Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ {{Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo}} {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Fs}} == Overview == == Diagnostic Study of Choice == === Study of choice === [Name of the investigation]...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (34 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Fs}} | {{CMG}}; {{AE}} {{Fs}} | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
The diagnostic study of choice for BPPV is [[patient]] history and observing [[nystagmus]] on [[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hall pike maneuver]]. | |||
== Diagnostic Study of Choice == | == Diagnostic Study of Choice == | ||
{| align="right" | |||
| | |||
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RNBJLed_Slc&t=4s|500}} | |||
|} | |||
=== Study of choice === | === Study of choice === | ||
[ | The diagnostic study of choice for BPPV is [[patient]] history and observing [[nystagmus]] on [[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hall pike maneuver]].<ref name="pmid20607044">{{cite journal |vauthors=Lee SH, Kim JS |title=Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo |journal=J Clin Neurol |volume=6 |issue=2 |pages=51–63 |date=June 2010 |pmid=20607044 |pmc=2895225 |doi=10.3988/jcn.2010.6.2.51 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid11771020">{{cite journal |vauthors=Chang MB, Bath AP, Rutka JA |title=Are all atypical positional nystagmus patterns reflective of central pathology? |journal=J Otolaryngol |volume=30 |issue=5 |pages=280–2 |date=October 2001 |pmid=11771020 |doi= |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid24642523">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dorresteijn PM, Ipenburg NA, Murphy KJ, Smit M, van Vulpen JK, Wegner I, Stegeman I, Grolman W |title=Rapid Systematic Review of Normal Audiometry Results as a Predictor for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo |journal=Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg |volume=150 |issue=6 |pages=919–24 |date=June 2014 |pmid=24642523 |doi=10.1177/0194599814527233 |url=}}</ref> | ||
Investigations: | |||
* Among the [[patients]] who present with clinical [[signs]] of BPPV, the [[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hallpike maneuver]] is the most specific test for the [[diagnosis]]. | |||
The following | ===== Diagnostic results ===== | ||
* [ | The following findings are confirmatory for BPPV: | ||
* Recurrent brief [[vertigo]] attack which starts with certain [[head]] movements. | |||
* [[Nystagmus]] on [[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hallpike maneuver]]. | |||
===== Sequence of Diagnostic Studies ===== | |||
The various investigations must be performed in the following order: | |||
* [[Patient history]] | |||
* | * [[Physical examination]] ([[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hall pike maneuver]]) | ||
* | If patients doesn't respond to treatment or doesn't show the typical [[nystagmus]] on [[Dix-Hallpike test|Dix-Hall pike maneuver]], in order to rule out other abnormalities we may perform some additional test such as: | ||
* [[Electronystagmography]] (ENG) or video nystagmography (VNG) | |||
* [[Audiometry]] | |||
* [[Neuroimaging]] | |||
[ | For more information about these tests, [[Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo other diagnostic studies|click here]]. | ||
=== Diagnostic criteria for posterial canal BPPV === | |||
{| | {| | ||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Subtypes | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" |Explanation | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | | |||
! style="background: #4479BA; color: #FFFFFF; text-align: center;" | | |||
|- | |- | ||
! style="background: # | ! style="background: #DCDCDC; text-align: center;" |History | ||
| style="background: # | | style="background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
* Brief recurrent vertigo attack starts with change in head position | |||
|- | |- | ||
! style="background: # | ! style="background: #DCDCDC; text-align: center;" |Physical exam | ||
| style="background: # | | style="background: #F5F5F5;" | | ||
* Vertigo and nystagmus after Dix-Hall pike maneuver | |||
* Brief delay between performing Dix-Hall pike maneuver and vertigo | |||
* The vertigo and nystagmus will resolve after 60 seconds | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== Diagnostic approach === | |||
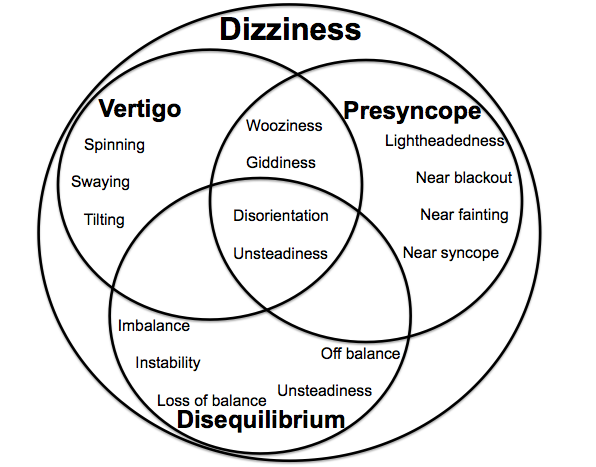
[[Image:Dizziness.png|550px]] | |||
Diagnostic approach to a [[patient]] with [[dizziness]]: | |||
{{familytree/start}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | A01 | | | | |A01=Patient present with [[dizziness]]<ref name="pmid27719862">{{cite journal |vauthors=Dieterich M, Staab JP, Brandt T |title=Functional (psychogenic) dizziness |journal=Handb Clin Neurol |volume=139 |issue= |pages=447–468 |date=2016 |pmid=27719862 |doi=10.1016/B978-0-12-801772-2.00037-0 |url=}}</ref><ref name="pmid28375909">{{cite journal |vauthors=Cheshire WP |title=Syncope |journal=Continuum (Minneap Minn) |volume=23 |issue=2, Selected Topics in Outpatient Neurology |pages=335–358 |date=April 2017 |pmid=28375909 |doi=10.1212/CON.0000000000000444 |url=}}</ref><ref name="Chan2009">{{cite journal|last1=Chan|first1=Yvonne|title=Differential diagnosis of dizziness|journal=Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery|volume=17|issue=3|year=2009|pages=200–203|issn=1068-9508|doi=10.1097/MOO.0b013e32832b2594}}</ref><ref name="Brandt2001">{{cite journal|last1=Brandt|first1=T|title=NOSOLOGICAL ENTITIES?: Cervical vertigo|journal=Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry|volume=71|issue=1|year=2001|pages=8–12|issn=00223050|doi=10.1136/jnnp.71.1.8}}</ref>}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | A02 | | | | | |A02=Loss of consciousness?}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | |,|-|-|-|-|^|-|-|-|-|-|-|.| | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | B01 | | | | | | | | | | B02 | | |B01=Yes|B02=No}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | | | | C02 | | |C02=Sense of motion/<br>spinning?}} | |||
{{familytree | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|.| | | | |,|-|-|^|-|-|.| | }} | |||
{{familytree | D01 | | D02 | | D00 | | | D03 | | | | D04 |D01=Other|D02=Sweating<br>Heaviness sensation in the legs<br>"Tunnel" vision<br>Feeling warm or hot<br>Nausea<br>Vomiting|D00=History of seizure<br>Aura<br>Post-ictal phase<br>Uncontrollable muscle spasms<br>Drooling or frothing at the mouth<br>Teeth clenching<br>Tongue biting<br>Sudden, rapid eye movements|D03=Yes|D04=No}} | |||
{{familytree | |!| | | |!| | | |!| | | | |!| | | | | |!| | }} | |||
{{familytree | E01 | | E02 | | E00 | | | E03 | | | | |!| |E01=Electrolyte imbalance/<br>Intracranial process|E02=[[Syncope]]|E00=[[Seizure]]|E03=[[Vertigo]]}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | M01 | | M02 | | | F02 | | | | |!| |M01=Sudden, and generally momentary, loss of consciousness, or blacking out caused by the Central Ischaemic Response|M02=Temporary abnormal electro-physiologic phenomenon of the brain, resulting in abnormal synchronization of electrical neuronal activity|F02=Sudden onset?<br>Horizental [[nystagmus]]?<br>[[Auditory]] [[symptoms]]?<br>No neurological problem?}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | | | X02 | | X01 | | | |!| | | | | |!| | | | | | | |X02=Causes:<br>•[[Hemorrhage]]<br>•[[Hypotension]]<br>•[[Hypoxia]]<br>•[[Pulmonary embolism]]<br>•Ruptured [[abdominal aortic aneurysm]]<br>•[[Ventricular arrhythmia]]<br>•[[Arrhythmia]]<br>•[[Medication]]<br>•[[Orthostatic hypotension]]<br>•[[Vagal]] stimulation<br>•Vertebrobasilar insufficiency|X01=Causes:<br>•[[Brain damage]] <br>•[[Congenital abnormalities]]<br>•[[Stroke]] <br>•[[Infection]]<br>•Genetic [[syndromes]]<br>•[[Brain tumor]]<br>•[[Epilepsy]]}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | |,|-|^|-|.| | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | G01 | | G02 | | |!| | | | | | | |G01=Yes|G02=No}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | H01 | | H02 | | |!| | | | | | | |H01=Peripheral|H02=Central}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | | | | | | | | | | I01 | | I02 | | |!| | | | | | | |I01=[[BPPV]]<br>[[Vestibular neuritis]]<br>[[HSV oticus]]<br>[[Meniere disease]]<br>[[Labyrinthine concussion]]<br>[[Perilymphatic fistula]]<br>[[Semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome]]<br>[[Vestibular paroxysma]]<br>[[Cogan syndrome]]<br>[[Vestibular schwannoma]]<br>[[Otitis media]]<br>[[Aminoglycoside toxicity]]<br>Recurrent [[vestibulopathy]]|I02=[[Vestibular migraine]]<br>[[Epileptic vertigo]]<br>[[Multiple sclerosis]]<br>[[Brain tumors]]<br>Crebellar infarction/hemorrhage<br>[[Brain stem ischemia]]<br>[[Chiari malformation]]<br>[[Parkinson]]}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|-|-|.| | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | J01 | | J02 | | | | J03 |J01=Hyperventilation<br>Psychiatric symptoms|J02=Balance<br>problem|J03=Sweating<br>Tunnel Vision<br>Nausea <br>Heart palpitations <br>Abdominal discomfort<br>Slurred speech}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | | | |!| | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | K01 | | K02 | | | | K03 | |K01=Psychogenic<br>dizziness|K02=[[Dysequilibrium]]|K03=[[Presyncope]]}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | | | |!| | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | L01 | | L02 | | | | L03 | |L01=Dizziness which is not characterized by true vertigo and it can be replicated by hyperventilation and psychiatric symptoms that usually precede its onset.|L02=Impaired sense or absence of balance or equilibrioception that primarily occurs during standing or walking|L03=Feeling of lightheadedness that can lead to syncope|}} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |!| | | |!| | | | | |!| | | }} | |||
{{familytree |boxstyle=text-align: left; | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Y01 | | Y02 | | | | Y03 | |Y01=Causes:<br>•[[Alcohol dependence]]<br>•[[Conversion disorder]]<br>•[[Fibromyalgia]]<br>•[[Generalized anxiety]]<br>•[[Hyperventilation]]<br>•[[Major depression]]<br>•[[Panic disorder]]|Y02=Causes:<br>•[[Arrhythmia]]<br>•[[Asthma]] exacerbation<br>•Cerebellar hemorrhage<br>•[[Compartment syndrome]]<br>•[[Endophthalmitis]]<br>•[[Epilepsy]]<br>•[[Hypoglycemia]]<br>•[[Organophosphates]]<br>•[[Cerebellar]] disorders<br>•[[Gait abnormality]]<br>•[[Hypoglycemia]]<br>•[[Paralysis]]<br>•[[Peripheral neuropathy]]<br>•Vestibular disorders<br>•Visual impairment|Y03=Causes:<br>•[[Hemorrhage]]<br>•[[Hypotension]]<br>•[[Hypoxia]]<br>•[[Pulmonary embolism]]<br>•Ruptured [[abdominal aortic aneurysm]]<br>•[[Ventricular arrhythmia]]<br>•[[Arrhythmia]]<br>•[[Medication]]<br>•[[Orthostatic hypotension]]<br>•[[Vagal stimulation]]<br>•[[Vertebrobasilar insufficiency]] }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | }} | |||
{{familytree/end}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:13, 29 October 2019
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo from other Diseases |
|---|
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice |
|
FDA on Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice |
|
CDC on Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice |
|
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice in the news |
|
Blogs on Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo diagnostic study of choice |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Fahimeh Shojaei, M.D.
Overview
The diagnostic study of choice for BPPV is patient history and observing nystagmus on Dix-Hall pike maneuver.
Diagnostic Study of Choice
|
{{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RNBJLed_Slc&t=4s%7C500}} |
Study of choice
The diagnostic study of choice for BPPV is patient history and observing nystagmus on Dix-Hall pike maneuver.[1][2][3]
Investigations:
- Among the patients who present with clinical signs of BPPV, the Dix-Hallpike maneuver is the most specific test for the diagnosis.
Diagnostic results
The following findings are confirmatory for BPPV:
- Recurrent brief vertigo attack which starts with certain head movements.
- Nystagmus on Dix-Hallpike maneuver.
Sequence of Diagnostic Studies
The various investigations must be performed in the following order:
If patients doesn't respond to treatment or doesn't show the typical nystagmus on Dix-Hall pike maneuver, in order to rule out other abnormalities we may perform some additional test such as:
- Electronystagmography (ENG) or video nystagmography (VNG)
- Audiometry
- Neuroimaging
For more information about these tests, click here.
Diagnostic criteria for posterial canal BPPV
| Subtypes | Explanation |
|---|---|
| History |
|
| Physical exam |
|
Diagnostic approach
Diagnostic approach to a patient with dizziness:
| Patient present with dizziness[4][5][6][7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss of consciousness? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sense of motion/ spinning? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | Sweating Heaviness sensation in the legs "Tunnel" vision Feeling warm or hot Nausea Vomiting | History of seizure Aura Post-ictal phase Uncontrollable muscle spasms Drooling or frothing at the mouth Teeth clenching Tongue biting Sudden, rapid eye movements | Yes | No | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrolyte imbalance/ Intracranial process | Syncope | Seizure | Vertigo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sudden, and generally momentary, loss of consciousness, or blacking out caused by the Central Ischaemic Response | Temporary abnormal electro-physiologic phenomenon of the brain, resulting in abnormal synchronization of electrical neuronal activity | Sudden onset? Horizental nystagmus? Auditory symptoms? No neurological problem? | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes: •Hemorrhage •Hypotension •Hypoxia •Pulmonary embolism •Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm •Ventricular arrhythmia •Arrhythmia •Medication •Orthostatic hypotension •Vagal stimulation •Vertebrobasilar insufficiency | Causes: •Brain damage •Congenital abnormalities •Stroke •Infection •Genetic syndromes •Brain tumor •Epilepsy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peripheral | Central | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BPPV Vestibular neuritis HSV oticus Meniere disease Labyrinthine concussion Perilymphatic fistula Semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome Vestibular paroxysma Cogan syndrome Vestibular schwannoma Otitis media Aminoglycoside toxicity Recurrent vestibulopathy | Vestibular migraine Epileptic vertigo Multiple sclerosis Brain tumors Crebellar infarction/hemorrhage Brain stem ischemia Chiari malformation Parkinson | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hyperventilation Psychiatric symptoms | Balance problem | Sweating Tunnel Vision Nausea Heart palpitations Abdominal discomfort Slurred speech | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Psychogenic dizziness | Dysequilibrium | Presyncope | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dizziness which is not characterized by true vertigo and it can be replicated by hyperventilation and psychiatric symptoms that usually precede its onset. | Impaired sense or absence of balance or equilibrioception that primarily occurs during standing or walking | Feeling of lightheadedness that can lead to syncope | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Causes: •Alcohol dependence •Conversion disorder •Fibromyalgia •Generalized anxiety •Hyperventilation •Major depression •Panic disorder | Causes: •Arrhythmia •Asthma exacerbation •Cerebellar hemorrhage •Compartment syndrome •Endophthalmitis •Epilepsy •Hypoglycemia •Organophosphates •Cerebellar disorders •Gait abnormality •Hypoglycemia •Paralysis •Peripheral neuropathy •Vestibular disorders •Visual impairment | Causes: •Hemorrhage •Hypotension •Hypoxia •Pulmonary embolism •Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm •Ventricular arrhythmia •Arrhythmia •Medication •Orthostatic hypotension •Vagal stimulation •Vertebrobasilar insufficiency | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- ↑ Lee SH, Kim JS (June 2010). "Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo". J Clin Neurol. 6 (2): 51–63. doi:10.3988/jcn.2010.6.2.51. PMC 2895225. PMID 20607044.
- ↑ Chang MB, Bath AP, Rutka JA (October 2001). "Are all atypical positional nystagmus patterns reflective of central pathology?". J Otolaryngol. 30 (5): 280–2. PMID 11771020.
- ↑ Dorresteijn PM, Ipenburg NA, Murphy KJ, Smit M, van Vulpen JK, Wegner I, Stegeman I, Grolman W (June 2014). "Rapid Systematic Review of Normal Audiometry Results as a Predictor for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo". Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 150 (6): 919–24. doi:10.1177/0194599814527233. PMID 24642523.
- ↑ Dieterich M, Staab JP, Brandt T (2016). "Functional (psychogenic) dizziness". Handb Clin Neurol. 139: 447–468. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-801772-2.00037-0. PMID 27719862.
- ↑ Cheshire WP (April 2017). "Syncope". Continuum (Minneap Minn). 23 (2, Selected Topics in Outpatient Neurology): 335–358. doi:10.1212/CON.0000000000000444. PMID 28375909.
- ↑ Chan, Yvonne (2009). "Differential diagnosis of dizziness". Current Opinion in Otolaryngology & Head and Neck Surgery. 17 (3): 200–203. doi:10.1097/MOO.0b013e32832b2594. ISSN 1068-9508.
- ↑ Brandt, T (2001). "NOSOLOGICAL ENTITIES?: Cervical vertigo". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 71 (1): 8–12. doi:10.1136/jnnp.71.1.8. ISSN 0022-3050.