Betaxolol (tablet): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{drugbox | | {{drugbox | | ||
| image=betaxolol.png | | image=betaxolol.png | ||
| Line 25: | Line 22: | ||
|routes_of_administration = oral, [[ocular]] | |routes_of_administration = oral, [[ocular]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{SI}} | |||
{{EH}} | |||
'''Betaxolol''' (trade names '''Betoptic''', '''Betoptic S''', '''Lokren''', '''Kerlone''') is a selective [[beta blocker|beta<sub>1</sub> receptor blocker]] used in the treatment of [[hypertension]] and [[glaucoma]]. Being selective for beta<sub>1</sub> receptors, it typically has fewer systemic [[adverse drug reaction|side effect]]s than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing [[bronchospasm]] (mediated by beta<sub>2</sub> receptors) as [[timolol]] may. Betaxolol also shows greater affininty for beta<sub>1</sub> receptors than [[metoprolol]]. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye ([[intraocular pressure]]). This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid (which is called the [[aqueous humor]]) within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the [[optic nerve]] and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to [[glaucoma]]. | '''Betaxolol''' (trade names '''Betoptic''', '''Betoptic S''', '''Lokren''', '''Kerlone''') is a selective [[beta blocker|beta<sub>1</sub> receptor blocker]] used in the treatment of [[hypertension]] and [[glaucoma]]. Being selective for beta<sub>1</sub> receptors, it typically has fewer systemic [[adverse drug reaction|side effect]]s than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing [[bronchospasm]] (mediated by beta<sub>2</sub> receptors) as [[timolol]] may. Betaxolol also shows greater affininty for beta<sub>1</sub> receptors than [[metoprolol]]. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye ([[intraocular pressure]]). This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid (which is called the [[aqueous humor]]) within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the [[optic nerve]] and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to [[glaucoma]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:14, 8 July 2009
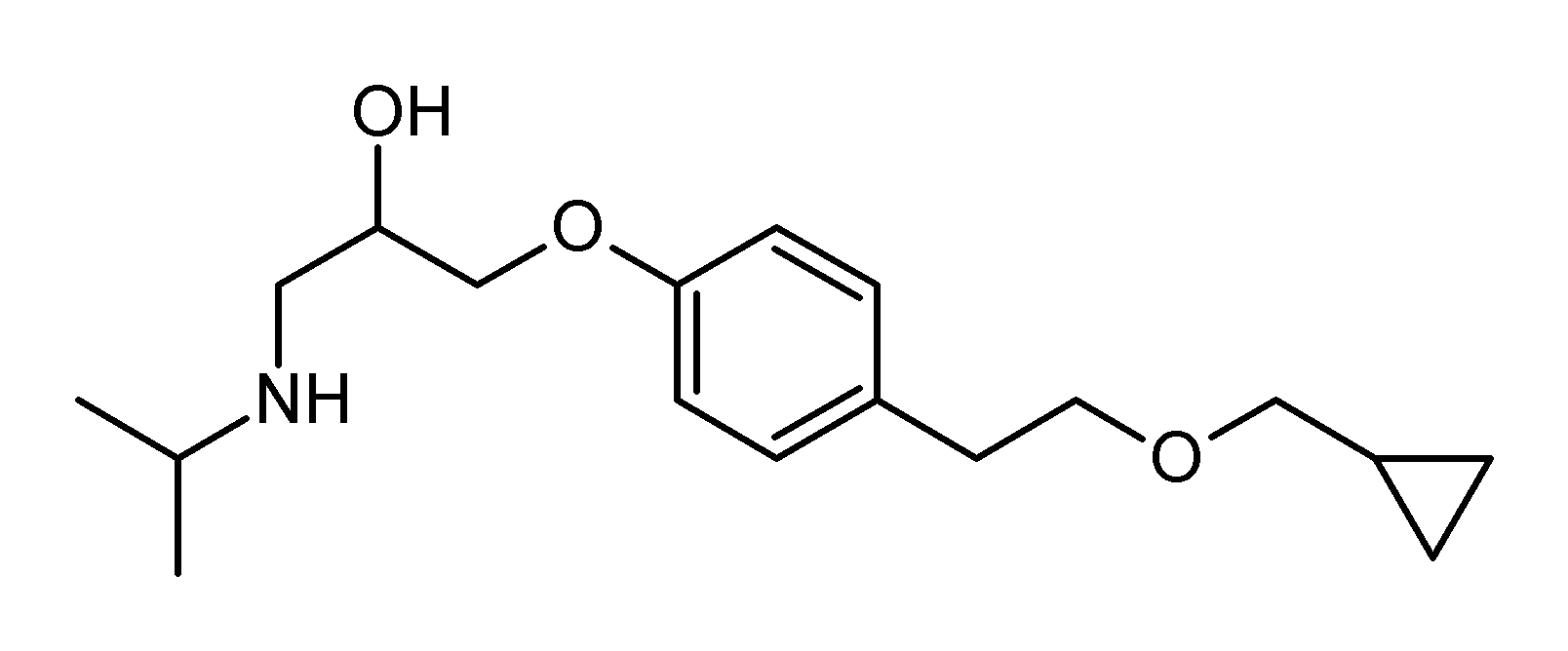 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | oral, ocular |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 89% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 14–22 hours |
| Excretion | Renal (20%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H29NO3 |
| Molar mass | 307.428 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Please Take Over This Page and Apply to be Editor-In-Chief for this topic: There can be one or more than one Editor-In-Chief. You may also apply to be an Associate Editor-In-Chief of one of the subtopics below. Please mail us [1] to indicate your interest in serving either as an Editor-In-Chief of the entire topic or as an Associate Editor-In-Chief for a subtopic. Please be sure to attach your CV and or biographical sketch.
Betaxolol (trade names Betoptic, Betoptic S, Lokren, Kerlone) is a selective beta1 receptor blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and glaucoma. Being selective for beta1 receptors, it typically has fewer systemic side effects than non-selective beta-blockers, for example, not causing bronchospasm (mediated by beta2 receptors) as timolol may. Betaxolol also shows greater affininty for beta1 receptors than metoprolol. In addition to its effect on the heart, betaxolol reduces the pressure within the eye (intraocular pressure). This effect is thought to be caused by reducing the production of the liquid (which is called the aqueous humor) within the eye. The precise mechanism of this effect is not known. The reduction in intraocular pressure reduces the risk of damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision in patients with elevated intraocular pressure due to glaucoma.
Betaxolol was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for ocular use as a 0.5% solution (Betoptic) in 1985 and as a 0.25% solution (Betoptic S) in 1989.
Clinical uses
- Oral: for the management of hypertension
- Ophthalmic: for the management of glaucoma
Dosage
- Oral: The initial dose in hypertension is ordinarily 10 mg once daily either alone or added to diuretic therapy.
- Ophthalmic: The recommended dose is one to two drops in the affected eye(s) twice daily.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the drug
- Patients with sinus bradycardia, heart block greater than first degree, cardiogenic shock, and overt cardiac failure
External links
See also
Template:Antiglaucoma preparations and miotics
Synonyms / Brand Names:
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert. Template:SIB
- Pages with script errors
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical articles with unknown parameter in Infobox drug
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Beta blockers
- Drugs