Diabetes mellitus type 2 physical examination: Difference between revisions
m (Bot: Removing from Primary care) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{CMG}};{{AE}}{{MehdiP}} | {{CMG}};{{AE}}{{MehdiP}} | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
Patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 often have normal physical examination findings unless complications develop in these patients. Common physical examination findings include pigmented skin patches and [[acanthosis nigricans]]. | Patients with [[diabetes mellitus type 2]] often have normal physical examination findings unless [[Complication (medicine)|complications]] develop in these patients. Common physical examination findings include pigmented skin patches and [[acanthosis nigricans]]. | ||
==Physical examination== | ==Physical examination== | ||
Patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 usually have normal physical examination findings unless complications develop in these patients.<ref name="pmid22873534">{{cite journal |vauthors=Inzucchi SE |title=Clinical practice. Diagnosis of diabetes |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=367 |issue=6 |pages=542–50 |year=2012 |pmid=22873534 |doi=10.1056/NEJMcp1103643 |url=}}</ref> | |||
* Patients with [[diabetes mellitus type 2]] usually have normal physical examination findings unless [[Complication (medicine)|complications]] develop in these patients.<ref name="pmid22873534">{{cite journal |vauthors=Inzucchi SE |title=Clinical practice. Diagnosis of diabetes |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=367 |issue=6 |pages=542–50 |year=2012 |pmid=22873534 |doi=10.1056/NEJMcp1103643 |url=}}</ref> | |||
===Appearance of the patient=== | ===Appearance of the patient=== | ||
Patients are usually well-appearing. | Patients are usually well-appearing. | ||
===Vital signs=== | ===Vital signs=== | ||
[[Hypertension|High blood pressure]] with normal pulse pressure may be seen. | |||
* [[Hypertension|High blood pressure]] with normal [[pulse pressure]] may be seen. | |||
===Skin=== | ===Skin=== | ||
*[[Acanthosis nigricans]] is suggestive of [[insulin resistance]]. | *[[Acanthosis nigricans]] is suggestive of [[insulin resistance]]. | ||
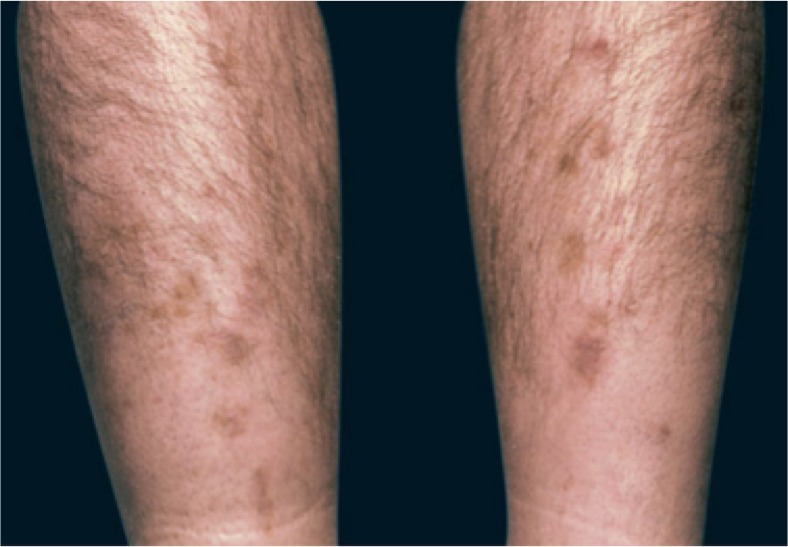
*Diabetic dermopathy (DD), one of the skin findings of [[diabetes mellitus]], appears as dull red [[Papule|papules]] which cause bilateral involvements on bony prominences. Nevertheless, involvement of pretibial region is the most common presentation, described as [[Pigmented lesions|pigmented]] pretibial patches.<ref name="pmid294659263">{{cite journal| author=Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A | display-authors=etal| title=Endotext | journal= | year= 2000 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=29465926 | doi= | pmc= | url= }}</ref> | |||
[[File:Diabetic Dermopathy.jpg|alt=Diabetic Dermopathy (DD)|center|thumb|530x530px|Diabetic Dermopathy (DD)<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK481900/|title=Skin Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus case courtesy by Jordan Rosen, BS|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref> which is appeared as pretibial patches]] | |||
<br /> | |||
*Skin thickening has been frequently seen on feet and hands. Skin appears waxy and [[Edema|edematous]].<ref name="pmid294659262">{{cite journal| author=Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A | display-authors=etal| title=Endotext | journal= | year= 2000 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=29465926 | doi= | pmc= | url= }}</ref> | |||
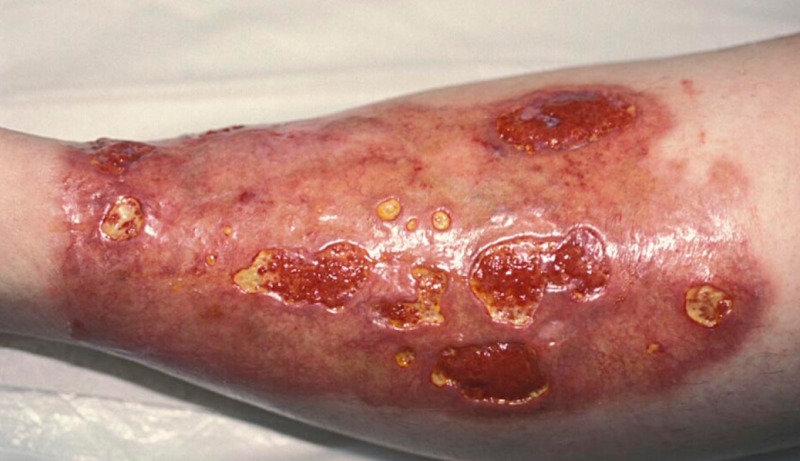
*[[Necrobiosis lipoidica]] ([[Necrobiosis lipoidica|NL]]): Although, it is usually found after the time of [[diagnosis]], still 14% to 24% of cases of [[Necrobiosis lipoidica|NL]] may occur before or at the time of [[diagnosis]].<ref name="pmid29465926">{{cite journal| author=Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A | display-authors=etal| title=Endotext | journal= | year= 2000 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=29465926 | doi= | pmc= | url= }}</ref> | |||
[[File:Necrobiosis lipoidica (NL).jpg|center|thumb|573x573px|[[Necrobiosis lipoidica]] ([[Necrobiosis lipoidica|NL]]) <ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK481900/|title=Skin Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus case courtesy by Jordan Rosen, BS|last=|first=|date=|website=|archive-url=|archive-date=|dead-url=|access-date=}}</ref>]] | |||
===HEENT=== | ===HEENT=== | ||
[[Periorbital edema]] is a finding in patients with [[diabetic nephropathy]]. | [[Periorbital edema]] is a finding in patients with [[diabetic nephropathy]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 6 August 2020
|
Diabetes mellitus type 2 Microchapters |
|
Differentiating Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 from other Diseases |
|
Diagnosis |
|
Treatment |
|
Medical therapy |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Seyedmahdi Pahlavani, M.D. [2]
Overview
Patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 often have normal physical examination findings unless complications develop in these patients. Common physical examination findings include pigmented skin patches and acanthosis nigricans.
Physical examination
- Patients with diabetes mellitus type 2 usually have normal physical examination findings unless complications develop in these patients.[1]
Appearance of the patient
Patients are usually well-appearing.
Vital signs
- High blood pressure with normal pulse pressure may be seen.
Skin
- Acanthosis nigricans is suggestive of insulin resistance.
- Diabetic dermopathy (DD), one of the skin findings of diabetes mellitus, appears as dull red papules which cause bilateral involvements on bony prominences. Nevertheless, involvement of pretibial region is the most common presentation, described as pigmented pretibial patches.[2]
- Skin thickening has been frequently seen on feet and hands. Skin appears waxy and edematous.[4]
- Necrobiosis lipoidica (NL): Although, it is usually found after the time of diagnosis, still 14% to 24% of cases of NL may occur before or at the time of diagnosis.[5]
HEENT
Periorbital edema is a finding in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Neck
Carotid bruits may be auscultated unilaterally using the bell of the stethoscope, it is a sign suggestive of atherosclerosis.
Lungs
Normal auscultation.
Heart
Normal findings unless complications occur which may lead to heart failure with preserved EF (HFpEF).
Abdomen
Normal physical examination findings.
Extremities
Signs of pretibial myxedema or ankle edema are findings in late diabetes.
Neuromuscular
- The patient is usually oriented in person, place, and time.
- Bilateral sensory loss in the upper and lower extremities may develop as neuropathy progresses.
References
- ↑ Inzucchi SE (2012). "Clinical practice. Diagnosis of diabetes". N. Engl. J. Med. 367 (6): 542–50. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1103643. PMID 22873534.
- ↑ Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A; et al. (2000). "Endotext". PMID 29465926.
- ↑ "Skin Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus case courtesy by Jordan Rosen, BS".
- ↑ Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A; et al. (2000). "Endotext". PMID 29465926.
- ↑ Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A; et al. (2000). "Endotext". PMID 29465926.
- ↑ "Skin Manifestations of Diabetes Mellitus case courtesy by Jordan Rosen, BS".