Gonadoblastoma pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
|[[File:1280px-Gonadoblastoma - low mag.jpg|thumb|none|300px|Microscopic pathology of gonadoblastoma [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gonadoblastoma_-_b_-_high_mag.jpg Source:Wikimedia Commons] ]] | |[[File:1280px-Gonadoblastoma - low mag.jpg|thumb|none|300px|Microscopic pathology of gonadoblastoma [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gonadoblastoma_-_b_-_high_mag.jpg Source:Wikimedia Commons] ]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Gonadoblastoma is formed from two different types of cells: | Gonadoblastoma is formed from two different types of cells:<ref name="CoolsStoop2006">{{cite journal|last1=Cools|first1=Martine|last2=Stoop|first2=Hans|last3=Kersemaekers|first3=Anne-Marie F.|last4=Drop|first4=Stenvert L. S.|last5=Wolffenbuttel|first5=Katja P.|last6=Bourguignon|first6=Jean-Pierre|last7=Slowikowska-Hilczer|first7=Jolanta|last8=Kula|first8=Krzysztof|last9=Faradz|first9=Sultana M. H.|last10=Oosterhuis|first10=J. Wolter|last11=Looijenga|first11=Leendert H. J.|title=Gonadoblastoma Arising in Undifferentiated Gonadal Tissue within Dysgenetic Gonads|journal=The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism|volume=91|issue=6|year=2006|pages=2404–2413|issn=0021-972X|doi=10.1210/jc.2005-2554}}</ref> | ||
*Larger cells resembling immature [[germ cells]] with varied degrees of [[atypia]] and that must be differentiated from the simultaneous invasive germ cell tumor | |||
*Smaller cells resembling the [[sex-cord stroma]] ([[Granulosa]] or Sertoli-like cells). | |||
*Another kind of stromal cells ([[Leydig cell|Leydig cells]] or Lutein-like cells) can also exist, but their presence is not essential for the diagnosis. They tend to be present greatly after puberty. | |||
The two essential type of cells forms a nest-like space in which, immature germ cells surrounded by sex-cord stromal cells. This nested arrangement is characteristic of gonadoblastoma. | |||
*The nest is encircled by a [[basement membrane]] which can be hyalinized or even calcified. | |||
*[[Calcification]] can be focal or extensive. | |||
* Focal calcification is found in more than 80% of the individuals. | |||
*The nodular pattern of hyalinized [[basement membrane]] encircled by stromal cells can also be present. | |||
Gonadoblastoma classified pathologically into three forms:<ref name="pmid4193741">{{cite journal |vauthors=Scully RE |title=Gonadoblastoma. A review of 74 cases |journal=Cancer |volume=25 |issue=6 |pages=1340–56 |date=June 1970 |pmid=4193741 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="UlbrightYoung2014">{{cite journal|last1=Ulbright|first1=Thomas M.|last2=Young|first2=Robert H.|title=Gonadoblastoma and selected other aspects of gonadal pathology in young patients with disorders of sex development|journal=Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology|volume=31|issue=5|year=2014|pages=427–440|issn=07402570|doi=10.1053/j.semdp.2014.07.001}}</ref> | Gonadoblastoma classified pathologically into three forms:<ref name="pmid4193741">{{cite journal |vauthors=Scully RE |title=Gonadoblastoma. A review of 74 cases |journal=Cancer |volume=25 |issue=6 |pages=1340–56 |date=June 1970 |pmid=4193741 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="UlbrightYoung2014">{{cite journal|last1=Ulbright|first1=Thomas M.|last2=Young|first2=Robert H.|title=Gonadoblastoma and selected other aspects of gonadal pathology in young patients with disorders of sex development|journal=Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology|volume=31|issue=5|year=2014|pages=427–440|issn=07402570|doi=10.1053/j.semdp.2014.07.001}}</ref> | ||
*Classical form which is described above thoroughly. | *Classical form which is described above thoroughly. | ||
*Burnt-out form, in which the cells regress and the remnant is calcified and forms a mulberry-shaped [[calcification]]. | *Burnt-out form, in which the cells regress and the remnant is calcified and forms a mulberry-shaped [[calcification]]. | ||
*Dissecting form which has a infiltrative and cord like pattern rather than a nested arrangement. The clinical relevance of this pathologic feature is that, it should be differentiated from [[germinoma]].<ref name="KaoIdrees2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kao|first1=Chia-Sui|last2=Idrees|first2=Muhammad T.|last3=Young|first3=Robert H.|last4=Ulbright|first4=Thomas M.|title=“Dissecting Gonadoblastoma” of Scully|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=40|issue=10|year=2016|pages=1417–1423|issn=0147-5185|doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000000704}}</ref> | *Dissecting form which has a infiltrative and cord like pattern rather than a nested arrangement. The clinical relevance of this pathologic feature is that, it should be differentiated from [[germinoma]].<ref name="KaoIdrees2016">{{cite journal|last1=Kao|first1=Chia-Sui|last2=Idrees|first2=Muhammad T.|last3=Young|first3=Robert H.|last4=Ulbright|first4=Thomas M.|title=“Dissecting Gonadoblastoma” of Scully|journal=The American Journal of Surgical Pathology|volume=40|issue=10|year=2016|pages=1417–1423|issn=0147-5185|doi=10.1097/PAS.0000000000000704}}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
Revision as of 16:37, 12 February 2019
|
Gonadoblastoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Gonadoblastoma pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Gonadoblastoma pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Gonadoblastoma pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sahar Memar Montazerin, M.D.[2]
Overview
The exact pathogenesis of gonadoblastoma is not fully understood. Gonadal development starts at 5 weeks of gestation and continues according to sex chromosomal contents. Any defects in this complicated process lead to defective gonadal development and gonadal dysgenesis and subsequently, it can be converted to gonadoblastoma in 20% to 30% of the cases.
Pathophysiology
Physiology
Gonadal development starts at 5 weeks of gestation and continues according to sex chromosomal contents. Any defects in this complicated process lead to defective gonadal development and gonadal dysgenesis.[1][2]
Pathogenesis
- The exact pathogenesis of gonadoblastoma is not completely understood.[3]
- Gonadoblastoma develop almost exclusively in dysgenetic gonads containing the Y chromosomal contents.
- The GBY gene locus, localized near the centromere of the Y chromosome, is hypothesized to be the culprit gene locus in the pathogenesis of gonadoblastoma.
- TSPY gene, one of the genes belonging to GBY locus, is observed to be overexpressed in the gonadoblastoma and other germ cell tumors, although its exact role is still unclear.
- There are case reports of genotypically normal women individuals with gonadoblastoma that suggests the existence of other mechanisms involving in the pathogenesis of gonadoblastoma.[4][5]
Genetics
Genes involved in the pathogenesis of gonadoblastoma include:
- TSPY
Associated Conditions
Conditions associated with gonadoblastoma include:
Gross Pathology
- Gross pathology of tumor greatly depends on the degree of germ cells overgrowth and calcification.[7]
- The tumor is firm and cartilaginous with a yellow to a brown-grey color.
- It can be calcified partly or almost completely.
- It can be very large especially with when accompanied by a dysgerminoma or be hardly detectable in gross examination.
Microscopic Pathology
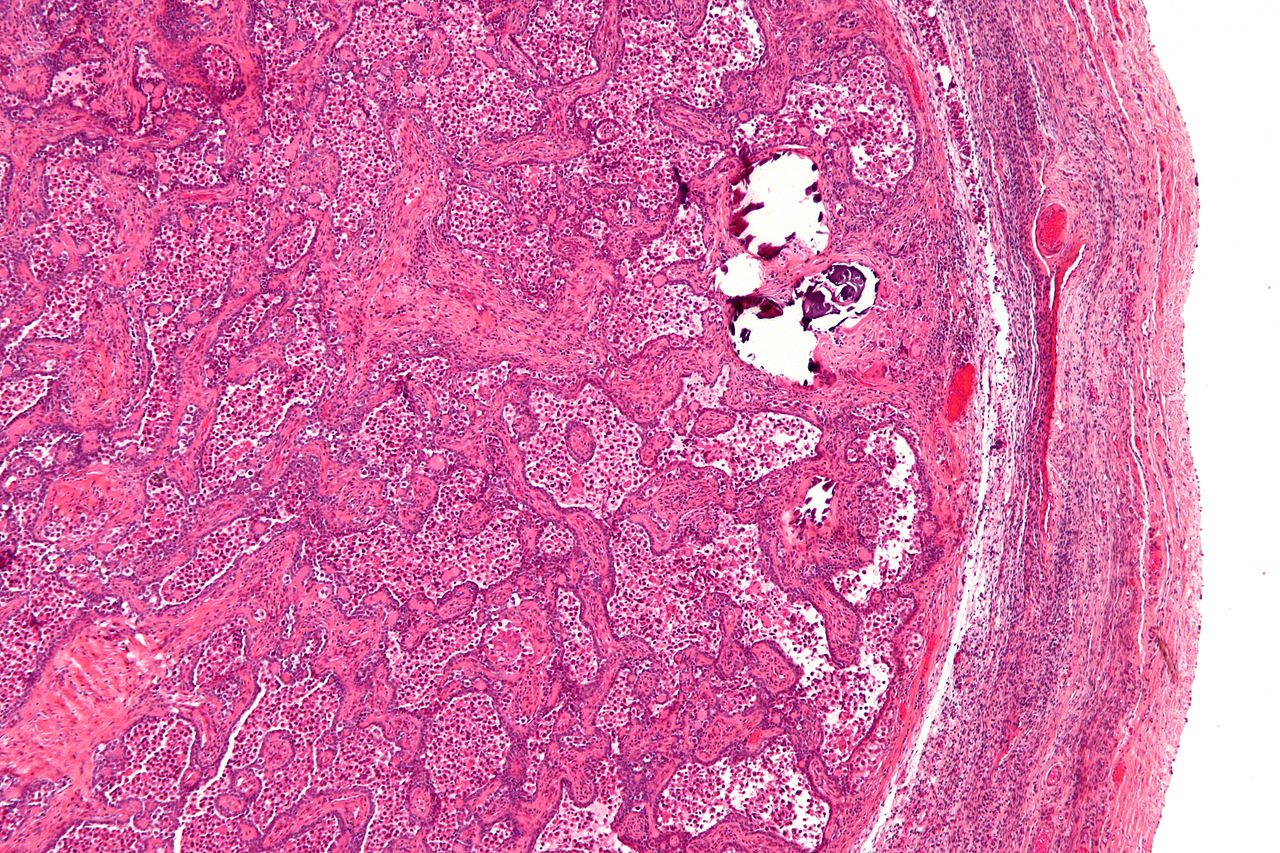 |
Gonadoblastoma is formed from two different types of cells:[8]
- Larger cells resembling immature germ cells with varied degrees of atypia and that must be differentiated from the simultaneous invasive germ cell tumor
- Smaller cells resembling the sex-cord stroma (Granulosa or Sertoli-like cells).
- Another kind of stromal cells (Leydig cells or Lutein-like cells) can also exist, but their presence is not essential for the diagnosis. They tend to be present greatly after puberty.
The two essential type of cells forms a nest-like space in which, immature germ cells surrounded by sex-cord stromal cells. This nested arrangement is characteristic of gonadoblastoma.
- The nest is encircled by a basement membrane which can be hyalinized or even calcified.
- Calcification can be focal or extensive.
- Focal calcification is found in more than 80% of the individuals.
- The nodular pattern of hyalinized basement membrane encircled by stromal cells can also be present.
Gonadoblastoma classified pathologically into three forms:[7][9]
- Classical form which is described above thoroughly.
- Burnt-out form, in which the cells regress and the remnant is calcified and forms a mulberry-shaped calcification.
- Dissecting form which has a infiltrative and cord like pattern rather than a nested arrangement. The clinical relevance of this pathologic feature is that, it should be differentiated from germinoma.[10]
References
- ↑ Carcangiu, M. L. (2014). WHO Classification of Tumours of Female Reproductive Organs. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer. ISBN 978-9283224358.
- ↑ Cools M, Stoop H, Kersemaekers AM, Drop SL, Wolffenbuttel KP, Bourguignon JP, Slowikowska-Hilczer J, Kula K, Faradz SM, Oosterhuis JW, Looijenga LH (June 2006). "Gonadoblastoma arising in undifferentiated gonadal tissue within dysgenetic gonads". J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91 (6): 2404–13. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2554. PMID 16608895.
- ↑ Kido, Tatsuo; Lau, Yun-Fai Chris (2008). "The human Y-encoded testis-specific protein interacts functionally with eukaryotic translation elongation factor eEF1A, a putative oncoprotein". International Journal of Cancer. 123 (7): 1573–1585. doi:10.1002/ijc.23697. ISSN 0020-7136.
- ↑ Bousquet G, Argenson C, Godeneche JL, Cisterne JP, Gazielly DF, Girardin P, Debiesse JL (1986). "[Recovery after aseptic loosening of cemented total hip arthroplasties with Bousquet's cementless prosthesis. Apropos of 136 cases]". Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot (in French). 72 Suppl 2: 70–4. PMID 3809670.
- ↑ Kulkarni MM, Sinai Khandeparkar SG, Joshi AR, Bhayekar PV (2016). "Unilateral gonadoblastoma with dysgerminoma in normal fertile woman having a child: Extremely rare occurrence with characteristic immunohistomorphology". Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 59 (4): 527–529. doi:10.4103/0377-4929.191815. PMID 27721289.
- ↑ "Emery and Rimoin's Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics and Genomics: Clinical Principles and Applications by Reed E. Pyeritz M.D., Ph.D., FACP, FACMG | | NOOK Book (eBook) | Barnes & Noble®".
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Scully RE (1970). "Gonadoblastoma. A review of 74 cases". Cancer. 25 (6): 1340–56. PMID 4193741.
- ↑ Cools, Martine; Stoop, Hans; Kersemaekers, Anne-Marie F.; Drop, Stenvert L. S.; Wolffenbuttel, Katja P.; Bourguignon, Jean-Pierre; Slowikowska-Hilczer, Jolanta; Kula, Krzysztof; Faradz, Sultana M. H.; Oosterhuis, J. Wolter; Looijenga, Leendert H. J. (2006). "Gonadoblastoma Arising in Undifferentiated Gonadal Tissue within Dysgenetic Gonads". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 91 (6): 2404–2413. doi:10.1210/jc.2005-2554. ISSN 0021-972X.
- ↑ Ulbright, Thomas M.; Young, Robert H. (2014). "Gonadoblastoma and selected other aspects of gonadal pathology in young patients with disorders of sex development". Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology. 31 (5): 427–440. doi:10.1053/j.semdp.2014.07.001. ISSN 0740-2570.
- ↑ Kao, Chia-Sui; Idrees, Muhammad T.; Young, Robert H.; Ulbright, Thomas M. (2016). ""Dissecting Gonadoblastoma" of Scully". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 40 (10): 1417–1423. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000704. ISSN 0147-5185.