Hydroxychloroquine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|drugClass= | |drugClass= | ||
antimalarial | |||
|indication= | |indication= | ||
acute attacks of [[malaria]] due to [[Plasmodium vivax]], [[P. malariae]], [[P. ovale]] and susceptible strains of [[P. falciparum]], discoid and [[systemic lupus erythematosus]], and [[rheumatoid arthritis]] | |||
acute attacks of malaria due to Plasmodium vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale and susceptible strains of P. falciparum, discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis | |||
|hasBlackBoxWarning= | |hasBlackBoxWarning= | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
|adverseReactions= | |adverseReactions= | ||
disorder of [[cornea]], [[headache]], [[dizziness]], [[diarrhea]], [[anorexia]], [[nausea]] and [[abdominal cramps]] | |||
<!--Black Box Warning--> | <!--Black Box Warning--> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
|blackBoxWarningBody= | |blackBoxWarningBody= | ||
<i><span style="color:#FF0000;"> | <i><span style="color:#FF0000;"> </span></i> | ||
*PHYSICIANS SHOULD COMPLETELY FAMILIARIZE THEMSELVES WITH THE COMPLETE CONTENTS OF THIS LEAFLET BEFORE PRESCRIBING HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE. | *PHYSICIANS SHOULD COMPLETELY FAMILIARIZE THEMSELVES WITH THE COMPLETE CONTENTS OF THIS LEAFLET BEFORE PRESCRIBING HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 51: | ||
:*One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base. | :*One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base. | ||
:*Malaria: Suppression–In adults, 400 mg (=310 mg base) on exactly the same day of each week. | :*[[Malaria]]: Suppression–In adults, 400 mg (=310 mg base) on exactly the same day of each week. | ||
:*If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in adults an initial double (loading) dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base). The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area. | :*If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in adults an initial double (loading) dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base). The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area. | ||
:*Treatment of the acute attack–In adults, an initial dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base) followed by 400 mg (=310 mg base) in six to eight hours and 400 mg (=310 mg base) on each of two consecutive days (total 2 g hydroxychloroquine sulfate or 1.55 g base). An alternative method, employing a single dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base), has also proved effective. | :*Treatment of the acute attack–In adults, an initial dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base) followed by 400 mg (=310 mg base) in six to eight hours and 400 mg (=310 mg base) on each of two consecutive days (total 2 g hydroxychloroquine sulfate or 1.55 g base). An alternative method, employing a single dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base), has also proved effective. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 72: | ||
:*Initial dosage–In adults from 400 mg to 600 mg (=310 mg to 465 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. In a small percentage of patients, troublesome side effects may require temporary reduction of the initial dosage. Later (usually from five to ten days), the dose may gradually be increased to the optimum response level, often without return of side effects. | :*Initial dosage–In adults from 400 mg to 600 mg (=310 mg to 465 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. In a small percentage of patients, troublesome side effects may require temporary reduction of the initial dosage. Later (usually from five to ten days), the dose may gradually be increased to the optimum response level, often without return of side effects. | ||
:*Maintenance dosage–When a good response is obtained (usually in four to twelve weeks), the dosage is reduced by 50 percent and continued at a usual maintenance level of 200 mg to 400 mg (=155 mg to 310 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. The incidence of retinopathy has been reported to be higher when this maintenance dose is exceeded. | :*Maintenance dosage–When a good response is obtained (usually in four to twelve weeks), the dosage is reduced by 50 percent and continued at a usual maintenance level of 200 mg to 400 mg (=155 mg to 310 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. The incidence of [[retinopathy]] has been reported to be higher when this maintenance dose is exceeded. | ||
:*Should a relapse occur after medication is withdrawn, therapy may be resumed or continued on an intermittent schedule if there are no ocular contraindications. | :*Should a relapse occur after medication is withdrawn, therapy may be resumed or continued on an intermittent schedule if there are no ocular contraindications. | ||
:*Corticosteroids and salicylates may be used in conjunction with this compound, and they can generally be decreased gradually in dosage or eliminated after the drug has been used for several weeks. When gradual reduction of steroid dosage is indicated, it may be done by reducing every four to five days the dose of cortisone by no more than from 5 mg to 15 mg; of hydrocortisone from 5 mg to 10 mg; of prednisolone and prednisone from 1 mg to 2.5 mg; of methylprednisolone and triamcinolone from 1 mg to 2 mg; and of dexamethasone from 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg. | :*[[Corticosteroids]] and [[salicylates]] may be used in conjunction with this compound, and they can generally be decreased gradually in dosage or eliminated after the drug has been used for several weeks. When gradual reduction of steroid dosage is indicated, it may be done by reducing every four to five days the dose of cortisone by no more than from 5 mg to 15 mg; of [[hydrocortisone]] from 5 mg to 10 mg; of [[prednisolone]] and [[prednisone]] from 1 mg to 2.5 mg; of [[methylprednisolone]] and [[triamcinolone]] from 1 mg to 2 mg; and of [[dexamethasone]] from 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg. | ||
<!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | <!--Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)--> | ||
| Line 112: | Line 111: | ||
:*One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base. | :*One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base. | ||
:*Malaria: Suppression– In infants and children, the weekly suppressive dosage is 5 mg, calculated as base, per kg of body weight, but should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight. | :*[[Malaria]]: Suppression– In infants and children, the weekly suppressive dosage is 5 mg, calculated as base, per kg of body weight, but should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight. | ||
:*If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in children 10 mg base/kg may be taken in two divided doses, six hours apart. The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area. | :*If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in children 10 mg base/kg may be taken in two divided doses, six hours apart. The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area. | ||
:*The dosage calculated on the basis of body weight; this method is preferred for infants and children. A total dose representing 25 mg of base per kg of body weight is administered in three days as follows: | :*The dosage calculated on the basis of body weight; this method is preferred for infants and children. A total dose representing 25 mg of base per kg of body weight is administered in three days as follows: | ||
| Line 149: | Line 148: | ||
|contraindications= | |contraindications= | ||
*Use of this drug is contraindicated (1) in the presence of retinal or visual field changes attributable to any 4-aminoquinoline compound, (2) in patients with known hypersensitivity to 4-aminoquinoline compounds, and (3) for long-term therapy in children. | *Use of this drug is contraindicated (1) in the presence of [[retinal]] or [[visual field]] changes attributable to any 4-aminoquinoline compound, (2) in patients with known hypersensitivity to 4-aminoquinoline compounds, and (3) for long-term therapy in children. | ||
<!--Warnings--> | <!--Warnings--> | ||
| Line 159: | Line 158: | ||
*Children are especially sensitive to the 4-aminoquinoline compounds. A number of fatalities have been reported following the accidental ingestion of chloroquine, sometimes in relatively small doses (0.75 g or 1 g in one 3-year-old child). Patients should be strongly warned to keep these drugs out of the reach of children. | *Children are especially sensitive to the 4-aminoquinoline compounds. A number of fatalities have been reported following the accidental ingestion of chloroquine, sometimes in relatively small doses (0.75 g or 1 g in one 3-year-old child). Patients should be strongly warned to keep these drugs out of the reach of children. | ||
*Use of hydroxychloroquine sulfate in patients with psoriasis may precipitate a severe attack of psoriasis. When used in patients with porphyria the condition may be exacerbated. The preparation should not be used in these conditions unless in the judgement of the physician the benefit to the patient outweighs the possible hazard. | *Use of hydroxychloroquine sulfate in patients with [[psoriasis]] may precipitate a severe attack of [[psoriasis]]. When used in patients with [[porphyria]] the condition may be exacerbated. The preparation should not be used in these conditions unless in the judgement of the physician the benefit to the patient outweighs the possible hazard. | ||
*Usage in Pregnancy - Usage of this drug during pregnancy should be avoided except in the suppression or treatment of malaria when in the judgement of the physician the benefit outweighs the possible hazard. It should be noted that radioactively-tagged chloroquine administered intravenously to pregnant, pigmented, CBA mice passed rapidly across the placenta. It accumulated selectively in the melanin structures of the fetal eyes and was retained in the ocular tissues for five months after the drug had been eliminated from the rest of the body. | *Usage in [[Pregnancy]] - Usage of this drug during pregnancy should be avoided except in the suppression or treatment of malaria when in the judgement of the physician the benefit outweighs the possible hazard. It should be noted that radioactively-tagged chloroquine administered intravenously to pregnant, pigmented, CBA mice passed rapidly across the placenta. It accumulated selectively in the melanin structures of the fetal eyes and was retained in the ocular tissues for five months after the drug had been eliminated from the rest of the body. | ||
====Precautions==== | ====Precautions==== | ||
* General - Antimalarial compounds should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or alcoholism or in conjunction with known hepatotoxic drugs. | * General - Antimalarial compounds should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or alcoholism or in conjunction with known [[hepatotoxic]] drugs. | ||
*Periodic blood cell counts should be made if patients are given prolonged therapy. If any severe blood disorder appears which is not attributable to the disease under treatment, discontinuation of the drug should be considered. The drug should be administered with caution in patients having G-6-PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency. | *Periodic blood cell counts should be made if patients are given prolonged therapy. If any severe blood disorder appears which is not attributable to the disease under treatment, discontinuation of the drug should be considered. The drug should be administered with caution in patients having G-6-PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency. | ||
| Line 175: | Line 174: | ||
|clinicalTrials= | |clinicalTrials= | ||
*Following the administration in doses adequate for the treatment of an acute malarial attack, mild and transient headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal complaints (diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, abdominal cramps and, on rare occasions, vomiting) may occur. Cardiomyopathy has been rarely reported with high daily dosages of hydroxychloroquine. | *Following the administration in doses adequate for the treatment of an acute malarial attack, mild and transient [[headache]], [[dizziness]], and [[gastrointestinal]] complaints ([[diarrhea]], [[anorexia]], [[nausea]], [[abdominal cramps]] and, on rare occasions, vomiting) may occur. [[Cardiomyopathy]] has been rarely reported with high daily dosages of hydroxychloroquine. | ||
*Not all of the following reactions have been observed with every 4-aminoquinoline compound during long-term therapy, but they have been reported with one or more and should be borne in mind when drugs of this class are administered. Adverse effects with different compounds vary in type and frequency. | *Not all of the following reactions have been observed with every 4-aminoquinoline compound during long-term therapy, but they have been reported with one or more and should be borne in mind when drugs of this class are administered. Adverse effects with different compounds vary in type and frequency. | ||
=====CNS Reactions===== | =====CNS Reactions===== | ||
Irritability, nervousness, emotional changes, nightmares, psychosis, headache, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, nystagmus, nerve deafness, convulsions, ataxia. | Irritability, [[nervousness]], emotional changes, nightmares, [[psychosis]], [[headache]], [[dizziness]], [[vertigo]], [[tinnitus]], [[nystagmus]], nerve deafness, convulsions, [[ataxia]]. | ||
=====Neuromuscular Reactions===== | =====Neuromuscular Reactions===== | ||
Skeletal muscle palsies or skeletal muscle myopathy or neuromyopathy leading to progressive weakness and atrophy of proximal muscle groups which may be associated with mild sensory changes, depression of tendon reflexes and abnormal nerve conduction. | [[Skeletal muscle]] palsies or skeletal muscle [[myopathy]] or [[neuromyopathy]] leading to progressive weakness and [[atrophy]] of [[proximal muscle]] groups which may be associated with mild sensory changes, depression of [[tendon reflexes]] and abnormal nerve conduction. | ||
=====Ocular Reactions===== | =====Ocular Reactions===== | ||
*Ciliary body: Disturbance of accommodation with symptoms of blurred vision. This reaction is dose related and reversible with cessation of therapy. | *[[Ciliary body]]: Disturbance of accommodation with symptoms of blurred vision. This reaction is dose related and reversible with cessation of therapy. | ||
*Cornea: Transient edema, punctate to lineal opacities, decreased corneal sensitivity. The corneal changes, with or without accompanying symptoms (blurred vision, halos around lights, photophobia), are fairly common, but reversible. Corneal deposits may appear as early as three weeks following initiation of therapy. | *[[Cornea]]: Transient [[edema]], punctate to lineal opacities, decreased corneal sensitivity. The [[corneal]] changes, with or without accompanying symptoms ([[blurred vision]], [[halos]] around lights, [[photophobia]]), are fairly common, but reversible. Corneal deposits may appear as early as three weeks following initiation of therapy. | ||
*The incidence of corneal changes and visual side effects appears to be considerably lower with hydroxychloroquine than with chloroquine. | *The incidence of corneal changes and visual side effects appears to be considerably lower with hydroxychloroquine than with chloroquine. | ||
*Retina: Macula: Edema, atrophy, abnormal pigmentation (mild pigment stippling to a “bulls-eye” appearance), loss of foveal reflex, increased macular recovery time following exposure to a bright light (photo-stress test), elevated retinal threshold to red light in macular, paramacular and peripheral retinal areas. | *[[Retina]]: [[Macula]]: [[Edema]], atrophy, abnormal pigmentation (mild pigment stippling to a “bulls-eye” appearance), loss of [[foveal reflex]], increased [[macular]] recovery time following exposure to a bright light (photo-stress test), elevated retinal threshold to red light in macular, paramacular and peripheral retinal areas. | ||
*Other fundus changes include optic disc pallor and atrophy, attenuation of retinal arterioles, fine granular pigmentary disturbances in the peripheral retina and prominent choroidal patterns in advanced stage. | *Other [[fundus]] changes include optic disc pallor and atrophy, attenuation of retinal arterioles, fine granular pigmentary disturbances in the peripheral [[retina]] and prominent [[choroidal]] patterns in advanced stage. | ||
*Visual field defects: Pericentral or paracentral scotoma, central scotoma with decreased visual acuity, rarely field constriction. | *Visual field defects: Pericentral or paracentral [[scotoma]], [[central scotoma]] with decreased [[visual acuity]], rarely field constriction. | ||
*The most common visual symptoms attributed to the retinopathy are: reading and seeing difficulties (words, letters, or parts of objects missing), photophobia, blurred distance vision, missing or blacked out areas in the central or peripheral visual field, light flashes and streaks. | *The most common visual symptoms attributed to the [[retinopathy]] are: reading and seeing difficulties (words, letters, or parts of objects missing), [[photophobia]], blurred distance vision, missing or blacked out areas in the central or peripheral [[visual field]], light flashes and streaks. | ||
*Retinopathy appears to be dose related and has occurred within several months (rarely) to several years of daily therapy; a small number of cases have been reported several years after antimalarial drug therapy was discontinued. It has not been noted during prolonged use of weekly doses of the 4-aminoquinoline compounds for suppression of malaria. | *[[Retinopathy]] appears to be dose related and has occurred within several months (rarely) to several years of daily therapy; a small number of cases have been reported several years after [[antimalarial drug]] therapy was discontinued. It has not been noted during prolonged use of weekly doses of the 4-aminoquinoline compounds for suppression of [[malaria]]. | ||
*Patients with retinal changes may have visual symptoms or may be asymptomatic (with or without visual field changes). Rarely scotomatous vision field defects may occur without obvious retinal change. | *Patients with retinal changes may have visual symptoms or may be asymptomatic (with or without visual field changes). Rarely scotomatous vision field defects may occur without obvious retinal change. | ||
*Retinopathy may progress even after the drug is discontinued. In a number of patients, early retinopathy (macular pigmentation sometimes with central field defects) diminished or regressed completely after therapy was discontinued. Paracentral scotoma to red targets (sometimes called “premaculopathy”) is indicative of early retinal dysfunction which is usually reversible with cessation of therapy. | *[[Retinopathy]] may progress even after the drug is discontinued. In a number of patients, early retinopathy (macular pigmentation sometimes with central field defects) diminished or regressed completely after therapy was discontinued. [[Paracentral scotoma]] to red targets (sometimes called “premaculopathy”) is indicative of early retinal dysfunction which is usually reversible with cessation of therapy. | ||
*A small number of cases of retinal changes have been reported as occurring in patients who received only hydroxychloroquine. These usually consisted of alteration in retinal pigmentation which was detected on periodic ophthalmologic examination; visual field defects were also present in some instances. A case of delayed retinopathy has been reported with loss of vision starting one year after administration of hydroxychloroquine had been discontinued. | *A small number of cases of retinal changes have been reported as occurring in patients who received only hydroxychloroquine. These usually consisted of alteration in retinal pigmentation which was detected on periodic ophthalmologic examination; visual field defects were also present in some instances. A case of delayed retinopathy has been reported with loss of vision starting one year after administration of hydroxychloroquine had been discontinued. | ||
=====Dermatologic Reactions===== | =====Dermatologic Reactions===== | ||
Bleaching of hair, alopecia, pruritus, skin and mucosal pigmentation, photosensitivity, and skin eruptions (urticarial, morbilliform, Iichenoid, maculopapular, purpuric, erythema annulare centrifugum, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and exfoliative dermatitis). | Bleaching of hair, [[alopecia]], [[pruritus]], skin and mucosal pigmentation, [[photosensitivity]], and skin eruptions (urticarial, morbilliform, Iichenoid, maculopapular, purpuric, erythema annulare centrifugum, [[Stevens-Johnson syndrome]], acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and [[exfoliative dermatitis]]). | ||
=====Hematologic Reactions===== | =====Hematologic Reactions===== | ||
Various blood dyscrasias such as aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia (hemolysis in individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase [G6-PD] deficiency). | Various blood dyscrasias such as [[aplastic anemia]], [[agranulocytosis]], [[leukopenia]], [[thrombocytopenia]] ([[hemolysis]] in individuals with [[glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase]] [G6-PD] deficiency). | ||
=====Gastrointestinal Reactions===== | =====Gastrointestinal Reactions===== | ||
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Isolated cases of abnormal liver function and fulminant hepatic failure. | [[Anorexia]], [[nausea]], [[vomiting]], [[diarrhea]], and abdominal cramps. Isolated cases of abnormal liver function and [[fulminant hepatic failure]]. | ||
=====Miscellaneous Reactions===== | =====Miscellaneous Reactions===== | ||
Weight loss, lassitude, exacerbation or precipitation of porphyria and nonlight-sensitive psoriasis. | [[Weight loss]], [[lassitude]], exacerbation or precipitation of [[porphyria]] and nonlight-sensitive psoriasis. | ||
*Cardiomyopathy has been rarely reported with high daily doses of hydroxychloroquine. | *[[Cardiomyopathy]] has been rarely reported with high daily doses of hydroxychloroquine. | ||
<!--Postmarketing Experience--> | <!--Postmarketing Experience--> | ||
| Line 231: | Line 230: | ||
|drugInteractions= | |drugInteractions= | ||
<!--Use in Specific Populations--> | <!--Use in Specific Populations--> | ||
| Line 299: | Line 295: | ||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | ====Signs and Symptoms==== | ||
*The 4-aminoquinoline compounds are very rapidly and completely absorbed after ingestion, and in accidental overdosage, or rarely with lower doses in hypersensitive patients, toxic symptoms may occur within 30 minutes. These consist of headache, drowsiness, visual disturbances, cardiovascular collapse, and convulsions, followed by sudden and early respiratory and cardiac arrest. The electrocardiogram may reveal atrial standstill, nodal rhythm, prolonged intraventricular conduction time, and progressive bradycardia leading to ventricular fibrillation and/or arrest | *The 4-aminoquinoline compounds are very rapidly and completely absorbed after ingestion, and in accidental overdosage, or rarely with lower doses in hypersensitive patients, toxic symptoms may occur within 30 minutes. These consist of [[headache]], [[drowsiness]], [[visual disturbances]], [[cardiovascular collapse]], and [[convulsions]], followed by sudden and early respiratory and [[cardiac arrest]]. The electrocardiogram may reveal atrial standstill, nodal rhythm, prolonged [[intraventricular]] conduction time, and progressive [[bradycardia]] leading to [[ventricular fibrillation]] and/or arrest. | ||
====Management==== | ====Management==== | ||
*Treatment is symptomatic and must be prompt with immediate evacuation of the stomach by [[emesis]] (at home, before transportation to the hospital) or gastric lavage until the stomach is completely emptied. If finely powdered, activated charcoal is introduced by the stomach tube, after lavage, and within 30 minutes after ingestion of the tablets, it may inhibit further intestinal absorption of the drug. To be effective, the dose of activated charcoal should be at least five times the estimated dose of hydroxychloroquine ingested. [[Convulsions]], if present, should be controlled before attempting [[gastric lavage]]. If due to cerebral stimulation, cautious administration of an ultrashort-acting [[barbiturate]] may be tried but, if due to anoxia, it should be corrected by oxygen administration, artificial respiration or, in shock with [[hypotension]], by vasopressor therapy. Because of the importance of supporting respiration, tracheal [[intubation]] or [[tracheostomy]], followed by [[gastric lavage]], may also be necessary. [[Exchange transfusions]] have been used to reduce the level of 4-aminoquinoline drug in the blood. | |||
*A patient who survives the acute phase and is asymptomatic should be closely observed for at least six hours. Fluids may be forced, and sufficient ammonium chloride (8 g daily in divided doses for adults) may be administered for a few days to acidify the urine to help promote urinary excretion in cases of both overdosage and sensitivity. | *A patient who survives the acute phase and is asymptomatic should be closely observed for at least six hours. Fluids may be forced, and sufficient ammonium chloride (8 g daily in divided doses for adults) may be administered for a few days to acidify the urine to help promote urinary excretion in cases of both overdosage and sensitivity. | ||
| Line 315: | Line 313: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{ | {{Drugbox2 | ||
| Verifiedfields = changed | | Verifiedfields = changed | ||
| verifiedrevid = 443862546 | | verifiedrevid = 443862546 | ||
| Line 374: | Line 372: | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
*The drug possesses antimalarial actions and also exerts a beneficial effect in lupus erythematosus (chronic discoid or systemic) and acute or chronic rheumatoid arthritis. The precise mechanism of action is not known. | *The drug possesses antimalarial actions and also exerts a beneficial effect in [[lupus erythematosus]] (chronic discoid or systemic) and acute or chronic [[rheumatoid arthritis]]. The precise mechanism of action is not known. | ||
*Malaria | *[[Malaria]] | ||
:*Like chloroquine phosphate, hydroxychloroquine sulfate is highly active against the erythrocytic forms of P. vivax and malariae and most strains of P. falciparum (but not the gametocytes of P. falciparum). | :*Like chloroquine phosphate, hydroxychloroquine sulfate is highly active against the [[erythrocytic]] forms of P. vivax and malariae and most strains of P. falciparum (but not the [[gametocytes]] of P. falciparum). | ||
:(Hydroxychloroquine sulfate does not prevent relapses in patients with vivax or malariae malaria because it is not effective against exo-erythrocytic forms of the parasite, nor will it prevent vivax or malariae infection when administered as a prophylactic. It is highly effective as a suppressive agent in patients with vivax or malariae malaria, in terminating acute attacks, and significantly lengthening the interval between treatment and relapse. In patients with falciparum malaria, it abolishes the acute attack and effects complete cure of the infection, unless due to a resistant strain of P. falciparum. | :(Hydroxychloroquine sulfate does not prevent relapses in patients with vivax or malariae [[malaria]] because it is not effective against exo-erythrocytic forms of the parasite, nor will it prevent vivax or malariae infection when administered as a prophylactic. It is highly effective as a suppressive agent in patients with vivax or malariae malaria, in terminating acute attacks, and significantly lengthening the interval between treatment and relapse. In patients with [[falciparum malaria]], it abolishes the acute attack and effects complete cure of the infection, unless due to a resistant strain of P. falciparum. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
| Line 442: | Line 440: | ||
|brandNames= | |brandNames= | ||
* HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE®<ref>{{Cite web | title = HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE- hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablet, coated | url = dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=adf36d25-d86e-4d2d-b90c-e29f1394667d }}</ref> | * HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE®<ref>{{Cite web | title = HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE- hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablet, coated | url = http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=adf36d25-d86e-4d2d-b90c-e29f1394667d }}</ref> | ||
<!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | <!--Look-Alike Drug Names--> | ||
| Line 483: | Line 481: | ||
[[Category:Drug]] | [[Category:Drug]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:malaria]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:44, 15 October 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
FAMILIARIZE WITH LEAFLET
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Overview
Hydroxychloroquine is an antimalarial that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of acute attacks of malaria due to Plasmodium vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale and susceptible strains of P. falciparum, discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include disorder of cornea, headache, dizziness, diarrhea, anorexia, nausea and abdominal cramps.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Malaria
- Dosing Information
- One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base.
- Malaria: Suppression–In adults, 400 mg (=310 mg base) on exactly the same day of each week.
- If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in adults an initial double (loading) dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base). The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area.
- Treatment of the acute attack–In adults, an initial dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base) followed by 400 mg (=310 mg base) in six to eight hours and 400 mg (=310 mg base) on each of two consecutive days (total 2 g hydroxychloroquine sulfate or 1.55 g base). An alternative method, employing a single dose of 800 mg (=620 mg base), has also proved effective.
- The dosage for adults may also be calculated on the basis of body weight; this method is preferred for infants and children. A total dose representing 25 mg of base per kg of body weight is administered in three days as follows:
- First dose: 10 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 620 mg base).
- Second dose: 5 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 310 mg base) 6 hours after first dose.
- Third dose: 5 mg base per kg 18 hours after second dose.
- Fourth dose: 5 mg base per kg 24 hours after third dose.
- For radical cure of vivax and malariae malaria concomitant therapy with an 8-aminoquinoline compound is necessary.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Dosing Information
- Initially, the average adult dose is 400 mg (=310 mg base) once or twice daily. This may be continued for several weeks or months, depending on the response of the patient. For prolonged maintenance therapy, a smaller dose, from 200 mg to 400 mg (=155 mg to 310 mg base) daily will frequently suffice.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Dosing Information
- Initial dosage–In adults from 400 mg to 600 mg (=310 mg to 465 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. In a small percentage of patients, troublesome side effects may require temporary reduction of the initial dosage. Later (usually from five to ten days), the dose may gradually be increased to the optimum response level, often without return of side effects.
- Maintenance dosage–When a good response is obtained (usually in four to twelve weeks), the dosage is reduced by 50 percent and continued at a usual maintenance level of 200 mg to 400 mg (=155 mg to 310 mg base) daily, each dose to be taken with a meal or a glass of milk. The incidence of retinopathy has been reported to be higher when this maintenance dose is exceeded.
- Should a relapse occur after medication is withdrawn, therapy may be resumed or continued on an intermittent schedule if there are no ocular contraindications.
- Corticosteroids and salicylates may be used in conjunction with this compound, and they can generally be decreased gradually in dosage or eliminated after the drug has been used for several weeks. When gradual reduction of steroid dosage is indicated, it may be done by reducing every four to five days the dose of cortisone by no more than from 5 mg to 15 mg; of hydrocortisone from 5 mg to 10 mg; of prednisolone and prednisone from 1 mg to 2.5 mg; of methylprednisolone and triamcinolone from 1 mg to 2 mg; and of dexamethasone from 0.25 mg to 0.5 mg.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Malaria; Prophylaxis
- Developed by: CDC
- Class of Recommendation: Class IIb
- Strength of Evidence: Category B
- Dosing Information
- Hydroxychloroquine once-weekly dosing started 1 to 2 weeks prior to travel.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Hydroxychloroquine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Malaria
- Dosing Information
- One tablet of 200 mg of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is equivalent to 155 mg base.
- Malaria: Suppression– In infants and children, the weekly suppressive dosage is 5 mg, calculated as base, per kg of body weight, but should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight.
- If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this, in children 10 mg base/kg may be taken in two divided doses, six hours apart. The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area.
- The dosage calculated on the basis of body weight; this method is preferred for infants and children. A total dose representing 25 mg of base per kg of body weight is administered in three days as follows:
- First dose: 10 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 620 mg base).
- Second dose: 5 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 310 mg base) 6 hours after first dose.
- Third dose: 5 mg base per kg 18 hours after second dose.
- Fourth dose: 5 mg base per kg 24 hours after third dose.
- For radical cure of vivax and malariae malaria concomitant therapy with an 8-aminoquinoline compound is necessary.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Malaria; Prophylaxis
- Developed by: CDC
- Class of Recommendation: Class IIb
- Strength of Evidence: Category B
- Dosing Information
- Hydroxychloroquine once-weekly dosing started 1 to 2 weeks prior to travel.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Hydroxychloroquine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Use of this drug is contraindicated (1) in the presence of retinal or visual field changes attributable to any 4-aminoquinoline compound, (2) in patients with known hypersensitivity to 4-aminoquinoline compounds, and (3) for long-term therapy in children.
Warnings
|
FAMILIARIZE WITH LEAFLET
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
- General - Hydroxychloroquine sulfate is not effective against chloroquine-resistant strains of P. falciparum.
- Children are especially sensitive to the 4-aminoquinoline compounds. A number of fatalities have been reported following the accidental ingestion of chloroquine, sometimes in relatively small doses (0.75 g or 1 g in one 3-year-old child). Patients should be strongly warned to keep these drugs out of the reach of children.
- Use of hydroxychloroquine sulfate in patients with psoriasis may precipitate a severe attack of psoriasis. When used in patients with porphyria the condition may be exacerbated. The preparation should not be used in these conditions unless in the judgement of the physician the benefit to the patient outweighs the possible hazard.
- Usage in Pregnancy - Usage of this drug during pregnancy should be avoided except in the suppression or treatment of malaria when in the judgement of the physician the benefit outweighs the possible hazard. It should be noted that radioactively-tagged chloroquine administered intravenously to pregnant, pigmented, CBA mice passed rapidly across the placenta. It accumulated selectively in the melanin structures of the fetal eyes and was retained in the ocular tissues for five months after the drug had been eliminated from the rest of the body.
Precautions
- General - Antimalarial compounds should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or alcoholism or in conjunction with known hepatotoxic drugs.
- Periodic blood cell counts should be made if patients are given prolonged therapy. If any severe blood disorder appears which is not attributable to the disease under treatment, discontinuation of the drug should be considered. The drug should be administered with caution in patients having G-6-PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Following the administration in doses adequate for the treatment of an acute malarial attack, mild and transient headache, dizziness, and gastrointestinal complaints (diarrhea, anorexia, nausea, abdominal cramps and, on rare occasions, vomiting) may occur. Cardiomyopathy has been rarely reported with high daily dosages of hydroxychloroquine.
- Not all of the following reactions have been observed with every 4-aminoquinoline compound during long-term therapy, but they have been reported with one or more and should be borne in mind when drugs of this class are administered. Adverse effects with different compounds vary in type and frequency.
CNS Reactions
Irritability, nervousness, emotional changes, nightmares, psychosis, headache, dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus, nystagmus, nerve deafness, convulsions, ataxia.
Neuromuscular Reactions
Skeletal muscle palsies or skeletal muscle myopathy or neuromyopathy leading to progressive weakness and atrophy of proximal muscle groups which may be associated with mild sensory changes, depression of tendon reflexes and abnormal nerve conduction.
Ocular Reactions
- Ciliary body: Disturbance of accommodation with symptoms of blurred vision. This reaction is dose related and reversible with cessation of therapy.
- Cornea: Transient edema, punctate to lineal opacities, decreased corneal sensitivity. The corneal changes, with or without accompanying symptoms (blurred vision, halos around lights, photophobia), are fairly common, but reversible. Corneal deposits may appear as early as three weeks following initiation of therapy.
- The incidence of corneal changes and visual side effects appears to be considerably lower with hydroxychloroquine than with chloroquine.
- Retina: Macula: Edema, atrophy, abnormal pigmentation (mild pigment stippling to a “bulls-eye” appearance), loss of foveal reflex, increased macular recovery time following exposure to a bright light (photo-stress test), elevated retinal threshold to red light in macular, paramacular and peripheral retinal areas.
- Other fundus changes include optic disc pallor and atrophy, attenuation of retinal arterioles, fine granular pigmentary disturbances in the peripheral retina and prominent choroidal patterns in advanced stage.
- Visual field defects: Pericentral or paracentral scotoma, central scotoma with decreased visual acuity, rarely field constriction.
- The most common visual symptoms attributed to the retinopathy are: reading and seeing difficulties (words, letters, or parts of objects missing), photophobia, blurred distance vision, missing or blacked out areas in the central or peripheral visual field, light flashes and streaks.
- Retinopathy appears to be dose related and has occurred within several months (rarely) to several years of daily therapy; a small number of cases have been reported several years after antimalarial drug therapy was discontinued. It has not been noted during prolonged use of weekly doses of the 4-aminoquinoline compounds for suppression of malaria.
- Patients with retinal changes may have visual symptoms or may be asymptomatic (with or without visual field changes). Rarely scotomatous vision field defects may occur without obvious retinal change.
- Retinopathy may progress even after the drug is discontinued. In a number of patients, early retinopathy (macular pigmentation sometimes with central field defects) diminished or regressed completely after therapy was discontinued. Paracentral scotoma to red targets (sometimes called “premaculopathy”) is indicative of early retinal dysfunction which is usually reversible with cessation of therapy.
- A small number of cases of retinal changes have been reported as occurring in patients who received only hydroxychloroquine. These usually consisted of alteration in retinal pigmentation which was detected on periodic ophthalmologic examination; visual field defects were also present in some instances. A case of delayed retinopathy has been reported with loss of vision starting one year after administration of hydroxychloroquine had been discontinued.
Dermatologic Reactions
Bleaching of hair, alopecia, pruritus, skin and mucosal pigmentation, photosensitivity, and skin eruptions (urticarial, morbilliform, Iichenoid, maculopapular, purpuric, erythema annulare centrifugum, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, and exfoliative dermatitis).
Hematologic Reactions
Various blood dyscrasias such as aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia (hemolysis in individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase [G6-PD] deficiency).
Gastrointestinal Reactions
Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Isolated cases of abnormal liver function and fulminant hepatic failure.
Miscellaneous Reactions
Weight loss, lassitude, exacerbation or precipitation of porphyria and nonlight-sensitive psoriasis.
- Cardiomyopathy has been rarely reported with high daily doses of hydroxychloroquine.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Postmarketing Experience of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Hydroxychloroquine Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Hydroxychloroquine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Hydroxychloroquine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine with respect to nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine with respect to pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine with respect to geriatric patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Hydroxychloroquine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Hydroxychloroquine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- The 4-aminoquinoline compounds are very rapidly and completely absorbed after ingestion, and in accidental overdosage, or rarely with lower doses in hypersensitive patients, toxic symptoms may occur within 30 minutes. These consist of headache, drowsiness, visual disturbances, cardiovascular collapse, and convulsions, followed by sudden and early respiratory and cardiac arrest. The electrocardiogram may reveal atrial standstill, nodal rhythm, prolonged intraventricular conduction time, and progressive bradycardia leading to ventricular fibrillation and/or arrest.
Management
- Treatment is symptomatic and must be prompt with immediate evacuation of the stomach by emesis (at home, before transportation to the hospital) or gastric lavage until the stomach is completely emptied. If finely powdered, activated charcoal is introduced by the stomach tube, after lavage, and within 30 minutes after ingestion of the tablets, it may inhibit further intestinal absorption of the drug. To be effective, the dose of activated charcoal should be at least five times the estimated dose of hydroxychloroquine ingested. Convulsions, if present, should be controlled before attempting gastric lavage. If due to cerebral stimulation, cautious administration of an ultrashort-acting barbiturate may be tried but, if due to anoxia, it should be corrected by oxygen administration, artificial respiration or, in shock with hypotension, by vasopressor therapy. Because of the importance of supporting respiration, tracheal intubation or tracheostomy, followed by gastric lavage, may also be necessary. Exchange transfusions have been used to reduce the level of 4-aminoquinoline drug in the blood.
- A patient who survives the acute phase and is asymptomatic should be closely observed for at least six hours. Fluids may be forced, and sufficient ammonium chloride (8 g daily in divided doses for adults) may be administered for a few days to acidify the urine to help promote urinary excretion in cases of both overdosage and sensitivity.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Hydroxychloroquine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
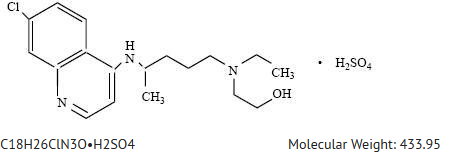
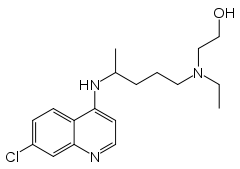
| (RS)-2-[{4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino]ethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | P01 |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 335.872 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | 1–2 months |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- The drug possesses antimalarial actions and also exerts a beneficial effect in lupus erythematosus (chronic discoid or systemic) and acute or chronic rheumatoid arthritis. The precise mechanism of action is not known.
- Like chloroquine phosphate, hydroxychloroquine sulfate is highly active against the erythrocytic forms of P. vivax and malariae and most strains of P. falciparum (but not the gametocytes of P. falciparum).
- (Hydroxychloroquine sulfate does not prevent relapses in patients with vivax or malariae malaria because it is not effective against exo-erythrocytic forms of the parasite, nor will it prevent vivax or malariae infection when administered as a prophylactic. It is highly effective as a suppressive agent in patients with vivax or malariae malaria, in terminating acute attacks, and significantly lengthening the interval between treatment and relapse. In patients with falciparum malaria, it abolishes the acute attack and effects complete cure of the infection, unless due to a resistant strain of P. falciparum.
Structure
- Hydroxychloroquine sulfate is a colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water to at least 20 percent; chemically the drug is (±)-2-[4-[(7-Chloro-4-quinolyl)amino]pentyl]-ethylamino]ethanol sulfate (1:1) (salt). It has the following structural formula:
- Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 200 mg of hydroxychloroquine sulfate. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, dextrates, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, maltodextrin, microcrystalline cellulose, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, starch (corn), titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacodynamics of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
How Supplied
- Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets USP, 200 mg are white to off-white, coated, oval tablets marked WATSON on one side and a partial score on the reverse side with 698 on one side of the score and 200 on the other side of the score supplied in bottles of 100 and 500.
- Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F).
- Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined by the USP.
- Certain manufacturing operations may have been performed by other firms.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Hydroxychloroquine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Hydroxychloroquine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Hydroxychloroquine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Hydroxychloroquine in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Hydroxychloroquine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Hydroxychloroquine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Hydroxychloroquine |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Hydroxychloroquine |Label Name=Hydroxychloroquine02.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Hydroxychloroquine |Label Name=Hydroxychloroquine03.png
}}