difference between revisions
Badria Munir (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Badria Munir (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Ultrasound== | ==Ultrasound== | ||
*[[Ultrasound]] findings associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma include:<ref name="radiowiki"> Mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Radiopedia. Dr Frank Gailliard. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/mucoepidermoid-carcinoma-of-salivary-glands Accessed on February 17, 2016 </ref> | *[[Ultrasound]] findings associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma include:<ref name="radiowiki"> Mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Radiopedia. Dr Frank Gailliard. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/mucoepidermoid-carcinoma-of-salivary-glands Accessed on February 17, 2016 </ref> | ||
New technologies, including high-resolution probes and harmonic imaging, can delineate location, homogeneity or heterogeneity, shape, vascularity, and margins of salivary tumors in the periauricular, buccal, and submandibular area. | |||
Ultrasonography may be able to reveal the type of tumor, [5] and new ultrasonographic contrast mediums can now demonstrate the vascularity of the tumor before surgery.<ref name="pmid24324278">{{cite journal |vauthors=Rong X, Zhu Q, Ji H, Li J, Huang H |title=Differentiation of pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin's tumor of the parotid gland: ultrasonographic features |journal=Acta Radiol |volume=55 |issue=10 |pages=1203–9 |date=December 2014 |pmid=24324278 |doi=10.1177/0284185113515865 |url=}}</ref> | |||
A study by Rong et al identified differences between the ultrasonographic characteristics of Warthin tumors and those of pleomorphic adenomas, including with regard to shape, vascularity, and the prevalence of cystic areas.<ref name="pmid19712813">{{cite journal |vauthors=Yuan WH, Hsu HC, Chou YH, Hsueh HC, Tseng TK, Tiu CM |title=Gray-scale and color Doppler ultrasonographic features of pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin's tumor in major salivary glands |journal=Clin Imaging |volume=33 |issue=5 |pages=348–53 |date=2009 |pmid=19712813 |doi=10.1016/j.clinimag.2008.12.004 |url=}}</ref> | |||
:*Well-circumscribed [[hypoechoic]] lesion | :*Well-circumscribed [[hypoechoic]] lesion | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 15 January 2019
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
FDA on Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
CDC on Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound in the news |
|
Blogs on Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Mucoepidermoid carcinoma echocardiography or ultrasound |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Badria Munir M.B.B.S.[2] , Maria Fernanda Villarreal, M.D. [3]
Overview
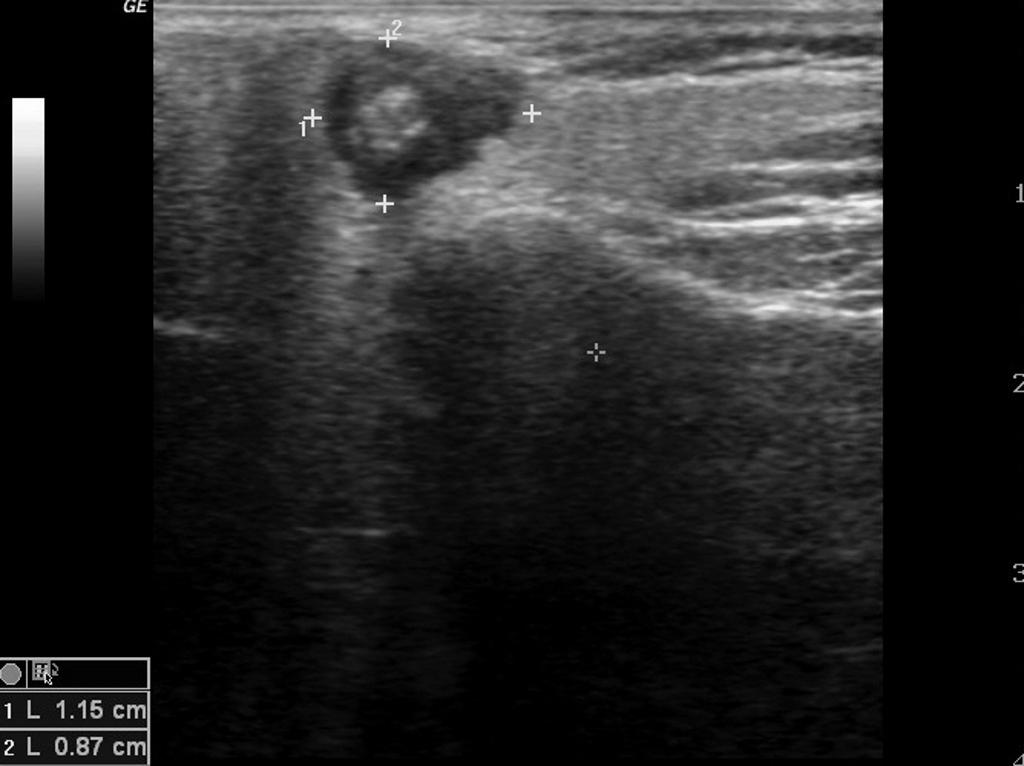
On ultrasound, characteristic findings of mucoepidermoid carcinoma include: a well-circumscribed hypoechoic lesion with a partial or completely cystic appearance, in contrast to the relatively hyperechoeic normal parotid gland.
Ultrasound
- Ultrasound findings associated with mucoepidermoid carcinoma include:[1]
New technologies, including high-resolution probes and harmonic imaging, can delineate location, homogeneity or heterogeneity, shape, vascularity, and margins of salivary tumors in the periauricular, buccal, and submandibular area.
Ultrasonography may be able to reveal the type of tumor, [5] and new ultrasonographic contrast mediums can now demonstrate the vascularity of the tumor before surgery.[2]
A study by Rong et al identified differences between the ultrasonographic characteristics of Warthin tumors and those of pleomorphic adenomas, including with regard to shape, vascularity, and the prevalence of cystic areas.[3]
- Well-circumscribed hypoechoic lesion
- Partial or completely cystic appearance
Gallery
References
- ↑ Mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Radiopedia. Dr Frank Gailliard. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/mucoepidermoid-carcinoma-of-salivary-glands Accessed on February 17, 2016
- ↑ Rong X, Zhu Q, Ji H, Li J, Huang H (December 2014). "Differentiation of pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin's tumor of the parotid gland: ultrasonographic features". Acta Radiol. 55 (10): 1203–9. doi:10.1177/0284185113515865. PMID 24324278.
- ↑ Yuan WH, Hsu HC, Chou YH, Hsueh HC, Tseng TK, Tiu CM (2009). "Gray-scale and color Doppler ultrasonographic features of pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin's tumor in major salivary glands". Clin Imaging. 33 (5): 348–53. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2008.12.004. PMID 19712813.