Meropenem: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
*There have been reports of individuals with a history of [[penicillin]] [[hypersensitivity]] who have experienced severe [[hypersensitivity]] reactions when treated with another [[β-lactam]]. | *There have been reports of individuals with a history of [[penicillin]] [[hypersensitivity]] who have experienced severe [[hypersensitivity]] reactions when treated with another [[β-lactam]]. | ||
*Before initiating therapy with Meropenem for injection (I.V.), careful inquiry should be made concerning previous [[hypersensitivity reactions]] to [[penicillins]], [[cephalosporins]], other [[β-lactams]], and other allergens. *If an allergic reaction to Meropenem for injection (I.V.) occurs, discontinue the drug immediately. | *Before initiating therapy with Meropenem for injection (I.V.), careful inquiry should be made concerning previous [[hypersensitivity reactions]] to [[penicillins]], [[cephalosporins]], other [[β-lactams]], and other allergens. *If an allergic reaction to Meropenem for injection (I.V.) occurs, discontinue the drug immediately. | ||
*Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine, oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation. Other therapy may also be administered as indicated. | *Serious [[anaphylactic reactions]] require immediate emergency treatment with [[epinephrine]], [[oxygen]], intravenous [[steroids]], and airway management, including intubation. Other therapy may also be administered as indicated. | ||
====Seizure Potential==== | |||
*[[Seizures]] and other adverse [[CNS]] experiences have been reported during treatment with Meropenem for injection (I.V.). | |||
*These experiences have occurred most commonly in patients with [[CNS]] disorders (e.g., [[brain]] lesions or history of [[seizures]]) or with [[bacterial meningitis]] and/or compromised [[renal function]]. | |||
*During clinical investigations, 2904 immunocompetent adult patients were treated for non-[[CNS]] infections with the overall [[seizure]] rate being 0.7% (based on 20 patients with this adverse event). | |||
*All meropenem-treated patients with [[seizures]] had pre-existing contributing factors. | |||
*Among these are included prior history of [[seizures]] or [[CNS]] abnormality and concomitant medications with [[seizure]] potential. | |||
*Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with advanced age and/or reduced [[renal function]]. | |||
*Close adherence to the recommended dosage regimens is urged, especially in patients with known factors that predispose to [[convulsive]] activity. | |||
*[[Anti-convulsant therapy]] should be continued in patients with known [[seizure]] disorders. | |||
*If focal [[tremors]], [[myoclonus]], or [[seizures]] occur, patients should be evaluated [[neurologically]], placed on [[anti-convulsant therapy]] if not already instituted, and the dosage of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) re-examined to determine whether it should be decreased or the [[antibiotic]] discontinued. | |||
====Interaction with Valproic Acid==== | |||
*Case reports in the literature have shown that co-administration of [[carbapenems]], including meropenem, to patients receiving [[valproic acid]] or [[divalproex sodium]] results in a reduction in [[valproic acid]] concentrations. | |||
*The [[valproic acid]] concentrations may drop below the therapeutic range as a result of this interaction, therefore increasing the risk of breakthrough [[seizures]]. | |||
*Increasing the dose of [[valproic acid]] or [[divalproex sodium]] may not be sufficient to overcome this interaction. | |||
*The concomitant use of meropenem and [[valproic acid]] or [[divalproex sodium]] is generally not recommended. | |||
*Antibacterials other than [[carbapenems]] should be considered to treat infections in patients whose [[seizures]] are well controlled on [[valproic acid]] or [[divalproex sodium]]. | |||
*If administration of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) is necessary, supplemental [[anti-convulsant therapy]] should be considered. | |||
====Clostridium difficile–Associated Diarrhea==== | |||
*[[Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea]] ([[CDAD]]) has been reported with use of nearly all [[antibacterial]] agents, including Meropenem for injection (I.V.), and may range in severity from mild [[diarrhea]] to fatal [[colitis]]. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of [[C. difficile]]. | |||
[[C. difficile]] produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of [[CDAD]]. Hypertoxin producing isolates of [[C. difficile]] cause increased [[morbidity]] and [[mortality]], as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require [[colectomy]]. [[CDAD]] must be considered in all patients who present with [[diarrhea]] following [[antibiotic]] use. Careful medical history is necessary since [[CDAD]] has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of [[antibacterial]] agents. | |||
If [[CDAD]] is suspected or confirmed, ongoing [[antibiotic]] use not directed against [[C. difficile]] may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, [[antibiotic]] treatment of [[C. difficile]], and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. | |||
====Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria==== | |||
Prescribing Meropenem for injection (I.V.) in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of [[drug-resistant]] bacteria. | |||
====Overgrowth of Nonsusceptible Organisms==== | |||
As with other [[broad-spectrum antibiotics]], prolonged use of meropenem may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient is essential. If superinfection does occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. | |||
==== Laboratory Tests==== | |||
While Meropenem for injection (I.V.) possesses the characteristic low toxicity of the beta-lactam group of antibiotics, periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy. | |||
====Patients with Renal Impairment==== | |||
In patients with renal impairment, thrombocytopenia has been observed but no clinical bleeding reported [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Use In Specific Populations (8.5) and (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |||
====Dialysis==== | |||
There is inadequate information regarding the use of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) in patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. | |||
====Potential for Neuromotor Impairment==== | |||
Patients receiving Meropenem for injection (I.V.) on an outpatient basis may develop adverse events such as seizures, headaches and/or paresthesias that could interfere with mental alertness and/or cause motor impairment. Until it is reasonably well established that Meropenem for injection (I.V.) is well tolerated, patients should not operate machinery or motorized vehicles [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. | |||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Meropenem interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=Alcohol-Meropenem interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 8 January 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Stefano Giannoni [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Meropenem is a Carbapenem that is FDA approved for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections, intra-abdominal infections, bacterial meningitis (pediatric patients).. Common adverse reactions include {{{adverseReactions}}}.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Skin and Skin Structure Infections
- Dosage: 500 mg IV every 8 hours.
Is indicated as a single agent therapy for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections due to:
- Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only)
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Viridans group streptococci
- Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Peptostreptococcus species
Intra-abdominal Infections
- 1 g IV every 8 hours
Is indicated as a single agent therapy for the treatment of complicated appendicitis and peritonitis caused by:
- Viridans group streptococci
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Bacteroides fragilis
- B. thetaiotaomicron
- Peptostreptococcus species
Meropenem for injection (I.V.) should be administered by intravenous infusion over approximately 15 to 30 minutes. Doses of 1 g may also be administered as an intravenous bolus injection (5 to 20 mL) over approximately 3-5 minutes.
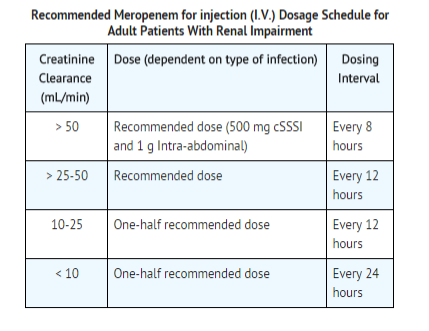
Use in Adult Patients with Renal Impairment
- Dosage should be reduced in patients with creatinine clearance of 50 mL/min or less.
- When only serum creatinine is available, the following formula (Cockcroft and Gault equation) may be used to estimate creatinine clearance.

There is inadequate information regarding the use of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) in patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Meropenem in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Cystic Fibrosis
- 120 mg/kg IV t.i.d. (maximum 2 g/dose)[1]
- In combination with tobramycin
Nosocomial Pneumonia
- 1 g IV t.i.d.[2]
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Skin and Skin Structure Infections (Pediatric Patients ≥ 3 Months only)
- 10m/kg IV every 8 hours.
- Up to a maximum Dose of 500 mg
- Pediatric patients weighing over 50 kg should be administered Meropenem for injection (I.V.) at a dose of 500 mg every 8 hours for complicated skin and skin structure infections.
Is indicated as a single agent therapy for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections due to:
- Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible isolates only)
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Viridans group streptococci
- Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Escherichia coli
- Proteus mirabilis
- Bacteroides fragilis
- Peptostreptococcus species
Intra-abdominal Infections (Pediatric Patients ≥ 3 Months only)
- 20 mg/kg IV every 8 hours
- Up to a maximum dose of 1g
- Pediatric patients weighing over 50 kg should be administered Meropenem for injection (I.V.) at a dose of 1 g every 8 hours for intra-abdominal infections.
Is indicated as a single agent therapy for the treatment of complicated appendicitis and peritonitis caused by:
- Viridans group streptococci
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Bacteroides fragilis
- B. thetaiotaomicron
- Peptostreptococcus species
Bacterial Meningitis (Pediatric Patients ≥ 3 Months only)
- 40 mg IV every 8 hours.
- Up to a maximum of 2 g.
Pediatric patients weighing over 50 kg should be administered Meropenem for injection (I.V.) at a dose of 2 g every 8 hours for meningitis. Meropenem for injection (I.V.) is indicated as a single agent therapy for the treatment of bacterial meningitis caused by:
Meropenem for injection (I.V.) should be given as intravenous infusion over approximately 15 to 30 minutes or as an intravenous bolus injection (5 to 20 mL) over approximately 3-5 minutes.
There is limited safety data available to support the administration of a 40 mg/kg (up to a maximum of 2 g) bolus dose. There is no experience in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Meropenem in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Cystic Fibrosis
- 120 mg/kg IV t.i.d. (maximum 2 g/dose)[1]
- In combination with tobramycin
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product or to other drugs in the same class
- Demonstrated anaphylactic reactions to β-lactams.
Warnings
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients receiving therapy with β-lactams.
- These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens.
- There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe hypersensitivity reactions when treated with another β-lactam.
- Before initiating therapy with Meropenem for injection (I.V.), careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, other β-lactams, and other allergens. *If an allergic reaction to Meropenem for injection (I.V.) occurs, discontinue the drug immediately.
- Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine, oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation. Other therapy may also be administered as indicated.
Seizure Potential
- Seizures and other adverse CNS experiences have been reported during treatment with Meropenem for injection (I.V.).
- These experiences have occurred most commonly in patients with CNS disorders (e.g., brain lesions or history of seizures) or with bacterial meningitis and/or compromised renal function.
- During clinical investigations, 2904 immunocompetent adult patients were treated for non-CNS infections with the overall seizure rate being 0.7% (based on 20 patients with this adverse event).
- All meropenem-treated patients with seizures had pre-existing contributing factors.
- Among these are included prior history of seizures or CNS abnormality and concomitant medications with seizure potential.
- Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with advanced age and/or reduced renal function.
- Close adherence to the recommended dosage regimens is urged, especially in patients with known factors that predispose to convulsive activity.
- Anti-convulsant therapy should be continued in patients with known seizure disorders.
- If focal tremors, myoclonus, or seizures occur, patients should be evaluated neurologically, placed on anti-convulsant therapy if not already instituted, and the dosage of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) re-examined to determine whether it should be decreased or the antibiotic discontinued.
Interaction with Valproic Acid
- Case reports in the literature have shown that co-administration of carbapenems, including meropenem, to patients receiving valproic acid or divalproex sodium results in a reduction in valproic acid concentrations.
- The valproic acid concentrations may drop below the therapeutic range as a result of this interaction, therefore increasing the risk of breakthrough seizures.
- Increasing the dose of valproic acid or divalproex sodium may not be sufficient to overcome this interaction.
- The concomitant use of meropenem and valproic acid or divalproex sodium is generally not recommended.
- Antibacterials other than carbapenems should be considered to treat infections in patients whose seizures are well controlled on valproic acid or divalproex sodium.
- If administration of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) is necessary, supplemental anti-convulsant therapy should be considered.
Clostridium difficile–Associated Diarrhea
- Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Meropenem for injection (I.V.), and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing isolates of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing Meropenem for injection (I.V.) in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Overgrowth of Nonsusceptible Organisms
As with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, prolonged use of meropenem may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient is essential. If superinfection does occur during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Laboratory Tests
While Meropenem for injection (I.V.) possesses the characteristic low toxicity of the beta-lactam group of antibiotics, periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment, thrombocytopenia has been observed but no clinical bleeding reported [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Use In Specific Populations (8.5) and (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dialysis
There is inadequate information regarding the use of Meropenem for injection (I.V.) in patients on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Potential for Neuromotor Impairment
Patients receiving Meropenem for injection (I.V.) on an outpatient basis may develop adverse events such as seizures, headaches and/or paresthesias that could interfere with mental alertness and/or cause motor impairment. Until it is reasonably well established that Meropenem for injection (I.V.) is well tolerated, patients should not operate machinery or motorized vehicles [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Meropenem in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Meropenem in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Meropenem during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Meropenem in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Meropenem in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Meropenem and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Meropenem overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Meropenem How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Meropenem |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Meropenem |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Meropenem interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Meropenem Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Latzin P, Fehling M, Bauernfeind A, Reinhardt D, Kappler M, Griese M (2008). "Efficacy and safety of intravenous meropenem and tobramycin versus ceftazidime and tobramycin in cystic fibrosis". J Cyst Fibros. 7 (2): 142–6. doi:10.1016/j.jcf.2007.07.001. PMID 17766190.
- ↑ Alvarez Lerma F, Serious Infection Study Group (2001). "Efficacy of meropenem as monotherapy in the treatment of ventilator-associated pneumonia". J Chemother. 13 (1): 70–81. doi:10.1179/joc.2001.13.1.70. PMID 11233804.
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [3]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [4]
Overview
Meropenem is an ultra-broad spectrum injectable antibiotic used to treat a wide variety of infections, including meningitis and pneumonia. It is a beta-lactam and belongs to the subgroup of carbapenem, similar to imipenem and ertapenem. Meropenem gained FDA approval in July 1996. It penetrates well into many tissues and body fluids including the cerebrospinal fluid,bile, heart valves, lung, and peritoneal fluid.[1]
Category
Carbapenem
US Brand Names
MERREM®
FDA Package Insert
Description | Clinical Pharmacology | Microbiology | Indications and Usage | Contraindications | Warnings | Precautions | Adverse Reactions | Overdosage | Clinical Studies | Dosage and Administration | Compatibility, Reconstitution, and Stability | How Supplied | Labels and Packages
Mechanism of action
Meropenem is bactericidal except against Listeria monocytogenes where it is bacteriostatic. It inhibits bacterial wall synthesis like other beta-lactam antibiotics. In contrast to other beta-lactams, it is highly resistant to degradation by beta-lactamase or cephalosporinase. Resistance generally arises due to mutations in penicillin binding proteins, production of metallo-beta-lactamases, or resistance to diffusion across the bacterial outer membrane.[2] Unlike imipenem, it is stable to dehydropeptidase-1 and can therefore be given without cilastatin.