Psoriatic arthritis x ray: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
** [[Arthritis]] mutilans: It may lead to telescoping of fingers caused by marked bony resorption and the subsequent collapse of soft tissue | ** [[Arthritis]] mutilans: It may lead to telescoping of fingers caused by marked bony resorption and the subsequent collapse of soft tissue | ||
** Asymmetrical [[sacroiliitis]] | ** Asymmetrical [[sacroiliitis]] | ||
** [[Spondylitis]]: Asymmetric paravertebral ossifications and relative sparing of the facet joints | ** [[Spondylitis]]: Asymmetric paravertebral ossifications and relative sparing of the facet [[Joint|joints]] | ||
[[File:Psoriatic-arthritis of hands.jpg|centre|thumb|Psoriatic-arthritis of hands showing pencil-in-cup deformity - By Case courtesy of Dr Jeremy Jones, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/8798">rID: 8798</a>]] | [[File:Psoriatic-arthritis of hands.jpg|centre|thumb|Psoriatic-arthritis of hands showing pencil-in-cup deformity - By Case courtesy of Dr Jeremy Jones, <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/">Radiopaedia.org</a>. From the case <a href="https://radiopaedia.org/cases/8798">rID: 8798</a>]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:16, 14 May 2018
|
Psoriatic arthritis Microchapters | |
|
Diagnosis | |
|---|---|
|
Treatment | |
|
Case Studies | |
|
Psoriatic arthritis x ray On the Web | |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Psoriatic arthritis x ray | |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Psoriatic arthritis x ray | |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Chandrakala Yannam, MD [2]
Overview
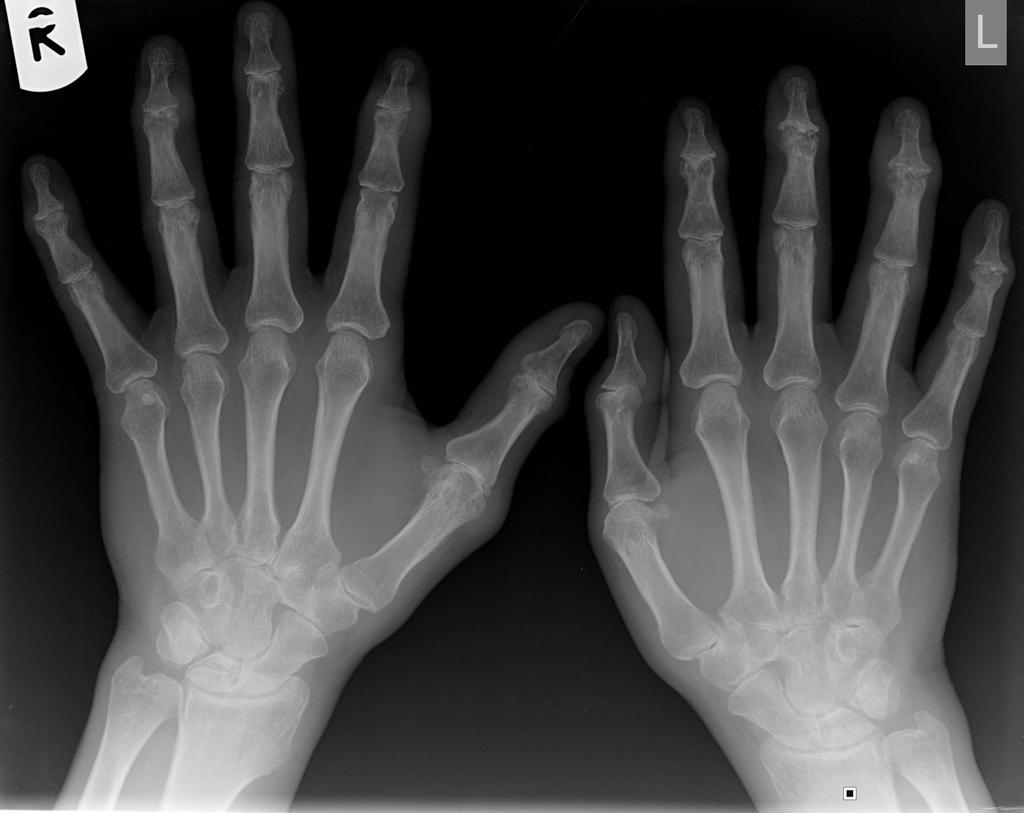
An x-ray may be helpful in the diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis. Findings on an x-ray suggestive psoriatic arthritis include bone erosion, characteristic "pencil-in-cup" deformities and proliferative changes. Psoriatic arthritis may also lead to periostitis, dactylitis, or arthritis mutilans.
X-ray of digits
- The following changes can be found on an x-ray:[1][2][3]
- Bone destructive changes including formation of subchondral cyst and erosions
- Fluffy periostitis
- Ankylosis
- Phalangeal tuft acroosteolysis
- New bone formation: Perisoteal and endosteal bone formation may result in increased bone density of an entire phalanx resulting in so called ivory phalanx.
- Pencil-in-cup deformity (osteolytic lesions) usually involving DIP joints but also affects PIP joints
- Osteolysis and ankylosis both coexists in the same joints of hands and foot
- Enthesitis
- Dactylitis (sausage digit)
- Gross finger deformity
- Arthritis mutilans: It may lead to telescoping of fingers caused by marked bony resorption and the subsequent collapse of soft tissue
- Asymmetrical sacroiliitis
- Spondylitis: Asymmetric paravertebral ossifications and relative sparing of the facet joints
References
- ↑ McGonagle D, Hermann KG, Tan AL (January 2015). "Differentiation between osteoarthritis and psoriatic arthritis: implications for pathogenesis and treatment in the biologic therapy era". Rheumatology (Oxford). 54 (1): 29–38. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keu328. PMC 4269795. PMID 25231177.
- ↑ Siannis F, Farewell VT, Cook RJ, Schentag CT, Gladman DD (April 2006). "Clinical and radiological damage in psoriatic arthritis". Ann. Rheum. Dis. 65 (4): 478–81. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.039826. PMC 1798082. PMID 16126794.
- ↑ Haddad A, Chandran V (2013). "Arthritis mutilans". Curr Rheumatol Rep. 15 (4): 321. doi:10.1007/s11926-013-0321-7. PMID 23430715.