Traveller vaccination hepatitis B: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Disease cause== | ==Disease cause== | ||
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) | [[Hepatitis B virus]] (HBV) | ||
==Transmission== | ==Transmission== | ||
May be transmitted perinatally from infected mothers to babies, through injection or transfusion of contaminated blood products or through penetration of the skin with contaminated needles. In addition, hepatitis B is frequently transmitted by sexual intercourse. | May be transmitted perinatally from infected mothers to babies, through injection or transfusion of contaminated blood products or through penetration of the skin with contaminated needles. In addition, [[hepatitis B]] is frequently transmitted by sexual intercourse. | ||
==Nature of the disease== | ==Nature of the disease== | ||
When contracted perinatally or in early childhood, the infection is rarely symptomatic but likely to develop into chronic liver disease that may develop into cirrhosis and/or cancer in the course of decades. Infection in older children and adults more often causes acute hepatitis, but rarely chronic liver disease. | When contracted perinatally or in early childhood, the infection is rarely symptomatic but likely to develop into chronic liver disease that may develop into [[cirrhosis]] and/or [[cancer]] in the course of decades. Infection in older children and adults more often causes acute hepatitis, but rarely [[chronic liver disease]]. | ||
==Geographical distribution== | ==Geographical distribution== | ||
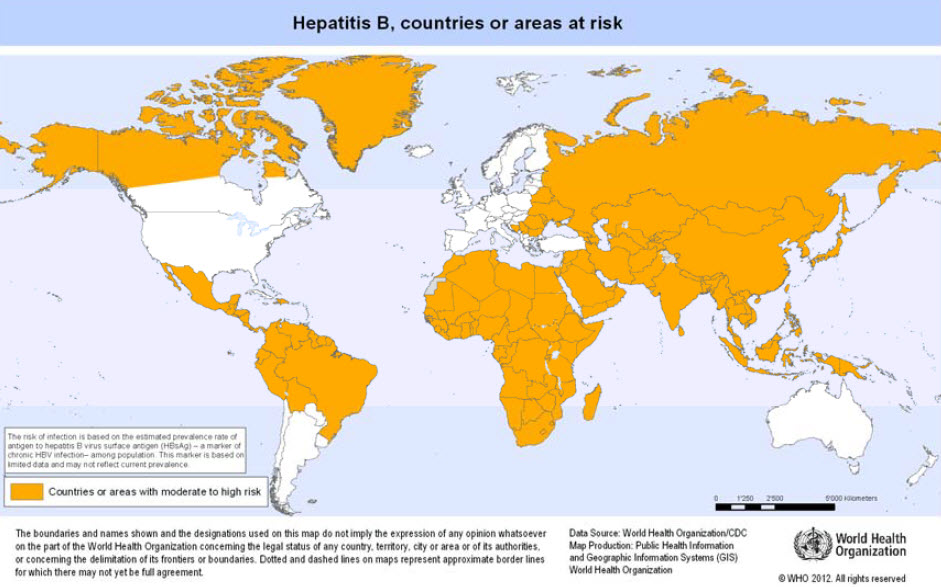
Prevalence assessments are based on presence of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) in serum. The highest prevalences are found in some African and eastern Asian countries with low coverage of hepatitis B vaccination. In well-vaccinated populations of industrialized countries the prevalence of hepatitis B is mostly low. Globally, very high prevalence rates may be found among certain sex workers and injecting drug users. | Prevalence assessments are based on presence of hepatitis B virus surface antigen ([[HBsAg]]) in serum. The highest prevalences are found in some African and eastern Asian countries with low coverage of hepatitis B vaccination. In well-vaccinated populations of industrialized countries the prevalence of [[hepatitis B]] is mostly low. Globally, very high prevalence rates may be found among certain sex workers and [[injecting drug users]]. | ||
[[image:Hepatitis B.jpg]] | [[image:Hepatitis B.jpg]] | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Risk for travellers== | ==Risk for travellers== | ||
The risk for non-immune travellers depends mainly on personal risk-taking behaviour and the prevalence of HBsAg in the concerned population. Except for nosocomial infection during emergency admission to poorly equipped health care facilities the risk of contracting hepatitis B is unlikely to be increased for the average traveller | The risk for non-immune travellers depends mainly on personal risk-taking behaviour and the prevalence of [[HBsAg]] in the concerned population. Except for nosocomial infection during emergency admission to poorly equipped health care facilities the risk of contracting hepatitis B is unlikely to be increased for the average traveller. | ||
==Vaccine== | ==Vaccine== | ||
The active ingredient of hepatitis B vaccine is HBsAg. The primary series of vaccination normally consists of one dose of monovalent vaccine at birth followed by 2 or 3 doses of monovalent or combined hepatitis B vaccine at intervals of one to several months. For older children and adults 3 doses at appropriate intervals are recommended, using a monovalent or conveniently, a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine. | The active ingredient of hepatitis B vaccine is [[HBsAg]]. The primary series of vaccination normally consists of one dose of monovalent vaccine at birth followed by 2 or 3 doses of monovalent or combined hepatitis B vaccine at intervals of one to several months. For older children and adults 3 doses at appropriate intervals are recommended, using a monovalent or conveniently, a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine. | ||
==Recommended for== | ==Recommended for== | ||
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all non-immune individuals who by choice of destination and/or lifestyle may be at risk of hepatitis B virus infection. | Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all non-immune individuals who by choice of destination and/or lifestyle may be at risk of hepatitis B virus infection. | ||
Revision as of 19:52, 20 April 2017
|
Traveler Vaccination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1];Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Usama Talib, BSc, MD [2]
Overview
Protection against hepatitis B is not specific to the needs of most travellers. In many countries hepatitis B vaccine is routinely administered in childhood. Missing vaccinations in travellers should be offered according to national recommendations.
Disease cause
Hepatitis B virus (HBV)
Transmission
May be transmitted perinatally from infected mothers to babies, through injection or transfusion of contaminated blood products or through penetration of the skin with contaminated needles. In addition, hepatitis B is frequently transmitted by sexual intercourse.
Nature of the disease
When contracted perinatally or in early childhood, the infection is rarely symptomatic but likely to develop into chronic liver disease that may develop into cirrhosis and/or cancer in the course of decades. Infection in older children and adults more often causes acute hepatitis, but rarely chronic liver disease.
Geographical distribution
Prevalence assessments are based on presence of hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) in serum. The highest prevalences are found in some African and eastern Asian countries with low coverage of hepatitis B vaccination. In well-vaccinated populations of industrialized countries the prevalence of hepatitis B is mostly low. Globally, very high prevalence rates may be found among certain sex workers and injecting drug users.
Risk for travellers
The risk for non-immune travellers depends mainly on personal risk-taking behaviour and the prevalence of HBsAg in the concerned population. Except for nosocomial infection during emergency admission to poorly equipped health care facilities the risk of contracting hepatitis B is unlikely to be increased for the average traveller.
Vaccine
The active ingredient of hepatitis B vaccine is HBsAg. The primary series of vaccination normally consists of one dose of monovalent vaccine at birth followed by 2 or 3 doses of monovalent or combined hepatitis B vaccine at intervals of one to several months. For older children and adults 3 doses at appropriate intervals are recommended, using a monovalent or conveniently, a combined hepatitis A and B vaccine.
Recommended for
Hepatitis B vaccination is recommended for all non-immune individuals who by choice of destination and/or lifestyle may be at risk of hepatitis B virus infection.