Angiomyolipoma pathophysiology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
==Pathophysiology== | ==Pathophysiology== | ||
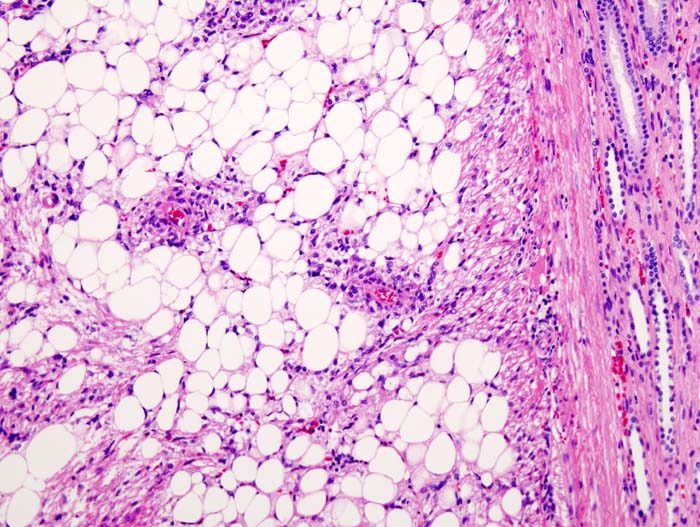
Three components of an angiomyolipoma include: | |||
*Vascular cells | |||
*Immature [[smooth muscle cells]] | |||
*Fat cells | |||
They are derived from a common [[progenitor cell]] that suffered the common second hit mutation. [[Angiomyolipoma]]s are members of the perivascular epithelioid cells tumour group (PEComas) and are composed of variable amounts of three components: | |||
*[[blood vessels]] (-angio) | |||
*plump [[spindle cells]] (-myo) | |||
*[[adipose tissue]] (-lipoma) | |||
===Pathology=== | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*Well circumscribed - uniform yellow | |||
===Variants=== | ===Variants=== | ||
*Epithelioid angiomyolipoma | |||
There is a special variant called an epithelioid angiomyolipoma, composed of more plump, epithelial looking cells, often with nuclear atypia, that have a described risk of malignant behaviour. | There is a special variant called an epithelioid angiomyolipoma, composed of more plump, epithelial looking cells, often with nuclear atypia, that have a described risk of malignant behaviour. | ||
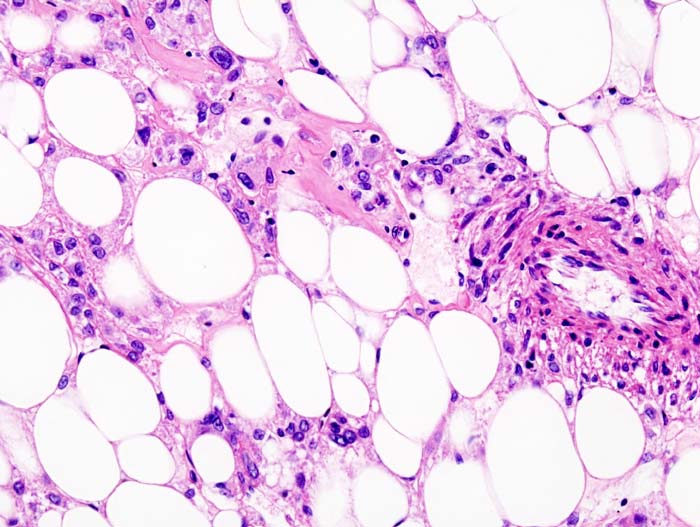
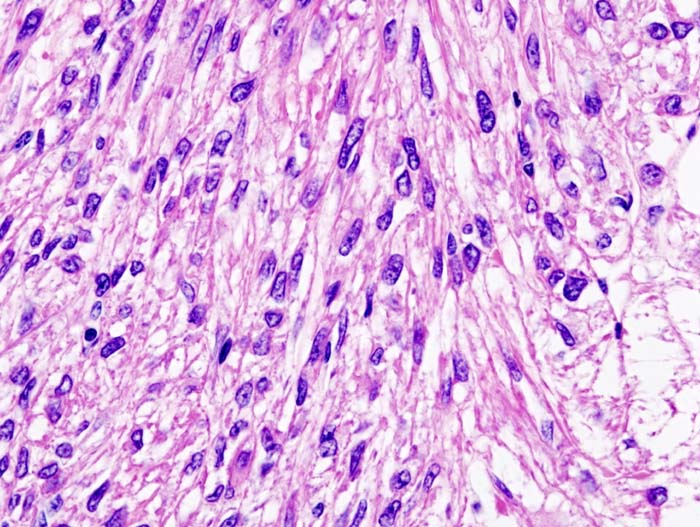
===Microscopic Pathology=== | ===Microscopic Pathology=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Smooth muscle. | *Smooth muscle. | ||
Revision as of 14:02, 23 September 2015
|
Angiomyolipoma Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Angiomyolipoma pathophysiology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Angiomyolipoma pathophysiology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Angiomyolipoma pathophysiology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2], Faizan Sheraz, M.D. [3]
Overview
Pathophysiology
Three components of an angiomyolipoma include:
- Vascular cells
- Immature smooth muscle cells
- Fat cells
They are derived from a common progenitor cell that suffered the common second hit mutation. Angiomyolipomas are members of the perivascular epithelioid cells tumour group (PEComas) and are composed of variable amounts of three components:
- blood vessels (-angio)
- plump spindle cells (-myo)
- adipose tissue (-lipoma)
Pathology
Gross
- Well circumscribed - uniform yellow
Variants
- Epithelioid angiomyolipoma
There is a special variant called an epithelioid angiomyolipoma, composed of more plump, epithelial looking cells, often with nuclear atypia, that have a described risk of malignant behaviour.
Microscopic Pathology
Features:
- Smooth muscle.
- Adipose tissue - not always present[1] - key feature.
- Abundant blood vessels.
Cytologic
Features[1]
- Nuclei - round/ovoid.
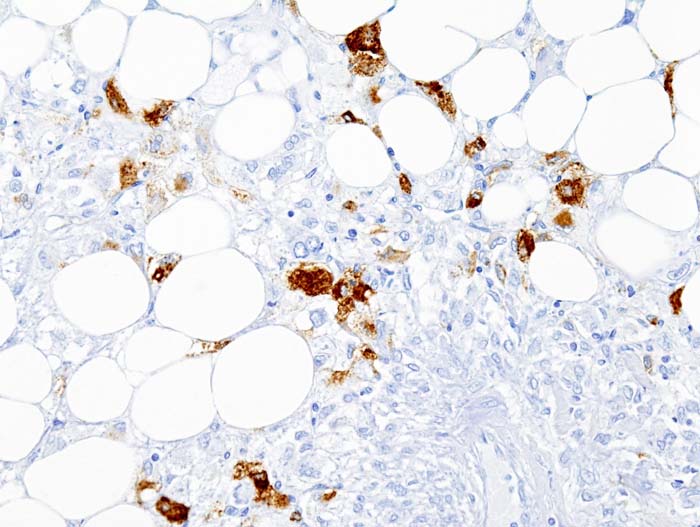
- Chromatin - bland.==IHC==
- Melanocytic markers +ve.[2]
- HMB-45 +ve in all cases (15/15).[3]
- Melan A +ve in ~87% of cases (13/15).
- Epithelial markers -ve[2], e.g. EMA and AE1/AE3.
- SMA +ve.
- CD117 +ve/-ve.
- Ki-67:[4]
- Epithelioid variant of AML +ve.
- Conventional AML -ve.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Crapanzano, JP. (2005). "Fine-needle aspiration of renal angiomyolipoma: cytological findings and diagnostic pitfalls in a series of five cases". Diagn Cytopathol. 32 (1): 53–7. doi:10.1002/dc.20179. PMID 15584043. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ 2.0 2.1 Template:Ref GUP
- ↑ Esheba, Gel S.; Esheba, Nel S. (2013). "Angiomyolipoma of the kidney: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study". J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 25 (3): 125–34. doi:10.1016/j.jnci.2013.05.002. PMID 23932749. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ooi, SM.; Vivian, JB.; Cohen, RJ. (2009). "The use of the Ki-67 marker in the pathological diagnosis of the epithelioid variant of renal angiomyolipoma". Int Urol Nephrol. 41 (3): 559–65. doi:10.1007/s11255-008-9473-1. PMID 18839327.