Axicabtagene ciloleucel
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Yashasvi Aryaputra[2];
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Black Box Warning
|
CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME and NEUROLOGIC TOXICITIES
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Overview
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is a Acetylcholine release inhibitor, Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the (type of indication of drug) of a list of indications, separated by commas.. There is a Black Box Warning for this drug as shown here. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
- None
Warnings
|
CYTOKINE RELEASE SYNDROME and NEUROLOGIC TOXICITIES
See full prescribing information for complete Boxed Warning.
|
Conidition 1
(Description)
Conidition 2
(Description)
Conidition 3
(Description)
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
There is limited information regarding Axicabtagene ciloleucel Drug Interactions in the drug label.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- There are no available data with YESCARTA use in pregnant women. No animal reproductive and developmental toxicity studies have been conducted with YESCARTA to assess whether it can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. It is not known if YESCARTA has the potential to be transferred to the fetus. Based on the mechanism of action, if the transduced cells cross the placenta, they may cause fetal toxicity, including B-cell lymphocytopenia. Therefore, YESCARTA is not recommended for women who are pregnant, and pregnancy after YESCARTA infusion should be discussed with the treating physician.
- In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Axicabtagene ciloleucel in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- There is no information regarding the presence of YESCARTA in human milk, the effect on the breastfed infant, and the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for YESCARTA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from YESCARTA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and efficacy of YESCARTA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
- Clinical trials of YESCARTA did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently or have different safety outcomes as compared to younger patients.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
Pregnancy Testing
- Pregnancy status of females with reproductive potential should be verified. Sexually-active females of reproductive potential should have a pregnancy test prior to starting treatment with YESCARTA.
Contraception
- See the prescribing information for fludarabine and cyclophosphamide for information on the need for effective contraception in patients who receive the lymphodepleting chemotherapy.
- There are insufficient exposure data to provide a recommendation concerning duration of contraception following treatment with YESCARTA.
Infertility
- There are no data on the effect of YESCARTA on fertility.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Axicabtagene ciloleucel in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Preparing Patient for YESCARTA Infusion
- Confirm availability of YESCARTA prior to starting the lymphodepleting regimen.
Pre-treatment
- Administer a lymphodepleting chemotherapy regimen of cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m2 intravenously and fludarabine 30 mg/m2 intravenously on the fifth, fourth, and third day before infusion of YESCARTA.
Premedication
- Administer acetaminophen 650 mg PO and diphenhydramine 12.5 mg intravenously or PO approximately 1 hour before YESCARTA infusion.
- Avoid prophylactic use of systemic corticosteroids, as it may interfere with the activity of YESCARTA.
Preparation of YESCARTA for Infusion
- Coordinate the timing of YESCARTA thaw and infusion. Confirm the infusion time in advance, and adjust the start time of YESCARTA thaw such that it will be available for infusion when the patient is ready.
- Confirm patient identity: Prior to YESCARTA preparation, match the patient’s identity with the patient identifiers on the YESCARTA cassette.
- Do not remove the YESCARTA product bag from the cassette if the information on the patient-specific label does not match the intended patient.
- Once patient identification is confirmed, remove the YESCARTA product bag from the cassette and check that the patient information on the cassette label matches the bag label.
- Inspect the product bag for any breaches of container integrity such as breaks or cracks before thawing. If the bag is compromised, follow the local guidelines (or call Kite at 1-844-454-KITE).
- Place the infusion bag inside a second sterile bag per local guidelines.
- Thaw YESCARTA at approximately 37°C using either a water bath or dry thaw method until there is no visible ice in the infusion bag. Gently mix the contents of the bag to disperse clumps of cellular material. If visible cell clumps remain continue to gently mix the contents of the bag. Small clumps of cellular material should disperse with gentle manual mixing. Do not wash, spin down, and/or re-suspend YESCARTA in new media prior to infusion.
- Once thawed, YESCARTA may be stored at room temperature (20°C to 25°C) for up to 3 hours.
Administration
- YESCARTA is for autologous use only. The patient’s identity must match the patient identifiers on the YESCARTA cassette and infusion bag. Do not infuse YESCARTA if the information on the patient-specific label does not match the intended patient.
- For autologous use only.
- Ensure that tocilizumab and emergency equipment are available prior to infusion and during the recovery period.
- Do NOT use a leukodepleting filter.
- Central venous access is recommended for the infusion of YESCARTA.
- Confirm the patient’s identity matches the patient identifiers on the YESCARTA product bag.
- Prime the tubing with normal saline prior to infusion.
- Infuse the entire contents of the YESCARTA bag within 30 minutes by either gravity or a peristaltic pump. YESCARTA is stable at room temperature for up to 3 hours after thaw.
- Gently agitate the product bag during YESCARTA infusion to prevent cell clumping.
- After the entire content of the product bag is infused, rinse the tubing with normal saline at the same infusion rate to ensure all product is delivered.
- YESCARTA contains human blood cells that are genetically modified with replication incompetent retroviral vector. Follow universal precautions and local biosafety guidelines for handling and disposal to avoid potential transmission of infectious diseases.
Monitoring
- Administer YESCARTA at a certified healthcare facility.
- Monitor patients at least daily for 7 days at the certified healthcare facility following infusion for signs and symptoms of CRS and neurologic toxicities.
- Instruct patients to remain within proximity of the certified healthcare facility for at least 4 weeks following infusion.
Management of Severe Adverse Reactions
Cytokine Release Syndrome
- Identify CRS based on clinical presentation. Evaluate for and treat other causes of fever, hypoxia, and hypotension. If CRS is suspected, manage according to the recommendations in Table 1. Patients who experience Grade 2 or higher CRS (e.g., hypotension, not responsive to fluids, or hypoxia requiring supplemental oxygenation) should be monitored with continuous cardiac telemetry and pulse oximetry. For patients experiencing severe CRS, consider performing an echocardiogram to assess cardiac function. For severe or life-threatening CRS, consider intensive care supportive therapy.
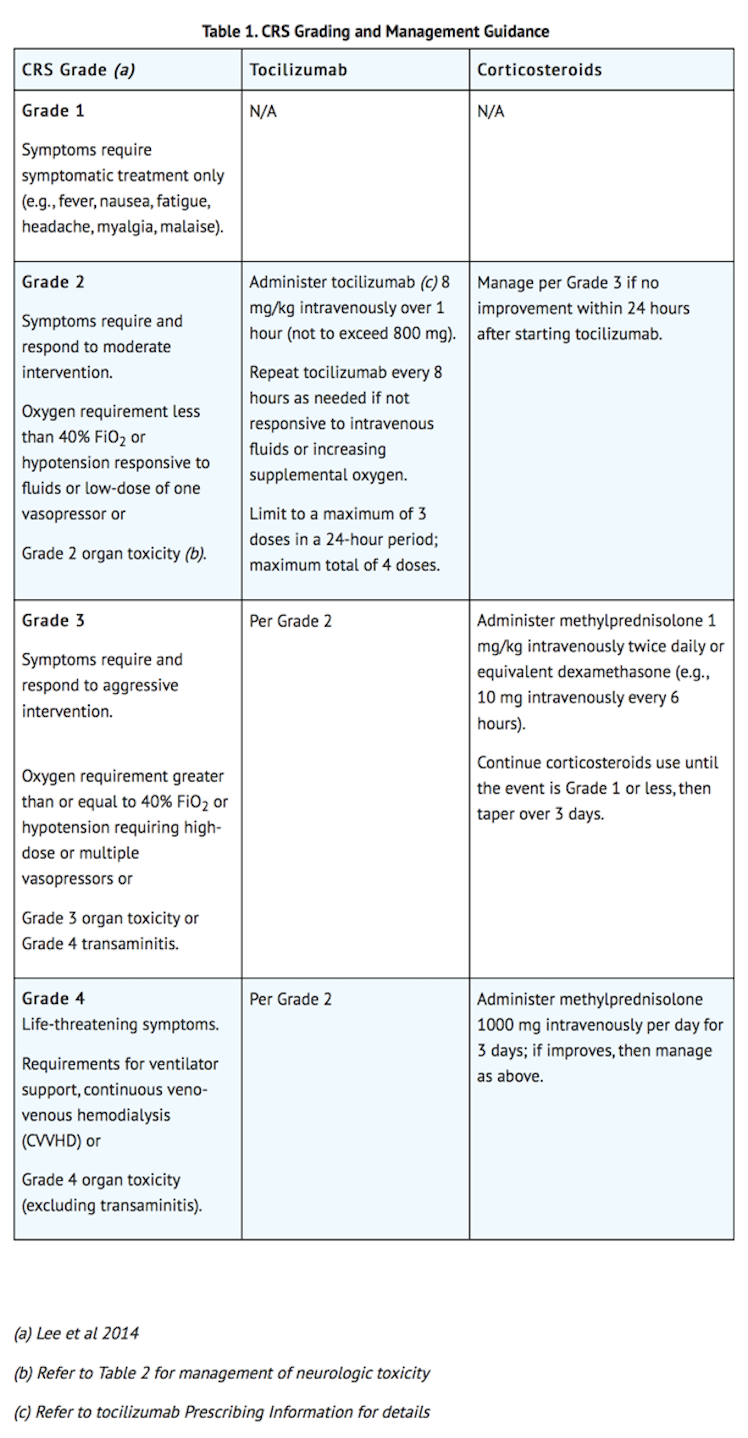
Neurologic Toxicity
- Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neurologic toxicities (Table 2). Rule out other causes of neurologic symptoms. Patients who experience Grade 2 or higher neurologic toxicities should be monitored with continuous cardiac telemetry and pulse oximetry. Provide intensive care supportive therapy for severe or life threatening neurologic toxicities. Consider non-sedating, anti-seizure medicines (e.g., levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis for any Grade 2 or higher neurologic toxicities.
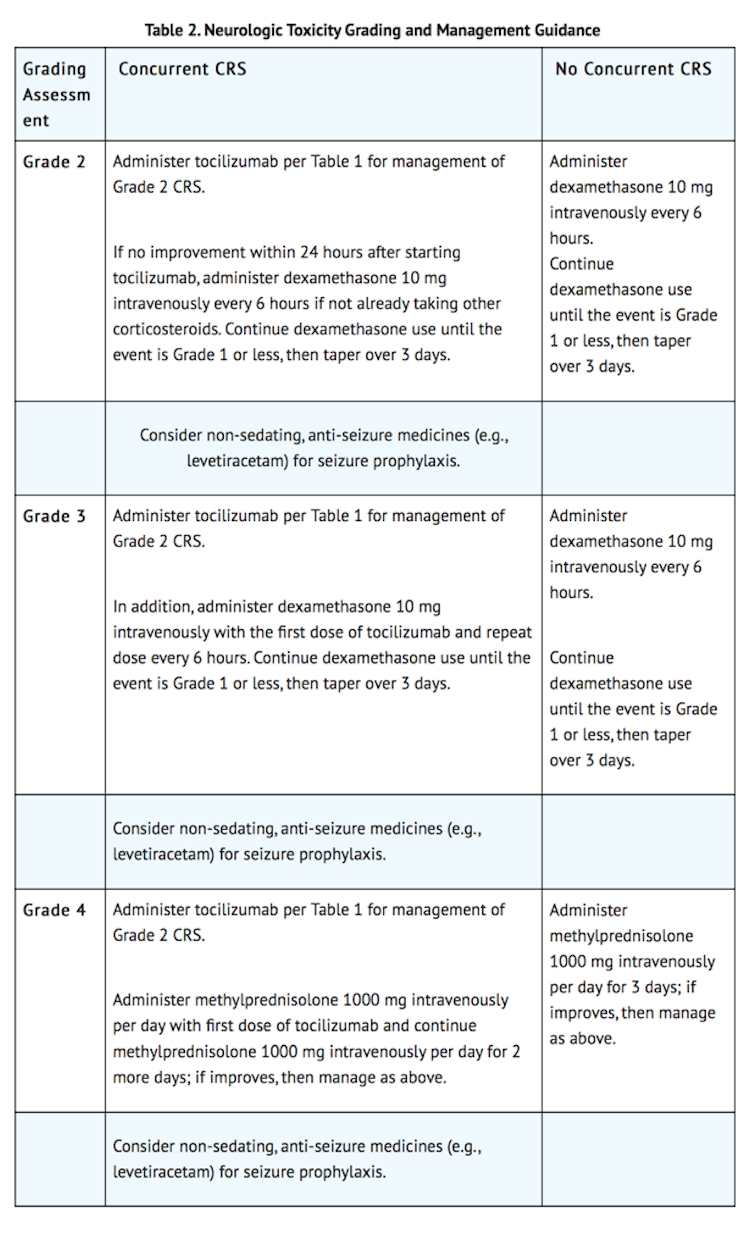
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Axicabtagene ciloleucel and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Axicabtagene ciloleucel overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
Axicabtagene ciloleucel
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | None |
| PubChem | ? |
| DrugBank | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status |
[[Prescription drug|Template:Unicode-only]](US) |
| Routes | Intravenous injection |
Mechanism of Action
- YESCARTA, a CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy, binds to CD19-expressing cancer cells and normal B cells. Studies demonstrated that following anti-CD19 CAR T cell engagement with CD19-expressing target cells, the CD28 and CD3-zeta co-stimulatory domains activate downstream signaling cascades that lead to T cell activation, proliferation, acquisition of effector functions and secretion of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This sequence of events leads to killing of CD19-expressing cells.
Structure
There is limited information regarding Axicabtagene ciloleucel Structure in the drug label.
Pharmacodynamics
- After YESCARTA infusion, pharmacodynamic responses were evaluated over a 4-week interval by measuring transient elevation of cytokines, chemokines and other molecules in blood. Levels of cytokines and chemokines such as IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-15, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and sIL2Rα were analyzed. Peak elevation was observed within the first 14 days after infusion, and levels generally returned to baseline within 28 days.
- Due to the on-target effect of YESCARTA, a period of B-cell aplasia is expected.
Pharmacokinetics
- Following infusion of YESCARTA, anti-CD19 CAR T cells exhibited an initial rapid expansion followed by a decline to near baseline levels by 3 months. Peak levels of anti-CD19 CAR T cells occurred within the first 7-14 days after YESCARTA infusion.
- Age (range: 23 – 76 years) and gender had no significant impact on AUC Day 0 - 28 and Cmax of YESCARTA.
- The number of anti-CD19 CAR T cells in blood was positively associated with objective response [complete remission (CR) or partial remission (PR)]. The median anti-CD19 CAR T cell Cmax levels in responders (n=73) were 205% higher compared to the corresponding level in nonresponders (n=23) (43.6 cells/μL vs 21.2 cells/μL). Median AUC Day 0 - 28 in responding patients (n=73) was 251% of the corresponding level in nonresponders (n=23) (557.1 days × cells/μL vs. 222.0 days × cells/μL).
- Some patients required tocilizumab and corticosteroids for management of CRS and neurologic toxicities. Patients treated with tocilizumab (n=44) had 262% and 232% higher anti-CD19 CAR T cells as measured by AUC Day 0 - 28 and Cmax respectively, as compared to patients who did not receive tocilizumab (n=57). Similarly, patients that received corticosteroids (n=26) had 217% and 155% higher AUC Day 0 - 28 and Cmax compared to patients who did not receive corticosteroids (n=75).
- Hepatic and renal impairment studies of YESCARTA were not conducted.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- No carcinogenicity or genotoxicity studies have been conducted with YESCARTA. No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effects of YESCARTA on fertility.
Clinical Studies
Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- A single-arm, open-label, multicenter trial evaluated the efficacy of a single infusion of YESCARTA in adult patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Eligible patients had refractory disease to the most recent therapy or relapse within 1 year after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). The study excluded patients with prior allogeneic HSCT, any history of central nervous system lymphoma, ECOG performance status of 2 or greater, absolute lymphocyte count less than 100/µL, creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/min, hepatic transaminases more than 2.5 times the upper limit of normal, cardiac ejection fraction less than 50%, or active serious infection.
- Following lymphodepleting chemotherapy, YESCARTA was administered as a single intravenous infusion at a target dose of 2 × 106 CAR-positive viable T cells/kg (maximum permitted dose: 2 × 108 cells). The lymphodepleting regimen consisted of cyclophosphamide 500 mg/m2 intravenously and fludarabine 30 mg/m2 intravenously, both given on the fifth, fourth, and third day before YESCARTA. Bridging chemotherapy between leukapheresis and lymphodepleting chemotherapy was not permitted. All patients were hospitalized for YESCARTA infusion and for a minimum of 7 days afterward.
- Of 111 patients who underwent leukapheresis, 101 received YESCARTA. Of the patients treated, the median age was 58 years (range: 23 to 76), 67% were male, and 89% were white. Most (76%) had DLBCL, 16% had transformed follicular lymphoma, and 8% had primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. The median number of prior therapies was 3 (range: 1 to 10), 77% of the patients had refractory disease to a second or greater line of therapy, and 21% had relapsed within 1 year of autologous HSCT.
- One out of 111 patients did not receive the product due to manufacturing failure. Nine other patients were not treated, primarily due to progressive disease or serious adverse reactions following leukapheresis. The median time from leukapheresis to product delivery was 17 days (range: 14 to 51 days), and the median time from leukapheresis to infusion was 24 days (range: 16 to 73 days). The median dose was 2.0 × 106 CAR-positive viable T cells/kg (range: 1.1 to 2.2 × 106 cells/kg).
- Efficacy was established on the basis of complete remission (CR) rate and duration of response (DOR), as determined by an independent review committee (Table 5 and Table 6). The median time to response was 0.9 months (range: 0.8 to 6.2 months). Response durations were longer in patients who achieved CR, as compared to patients with a best response of partial remission (PR) (Table 6). Of the 52 patients who achieved CR, 14 initially had stable disease (7 patients) or PR (7 patients), with a median time to improvement of 2.1 months (range: 1.6 to 5.3 months).
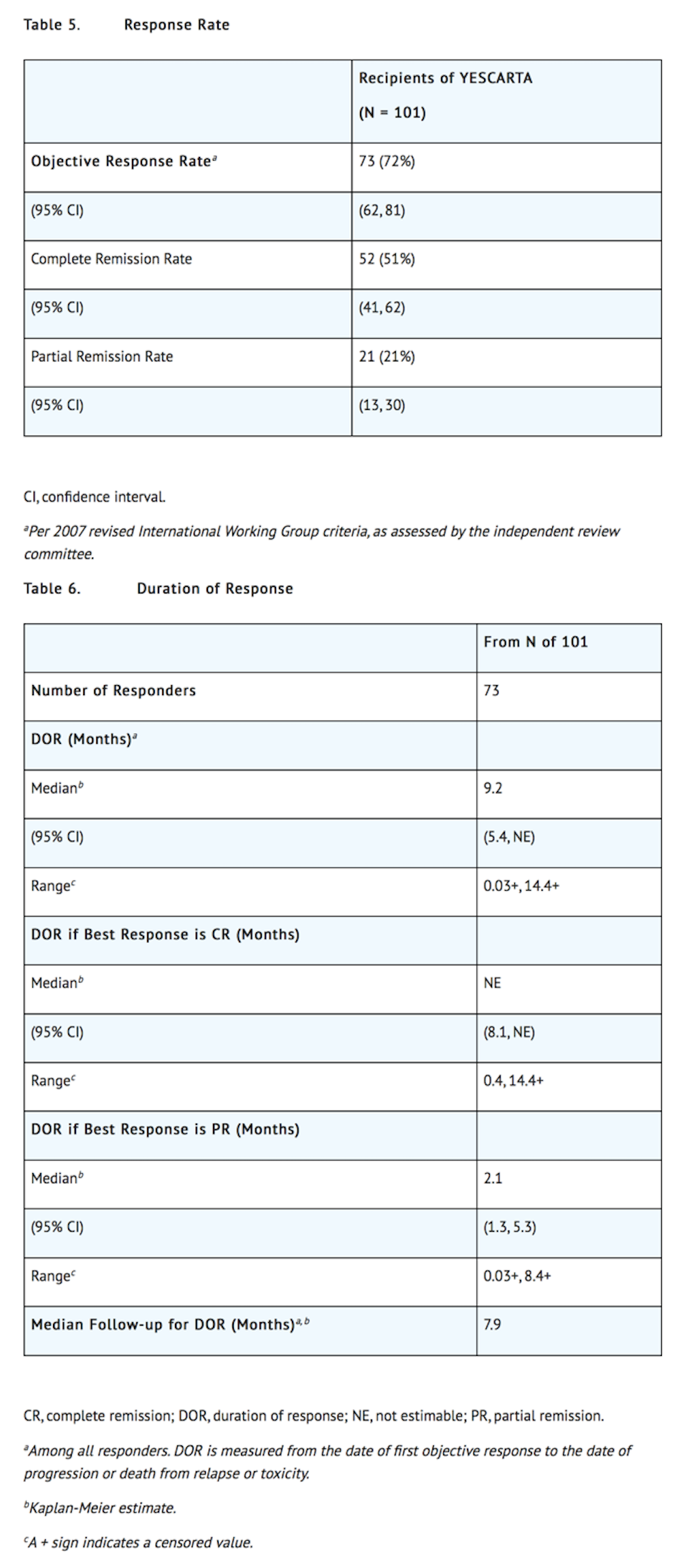
How Supplied
- YESCARTA is supplied in an infusion bag (NDC 71287-119-01) containing approximately 68 mL of frozen suspension of genetically modified autologous T cells in 5% DMSO and 2.5% albumin (human).
Storage
- Each YESCARTA infusion bag is individually packed in a metal cassette (NDC 71287-119-02). YESCARTA is stored in the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen and supplied in a liquid nitrogen dry shipper.
- Match the identity of the patient with the patient identifiers on the cassette and infusion bag upon receipt.
- Store YESCARTA frozen in the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen (less than or equal to minus 150ºC).
- Thaw before using.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Axicabtagene ciloleucel |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

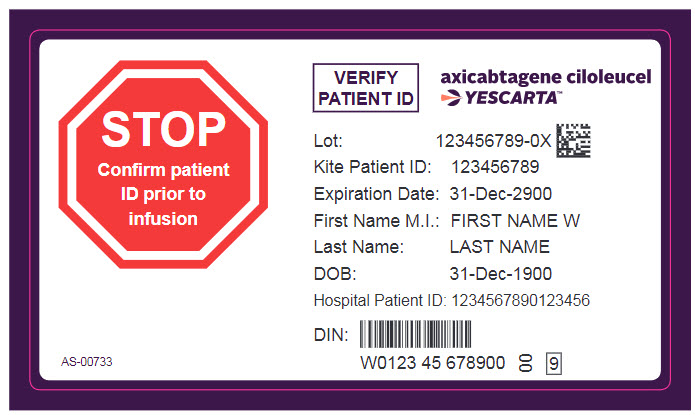

{{#ask: Label Page::Axicabtagene ciloleucel |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Ensure that patients understand the risk of manufacturing failure (1% in clinical trial). In case of a manufacturing failure, a second manufacturing of YESCARTA may be attempted. In addition, while the patient awaits the product, additional chemotherapy (not the lymphodepletion) may be necessary and may increase the risk of adverse events during the pre-infusion period.
- Advise patients to seek immediate attention for any of the following:
- Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) - Signs or symptoms associated with CRS including fever, chills, fatigue, tachycardia, nausea, hypoxia, and hypotension.
- Neurologic Toxicities – Signs or symptoms associated with neurologic events including encephalopathy, seizures, changes in level of consciousness, speech disorders, tremors, and confusion.
- Serious Infections - Signs or symptoms associated with infection.
- Prolonged Cytopenia - Signs or symptoms associated with bone marrow suppression including neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, or febrile neutropenia.
- Advise patients for the need to:
- Refrain from driving or operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery after YESCARTA infusion until at least 8 weeks after infusion.
- Have periodic monitoring of blood counts.
- Contact Kite at 1-844-454-KITE (5483) if they are diagnosed with a secondary malignancy.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Axicabtagene ciloleucel interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor regarding the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- Yescarta
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Axicabtagene ciloleucel Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.