Ezetimibe adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Sheng Shi, M.D. [2]
Adverse Reactions
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Liver enzyme abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Rhabdomyolysis]] and myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Monotherapy Studies: In the ZETIA controlled clinical trials database (placebo-controlled) of 2396 patients with a median treatment duration of 12 weeks (range 0 to 39 weeks), 3.3% of patients on ZETIA and 2.9% of patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions in the group of patients treated with ZETIA that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo were:
- Arthralgia (0.3%)
- Dizziness (0.2%)
- Gamma-glutamyltransferase increased (0.2%)
The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) in the ZETIA monotherapy controlled clinical trial database of 2396 patients were: upper respiratory tract infection (4.3%), diarrhea (4.1%), arthralgia (3.0%), sinusitis (2.8%), and pain in extremity (2.7%).
statin Coadministration Studies: In the ZETIA + statin controlled clinical trials database of 11,308 patients with a median treatment duration of 8 weeks (range 0 to 112 weeks), 4.0% of patients on ZETIA + statin and 3.3% of patients on statin alone discontinued due to adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions in the group of patients treated with ZETIA + statin that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than statin alone were:
- Alanine aminotransferase increased (0.6%)
- Myalgia (0.5%)
- Fatigue, aspartate aminotransferase increased, headache, and pain in extremity (each at 0.2%)
The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥2% and greater than statin alone) in the ZETIA + statin controlled clinical trial database of 11,308 patients were: nasopharyngitis (3.7%), myalgia (3.2%), upper respiratory tract infection (2.9%), arthralgia (2.6%) and diarrhea (2.5%).
Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Monotherapy
In 10 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials, 2396 patients with primary hyperlipidemia (age range 9–86 years, 50% women, 90% Caucasians, 5% Blacks, 3% Hispanics, 2% Asians) and elevated LDL-C were treated with ZETIA 10 mg/day for a median treatment duration of 12 weeks (range 0 to 39 weeks).
Adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ZETIA and at an incidence greater than placebo in placebo-controlled studies of ZETIA, regardless of causality assessment, are shown in Table 1.
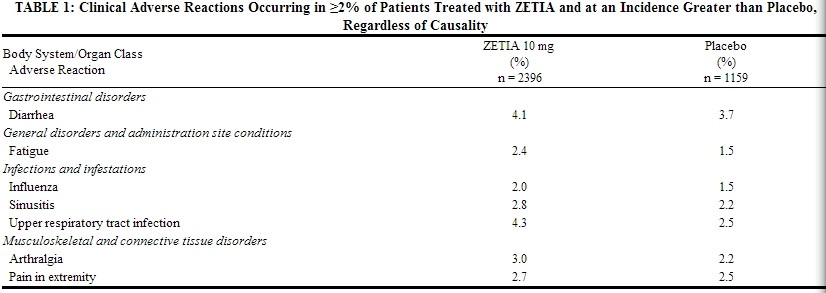 |
Combination with a statin
In 28 double-blind, controlled (placebo or active-controlled) clinical trials, 11,308 patients with primary hyperlipidemia (age range 10–93 years, 48% women, 85% Caucasians, 7% Blacks, 4% Hispanics, 3% Asians) and elevated LDL-C were treated with ZETIA 10 mg/day concurrently with or added to on-going statin therapy for a median treatment duration of 8 weeks (range 0 to 112 weeks).
The incidence of consecutive increased transaminases (≥3 × ULN) was higher in patients receiving ZETIA administered with statins (1.3%) than in patients treated with statins alone (0.4%). [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2).]
Clinical adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ZETIA + statin and at an incidence greater than statin, regardless of causality assessment, are shown inTable 2.
 |
Combination with Fenofibrate
This clinical study involving 625 patients with mixed dyslipidemia (age range 20–76 years, 44% women, 79% Caucasians, 0.1% Blacks, 11% Hispanics, 5% Asians) treated for up to 12 weeks and 576 patients treated for up to an additional 48 weeks evaluated coadministration of ZETIA and Fenofibrate. This study was not designed to compare treatment groups for infrequent events. Incidence rates (95% CI) for clinically important elevations (≥3 × ULN, consecutive) in hepatic transaminase levels were 4.5% (1.9, 8.8) and 2.7% (1.2, 5.4) for Fenofibrate monotherapy (n=188) and ZETIA coadministered with Fenofibrate (n=183), respectively, adjusted for treatment exposure. Corresponding incidence rates for cholecystectomy were 0.6% (95% CI: 0.0%, 3.1%) and 1.7% (95% CI: 0.6%, 4.0%) for Fenofibrate monotherapy and ZETIA coadministered with Fenofibrate, respectively [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. The numbers of patients exposed to coadministration therapy as well as Fenofibrate and ezetimibe monotherapy were inadequate to assess gallbladder disease risk. There were no CPK elevations >10 × ULN in any of the treatment groups.
Post-Marketing Experience
Because the reactions below are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ZETIA:
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria; erythema multiforme; arthralgia; myalgia; elevated creatine phosphokinase; myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis]] [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]; elevations in liver transaminases; hepatitis; abdominal pain; thrombocytopenia; pancreatitis; nausea; dizziness; paresthesia; depression; headache; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis.[1]
References
- ↑ "ZETIA (EZETIMIBE) TABLET [MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP.]". Retrieved 11 February 2014.