Colorectal cancer pathophysiology
|
Colorectal cancer Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Colorectal cancer pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Colorectal cancer pathophysiology |
To view the pathophysiology of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), click here
To view the pathophysiology of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), click here
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Saarah T. Alkhairy, M.D., Roukoz A. Karam, M.D.[2], Elliot B. Tapper, M.D.
Overview
The pathogenesis of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) involves the molecular pathways for both sporadic and colitis-associated CRC. Sporadic instability originates from the epithelial cells that line the colon or rectum. Colitis-associated CRC includes genetic instability, epigenetic alteration, chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and intestinal microbiota. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) histological classification, most colorectal tumors are carcinomas of which almost 90% are adenocarcinomas.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) involves the molecular pathways for both sporadic and colitis-associated CRC.
Sporadic colorectal cancers
The picture below depicts the molecular pathogenesis of sporadic colon cancer:[1]
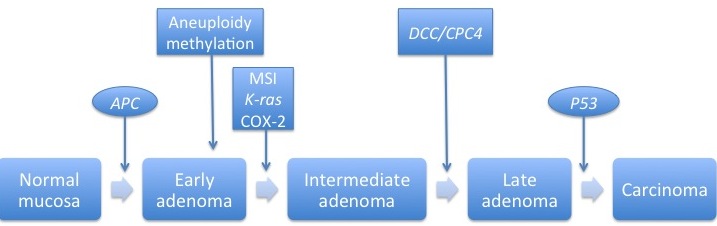
Sporadic colorectal cancer originates from the epithelial cells that line the colon or rectum; it may involve the following:[2]
- Produces the APC protein, which prevents the accumulation of β-catenin protein (responsible for stem cell renewal)
- Mutation of the APC protein leads to the accumulation of β-catenin protein and causes inappropriately high levels of stem cell renewal.
- Produces the p53 protein, which monitors cell division and promotes apoptosis if there are cell defects
- Mutations result in loss of control over cell division or apoptosis
- Usually responsible for apoptosis, but deactivated in colorectal cancer
- Stimulate cellular division
- Mutations lead to over-activation of cell proliferation
Colitis-associated colorectal cancers
The picture below depicts the molecular pathogenesis of colitis-associated colon cancer:[1]

At a microbiological level, the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancers (CRC) can be linked to defects within the cell cycle.[3]
Although it is poorly understood, the following five factors may be responsible for its neoplastic changes:[1]
- Genetic instability[4]
- Chromosomal instability (CIN) occurs when either whole chromosomes or parts of chromosomes are duplicated or deleted; it occurs with 85% frequency.
- Microsatellite instability (MSI) is the condition of genetic hypermutability that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair; it occurs with 15% frequency.
- Epigenetic alteration
- Sporadic CRC can develop from dysplasia in 1 or 2 foci of the colon, while colitis-associated CRC can develop from multifocal dysplasia.[5][6]
- This indicates a field change effect where large areas of cells within the colon are affected by carcinogenic alterations.
- Chronic inflammation[7]
- Oxidative stress[8]
- Oxidative stress results from inflammatory reactions which include inflammatory cells, activated neutrophils, and macrophages.
- Macrophages produce large amounts of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species.
- These reactive oxygen and nitrogen species can interact with key genes involved in carcinogenic pathways such as P53 and DNA mismatch repair genes.
- Intestinal microbiota[9]
- The Modification of enteric flora by probiotic lactobacilli is a proposed mechanism that may contribute to the development of colitis-associated cancer.
Genetics
From a genetic standpoint, colorectal cancer can be divided into three categories:[10]
- Sporadic (75% of cases)
- No indication of a hereditary component
- Familial (20% of cases)
- Resulting from multifactorial hereditary factors and/or environmental exposures to non-genetic risk factors
- Hereditary (10% of cases)
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) also known as Lynch Syndrome results from mutations in hMLH1, hMSH2, hMSH6, and PMS2
- Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) results from mutations in the APC gene located on chromosome 5p22.2
- MUTYH-associated polyposis (MAP) results from biallelic mutation of the MutY, E. Coli, Homolog gene which functions to remove adenine residues mispaired with 8-hydroxyguanine in DNA

Gross Pathology
- On gross pathology, a polypoid or fungating exophytic (growing outwards) lesion is characteristic of right-sided colorectal tumors including the ascending colon and cecum.[11]
- Left-sided tumours tend to be circumferential and annular producing an "apple-core" appearance on barium enema x-ray.[11]

Microscopic Pathology
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) histological classification, most colorectal tumors are carcinomas of which almost 90% are adenocarcinomas:[12]
- Carcinomas
- Adenocarcinoma
- Mucinous adenocarcinoma
- Signet-ring cell carcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Adenosquamous carcinoma
- Squamous cell
- Medullary carcinoma
- Undifferentiated carcinoma
- Neuroendocrine neoplasms
- Hamartomas
- Mesenchymas tumors
- Lymphomas
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kim, Eun Ran (2014). "Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: The risk, pathogenesis, prevention and diagnosis". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 20 (29): 9872. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.9872. ISSN 1007-9327.
- ↑ Markowitz SD, Bertagnolli MM (2009). "Molecular origins of cancer: Molecular basis of colorectal cancer". N Engl J Med. 361 (25): 2449–60. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0804588. PMC 2843693. PMID 20018966.
- ↑ Scully R (2010). "The spindle-assembly checkpoint, aneuploidy, and gastrointestinal cancer". The New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (27): 2665–6. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1008017. PMID 21190461. Retrieved 2011-12-12.
- ↑ Zivić R, Bjelaković G, Koraćević D (1975). "[Amino acid constitution of the urine in children with rheumatic fever]". Reumatizam. 22 (1): 21–5. PMID 1118685.
- ↑ Itzkowitz S (2003). "Colon carcinogenesis in inflammatory bowel disease: applying molecular genetics to clinical practice". J Clin Gastroenterol. 36 (5 Suppl): S70–4, discussion S94-6. PMID 12702969.
- ↑ Kraus S, Arber N (2009). "Inflammation and colorectal cancer". Curr Opin Pharmacol. 9 (4): 405–10. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2009.06.006. PMID 19589728.
- ↑ Elzagheid A, Emaetig F, Alkikhia L, Buhmeida A, Syrjänen K, El-Faitori O; et al. (2013). "High cyclooxygenase-2 expression is associated with advanced stages in colorectal cancer". Anticancer Res. 33 (8): 3137–43. PMID 23898071.
- ↑ Ullman TA, Itzkowitz SH (2011). "Intestinal inflammation and cancer". Gastroenterology. 140 (6): 1807–16. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.057. PMID 21530747.
- ↑ O'Mahony L, Feeney M, O'Halloran S, Murphy L, Kiely B, Fitzgibbon J; et al. (2001). "Probiotic impact on microbial flora, inflammation and tumour development in IL-10 knockout mice". Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 15 (8): 1219–25. PMID 11472326.
- ↑ Schlussel AT, Gagliano RA, Seto-Donlon S, Eggerding F, Donlon T, Berenberg J; et al. (2014). "The evolution of colorectal cancer genetics-Part 1: from discovery to practice". J Gastrointest Oncol. 5 (5): 326–35. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2014.069. PMC 4173047. PMID 25276405.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Weiss JM, Pfau PR, O'Connor ES, King J, LoConte N, Kennedy G; et al. (2011). "Mortality by stage for right- versus left-sided colon cancer: analysis of surveillance, epidemiology, and end results--Medicare data". J Clin Oncol. 29 (33): 4401–9. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.36.4414. PMC 3221523. PMID 21969498.
- ↑ Compton CC, Fielding LP, Burgart LJ, Conley B, Cooper HS, Hamilton SR; et al. (2000). "Prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999". Arch Pathol Lab Med. 124 (7): 979–94. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2000)124<0979:PFICC>2.0.CO;2. PMID 10888773.