Eflornithine: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|drugClass=hair growth retardant, ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor | |drugClass=hair growth retardant, ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor | ||
|indicationType=treatment | |indicationType=treatment | ||
|indication= reduction of unwanted facial hair in women. | |indication=reduction of unwanted facial hair in women. | ||
|adverseReactions=acne and stinging of skin | |adverseReactions=acne and stinging of skin | ||
|blackBoxWarningTitle=<b><span style="color:#FF0000;">TITLE</span></b> | |blackBoxWarningTitle=<b><span style="color:#FF0000;">TITLE</span></b> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
|offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Eflornithine in pediatric patients. | |offLabelPedGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Eflornithine in pediatric patients. | ||
|offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Eflornithine in pediatric patients. | |offLabelPedNoGuideSupport=There is limited information regarding <i>Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use</i> of Eflornithine in pediatric patients. | ||
|contraindications=contraindicated in patients with a history of sensitivity to any components of the preparation. | |||
|warnings=Discontinue use if hypersensitivity occurs. | |||
====Precautions==== | |||
======General====== | |||
*For external use only. | |||
*Transient stinging or burning may occur when applied to abraded or broken skin. | |||
======Information for Patients====== | |||
Patients using VANIQA® should receive the following information and instructions: | |||
*This medication is not a depilatory, but rather appears to retard hair growth to improve the condition and the patient's appearance. Patients will likely need to continue using a hair removal method (e.g., shaving, plucking, etc.) in conjunction with VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9%. | |||
*Onset of improvement was seen after as little as 4-8 weeks of treatment in the 24-week clinical trials. The condition may return to pretreatment levels 8 weeks after discontinuing treatment. | |||
*If skin irritation or intolerance develops, direct the patient to temporarily reduce the frequency of application (e.g., once a day). If irritation continues, the patient should discontinue use of the product. | |||
*Refer to the Patient Information Leaflet for additional important information and instructions. | |||
|clinicalTrials=Adverse events reported for most body systems occurred at similar frequencies in VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9% and vehicle control groups. The most frequent adverse events related to treatment with VANIQA® were skin-related. The following table notes the percentage of adverse events associated with the use of VANIQA® or its vehicle that occurred at greater than 1% in both the vehicle-controlled studies and the open-label safety studies up to 1 year of continuous use. | |clinicalTrials=Adverse events reported for most body systems occurred at similar frequencies in VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9% and vehicle control groups. The most frequent adverse events related to treatment with VANIQA® were skin-related. The following table notes the percentage of adverse events associated with the use of VANIQA® or its vehicle that occurred at greater than 1% in both the vehicle-controlled studies and the open-label safety studies up to 1 year of continuous use. | ||
[[file:Vaniqa AR.png|none|400px]] | [[file:Vaniqa AR.png|none|400px]] | ||
Treatment-related skin adverse events that occurred in less than 1% of the subjects treated with VANIQA® are: bleeding skin, cheilitis, contact dermatitis, swelling of lips, herpes simplex, numbness, and rosacea. | |||
Adverse events were primarily mild in intensity and generally resolved without medical treatment or discontinuation of VANIQA®. Only 2% of subjects discontinued studies due to an adverse event related to use of VANIQA®. | |||
=====Laboratory Test Abnormalities===== | |||
No laboratory test abnormalities have been consistently found to be associated with VANIQA®. In an open-label study, some patients showed an increase in their [[transaminases]]; however, the clinical significance of these findings is not known. | |||
|alcohol=Alcohol-Eflornithine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | |alcohol=Alcohol-Eflornithine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication. | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 23 January 2015
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alberto Plate [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Eflornithine is a hair growth retardant, ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor that is FDA approved for the treatment of reduction of unwanted facial hair in women.. Common adverse reactions include acne and stinging of skin.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Apply a thin layer of VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9% to affected areas of the face and adjacent involved areas under the chin and rub in thoroughly. Do not wash treated area for at least 4 hours. Use twice daily at least 8 hours apart or as directed by a physician. The patient should continue to use hair removal techniques as needed in conjunction with VANIQA®. (VANIQA® should be applied at least 5 minutes after hair removal.) Cosmetics or sunscreens may be applied over treated areas after cream has dried.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Eflornithine in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Eflornithine in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Eflornithine in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Eflornithine in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
contraindicated in patients with a history of sensitivity to any components of the preparation.
Warnings
Discontinue use if hypersensitivity occurs.
Precautions
General
- For external use only.
- Transient stinging or burning may occur when applied to abraded or broken skin.
Information for Patients
Patients using VANIQA® should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is not a depilatory, but rather appears to retard hair growth to improve the condition and the patient's appearance. Patients will likely need to continue using a hair removal method (e.g., shaving, plucking, etc.) in conjunction with VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9%.
- Onset of improvement was seen after as little as 4-8 weeks of treatment in the 24-week clinical trials. The condition may return to pretreatment levels 8 weeks after discontinuing treatment.
- If skin irritation or intolerance develops, direct the patient to temporarily reduce the frequency of application (e.g., once a day). If irritation continues, the patient should discontinue use of the product.
- Refer to the Patient Information Leaflet for additional important information and instructions.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Adverse events reported for most body systems occurred at similar frequencies in VANIQA® (eflornithine hydrochloride) cream, 13.9% and vehicle control groups. The most frequent adverse events related to treatment with VANIQA® were skin-related. The following table notes the percentage of adverse events associated with the use of VANIQA® or its vehicle that occurred at greater than 1% in both the vehicle-controlled studies and the open-label safety studies up to 1 year of continuous use.
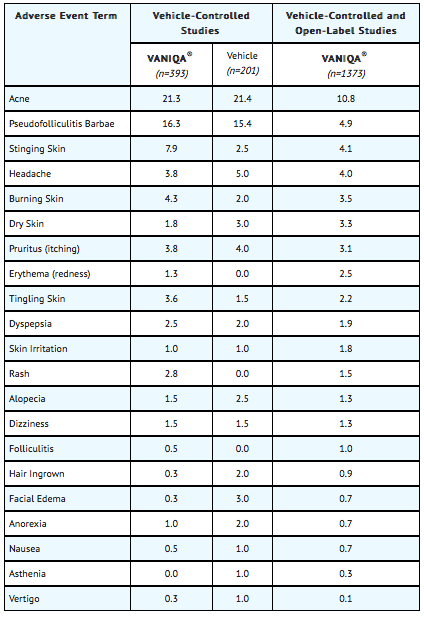
Treatment-related skin adverse events that occurred in less than 1% of the subjects treated with VANIQA® are: bleeding skin, cheilitis, contact dermatitis, swelling of lips, herpes simplex, numbness, and rosacea.
Adverse events were primarily mild in intensity and generally resolved without medical treatment or discontinuation of VANIQA®. Only 2% of subjects discontinued studies due to an adverse event related to use of VANIQA®.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
No laboratory test abnormalities have been consistently found to be associated with VANIQA®. In an open-label study, some patients showed an increase in their transaminases; however, the clinical significance of these findings is not known.
Postmarketing Experience
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Postmarketing Experience in the drug label.
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
There is no FDA guidance on usage of Eflornithine in women who are pregnant.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Eflornithine in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Eflornithine during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in women who are nursing.
Pediatric Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in pediatric settings.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Eflornithine in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Eflornithine in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Administration in the drug label.
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Eflornithine and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Mechanism of Action in the drug label.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Pharmacodynamics in the drug label.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Pharmacokinetics in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Nonclinical Toxicology in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Clinical Studies in the drug label.
How Supplied
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine How Supplied in the drug label.
Storage
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Eflornithine |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Eflornithine |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Patient Counseling Information in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Eflornithine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Eflornithine Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
| File:Eflornithine-2D-skeletal.png | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| [[Regulation of therapeutic goods |Template:Engvar data]] |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous (discontinued) Dermal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% (Intravenous) 13% (Dermal) |
| Metabolism | Not metabolised |
| Elimination half-life | 8 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H12F2N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 182.2 g/mol |
Overview
Eflornithine (α-difluoromethylornithine or DFMO) is a drug manufactured by Sanofi-Aventis which has various uses. It was initially developed for cancer treatment, but while having little use in treating malignancies, it was found to be highly effective in African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness), especially the West African form (Trypanosoma brucei gambiense).[1] In the United States it is known by the brand name Ornidyl®.[2]
Sleeping sickness treatment
Function
Eflornithine appears to kill trypanosomes by acting as a suicide inhibitor of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.17), this enzyme regulates cell division by catalysing the first step in polyamine biosynthesis.
Eflornithine's effects against Trypanosoma brucei gambiense were discovered by chance and because of its ability to bring patients back from coma, it became known as "Resurrection Drug".
It is hoped that eflornithine will replace the relatively toxic melarsoprol.
Production
Supplies of eflornithine are limited as its manufacturer does not consider it cost effective.
Its production was halted by its manufacturer, Aventis, in 1995 because the company did not consider it a profitable drug. The disease mainly affects poor people unable to pay for any sort of treatment.
In 2001, after lobbying at the WHO World Health Organization by Médecins Sans Frontières ("Doctors Without Borders"), the manufacturer resumed production of eflornithine, melarsoprol and pentamidine in sufficient amounts to cover existing needs. This 5-year agreement with the WHO also envisaged MSF working on the distribution of the drugs. The yearly value of the drugs donated by Aventis under this agreement is US$5 million. In addition, under the agreement, Bristol-Myers Squibb, the manufacturer of Vaniqa, will pay for part of the eflornithine. The 5-year agreement expired in 2006.[3] The trade name of eflornithine as manufactured for the treatment of sleeping sickness is Ornidyl®.
Once the five years period is over, Sanofi-Aventis (its new name after merging with another drugs company, Sanofi-Synthélabo) would start transferring technology and giving technical assistance to any possible manufacturer willing to continue production on their own.[4]
As of September 2005, the World Health Organization reports that the India Institute of Chemical Technology in Hyderabad, India and ILEX Oncology in Texas, United States are both working on new ways of making eflornithine more cheaply. The WHO goes on to say that ILEX is experimenting with an oral formulation of the drug as a treatment for cancer and that trials of the new oral formulation for efficacy against sleeping sickness are underway.
Dosing
When used for sleeping sickness, eflornithine is given intravenously, 50 mg/kg every six hours for 14 days.[5]
Hair growth inhibitor cream
Eflornithine is also an effective hair growth inhibiting agent. As a topical application, the drug has been shown to be an effective hair growth retardant in some patients, and is sold under the brand name Vaniqa® (eflornithine hydrochloride 13.9%). Efficacy data submitted to Food and Drug Administration (FDA) observed about 58% of women using it on facial hair had improvement.[6] This study suggested it may be particularly effective in postmenopausal women. One large published study on safety found the product rarely caused significant side effects such as acne, follicle irritation, itching or dryness.[7] This corroborates unpublished data submitted to FDA showing about 2% of subjects discontinued use due to adverse reactions.
It is partly the development of the hair removal market that encouraged Aventis to re-start the manufacture of eflornithine, and which allowed it to once again become available for use in sleeping sickness.
References
- ↑ Pepin J, Milord F, Guern C, Schechter PJ. Difluoromethylornithine for arseno-resistant Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness. Lancet 1987;2(8573):1431-3. PMID 2891995
- ↑ http://www.drugs.com/cons/Ornidyl.html
- ↑ http://www.ifpma.org/Health/other_infect/health_sleep.aspx
- ↑ Template:Es icon http://www.dndi.org.br/Espanhol/doenca_sono.aspx
- ↑ van Nieuwenhove S, Schechter PJ, Declercq J; et al. (1985). "Treatment of gambiense sleeping sickness in the Sudan with oral DFMO (DL-alfa-difluoromethyl ornithine) an inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase: first field trial". Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 79 (5): 692&ndash, 8.
- ↑ Vaniqa package insert
- ↑ Hickman JG, Huber F, Palmisano M. Human dermal safety studies with eflornithine HCl 13.9% cream (Vaniqa), a novel treatment for excessive facial hair. Curr Med Res Opin 2001;16:235-44. PMID 11268707.
External links
- Pages with script errors
- CS1 maint: Explicit use of et al.
- CS1 maint: Multiple names: authors list
- Pages with broken file links
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Antiprotozoal agents
- Health in Africa
- Orphan drugs
- Organofluorides
- Amines
- Carboxylic acids