Cowden syndrome physical examination: Difference between revisions
(→Neck) |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
** The most common locations of [[facial]] [[papules]] are located in periorificial regions and [[nostrils]]. | ** The most common locations of [[facial]] [[papules]] are located in periorificial regions and [[nostrils]]. | ||
* '''Oral papules and papillomas''' | * '''Oral papules and papillomas''' | ||
** The location of oral [[papules]] and [[papillomas]] are most commonly in [[lips]] and [[buccal]] [[mucous membranes]] which are pink in colour and 1 to 4 mm in diameter size.<ref name="pmid465314">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bikowski JB, Lupulescu A, Patterson JC |title=The dermatopathology of Cowden's syndrome |journal=Br. J. Dermatol. |volume=100 |issue=6 |pages=667–73 |date=June 1979 |pmid=465314 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ** The location of oral [[papules]] and [[papillomas]] are most commonly in [[lips]] and [[buccal]] [[mucous membranes]] which are pink in colour and 1 to 4 mm in diameter size.<ref name="pmid218867593">{{cite journal |vauthors=Masmoudi A, Chermi ZM, Marrekchi S, Raida BS, Boudaya S, Mseddi M, Jalel MT, Turki H |title=Cowden syndrome |journal=J Dermatol Case Rep |volume=5 |issue=1 |pages=8–13 |date=March 2011 |pmid=21886759 |pmc=3163352 |doi=10.3315/jdcr.2011.1063 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid465314">{{cite journal |vauthors=Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bikowski JB, Lupulescu A, Patterson JC |title=The dermatopathology of Cowden's syndrome |journal=Br. J. Dermatol. |volume=100 |issue=6 |pages=667–73 |date=June 1979 |pmid=465314 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | ||
** When the [[papules]] coalesce they form as cobblestone appearance. | ** When the [[papules]] coalesce they form as cobblestone appearance. | ||
Revision as of 19:07, 5 March 2019
|
Cowden syndrome Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Cowden syndrome physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Cowden syndrome physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Cowden syndrome physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vamsikrishna Gunnam M.B.B.S [2]
Overview
Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance]. Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
Common physical examination findings of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Physical Examination
Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with cowden syndrome usually appear normal.
Vital Signs
- Vital signs are normal in patients with cowden syndrome.
Skin
- Skin examination of patients with cowden syndrome is very important and helps in the diagnosis
- Trichilemmomas:
- Trichilemmomas are solitary sporadic lesion which arise from the outer root sheath of the hair follicle.[1][2][3]
- Trichilemmomas are most commonly occurs in face and neck areas of the body parts.
- Trichilemmomas are hallmark clinical sign of cowden syndrome patients.
- On gross examination trichilemmomas are wart-like and skin-colored papules.
- On histology examination trichilemmomas are contain large glycogen-rich cells.
- Biopsy of the trichilemmomas helps in the diagnosis of the cowden syndrome .
- Trichilemmomas:
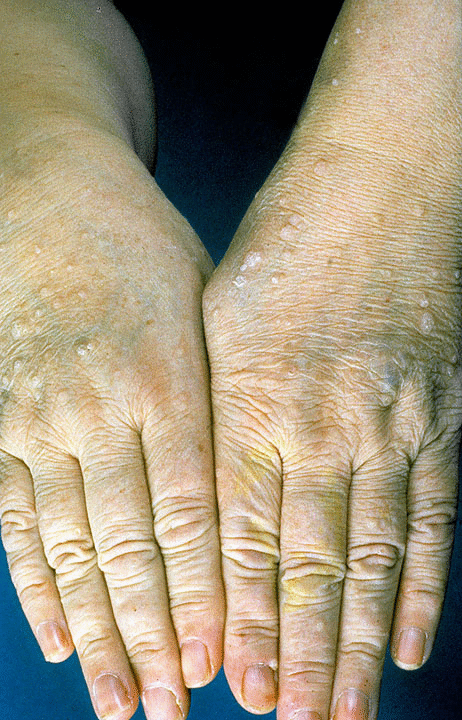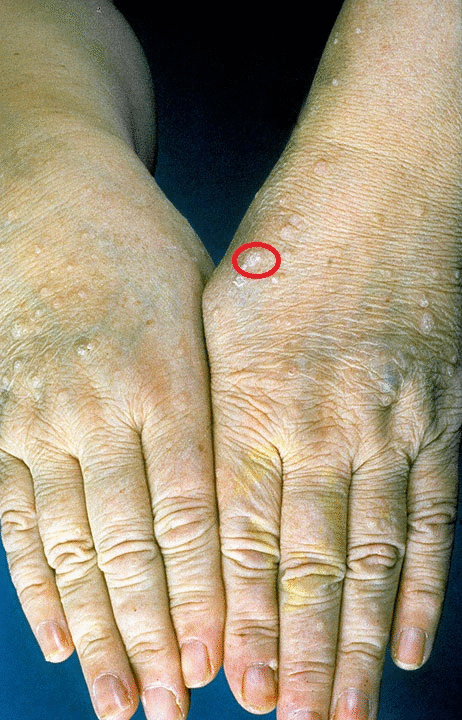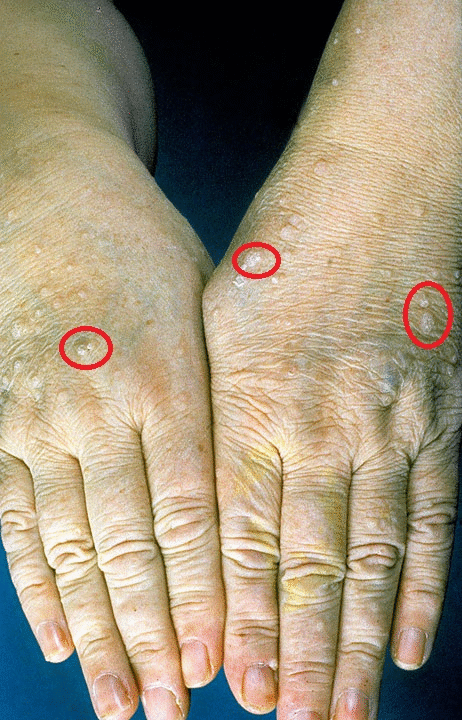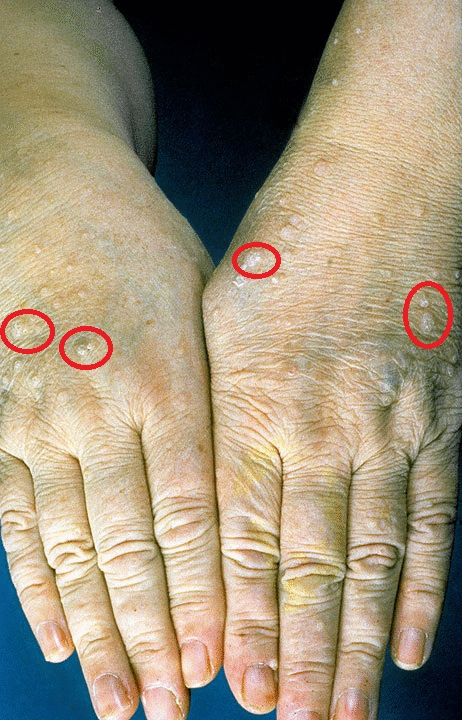
- Acral keratoses:
- Facial papules
- Oral papules and papillomas
- The location of oral papules and papillomas are most commonly in lips and buccal mucous membranes which are pink in colour and 1 to 4 mm in diameter size.[8][9]
- When the papules coalesce they form as cobblestone appearance.
Neck
- Neck examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
- The most common locations of
OR
- Jugular venous distension
- Carotid bruits may be auscultated unilaterally/bilaterally using the bell/diaphragm of the otoscope
- Lymphadenopathy (describe location, size, tenderness, mobility, and symmetry)
- Thyromegaly / thyroid nodules
- Hepatojugular reflux
Lungs
- Pulmonary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Asymmetric chest expansion OR decreased chest expansion
- Lungs are hyporesonant OR hyperresonant
- Fine/coarse crackles upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally
- Rhonchi
- Vesicular breath sounds OR distant breath sounds
- Expiratory wheezing OR inspiratory wheezing with normal OR delayed expiratory phase
- Wheezing may be present
- Egophony present/absent
- Bronchophony present/absent
- Normal/reduced tactile fremitus
Heart
- Cardiovascular examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Chest tenderness upon palpation
- PMI within 2 cm of the sternum (PMI) / Displaced point of maximal impulse (PMI) suggestive of ____
- Heave / thrill
- Friction rub
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
- Gallops
- A high/low grade early/late systolic murmur / diastolic murmur best heard at the base/apex/(specific valve region) may be heard using the bell/diaphgram of the stethoscope
Abdomen
- Abdominal examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Abdominal distension
- Abdominal tenderness in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Rebound tenderness (positive Blumberg sign)
- A palpable abdominal mass in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Guarding may be present
- Hepatomegaly / splenomegaly / hepatosplenomegaly
- Additional findings, such as obturator test, psoas test, McBurney point test, Murphy test
Back
- Back examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Point tenderness over __ vertebrae (e.g. L3-L4)
- Sacral edema
- Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally
- Buffalo hump
Genitourinary
- Genitourinary examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- A pelvic/adnexal mass may be palpated
- Inflamed mucosa
- Clear/(color), foul-smelling/odorless penile/vaginal discharge
Neuromuscular
- Neuromuscular examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Patient is usually oriented to persons, place, and time
- Altered mental status
- Glasgow coma scale is ___ / 15
- Clonus may be present
- Hyperreflexia / hyporeflexia / areflexia
- Positive (abnormal) Babinski / plantar reflex unilaterally/bilaterally
- Muscle rigidity
- Proximal/distal muscle weakness unilaterally/bilaterally
- ____ (finding) suggestive of cranial nerve ___ (roman numerical) deficit (e.g. Dilated pupils suggestive of CN III deficit)
- Unilateral/bilateral upper/lower extremity weakness
- Unilateral/bilateral sensory loss in the upper/lower extremity
- Positive straight leg raise test
- Abnormal gait (describe gait: e.g. ataxic (cerebellar) gait / steppage gait / waddling gait / choeiform gait / Parkinsonian gait / sensory gait)
- Positive/negative Trendelenburg sign
- Unilateral/bilateral tremor (describe tremor, e.g. at rest, pill-rolling)
- Normal finger-to-nose test / Dysmetria
- Absent/present dysdiadochokinesia (palm tapping test)
Extremities
- Extremities examination of patients with [disease name] is usually normal.
OR
- Clubbing
- Cyanosis
- Pitting/non-pitting edema of the upper/lower extremities
- Muscle atrophy
- Fasciculations in the upper/lower extremity
References
- ↑ Al-Zaid T, Ditelberg JS, Prieto VG, Lev D, Luthra R, Davies MA, Diwan AH, Wang WL, Lazar AJ (May 2012). "Trichilemmomas show loss of PTEN in Cowden syndrome but only rarely in sporadic tumors". J. Cutan. Pathol. 39 (5): 493–9. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.2012.01888.x. PMID 22486434.
- ↑ Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bikowski JB, Lupulescu A, Patterson JC (June 1979). "The dermatopathology of Cowden's syndrome". Br. J. Dermatol. 100 (6): 667–73. PMID 465314.
- ↑ Tellechea O, Cardoso JC, Reis JP, Ramos L, Gameiro AR, Coutinho I, Baptista AP (2015). "Benign follicular tumors". An Bras Dermatol. 90 (6): 780–96, quiz 797–8. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20154114. PMC 4689065. PMID 26734858.
- ↑ Masmoudi A, Chermi ZM, Marrekchi S, Raida BS, Boudaya S, Mseddi M, Jalel MT, Turki H (March 2011). "Cowden syndrome". J Dermatol Case Rep. 5 (1): 8–13. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2011.1063. PMC 3163352. PMID 21886759.
- ↑ Starink TM, van der Veen JP, Arwert F, de Waal LP, de Lange GG, Gille JJ, Eriksson AW (March 1986). "The Cowden syndrome: a clinical and genetic study in 21 patients". Clin. Genet. 29 (3): 222–33. PMID 3698331.
- ↑ Masmoudi A, Chermi ZM, Marrekchi S, Raida BS, Boudaya S, Mseddi M, Jalel MT, Turki H (March 2011). "Cowden syndrome". J Dermatol Case Rep. 5 (1): 8–13. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2011.1063. PMC 3163352. PMID 21886759.
- ↑ Starink TM, van der Veen JP, Arwert F, de Waal LP, de Lange GG, Gille JJ, Eriksson AW (March 1986). "The Cowden syndrome: a clinical and genetic study in 21 patients". Clin. Genet. 29 (3): 222–33. PMID 3698331.
- ↑ Masmoudi A, Chermi ZM, Marrekchi S, Raida BS, Boudaya S, Mseddi M, Jalel MT, Turki H (March 2011). "Cowden syndrome". J Dermatol Case Rep. 5 (1): 8–13. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2011.1063. PMC 3163352. PMID 21886759.
- ↑ Brownstein MH, Mehregan AH, Bikowski JB, Lupulescu A, Patterson JC (June 1979). "The dermatopathology of Cowden's syndrome". Br. J. Dermatol. 100 (6): 667–73. PMID 465314.