Sandbox:Mehrian: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (Bot: Automated text replacement (-Category:Primary care +)) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| class="infobox bordered" style="width: 15em; text-align: left; font-size: 90%; background:AliceBlue" | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="1" style="text-align:center; background:LightGrey" | | |||
'''Diabetes mellitus Main page''' | |||
|- bgcolor="LightGrey" | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
Patient Information | |||
: [[Diabetes mellitus type 1 (patient information)|Type 1]] | |||
: [[Diabetes mellitus type 2 (patient information)|Type 2]] | |||
|- | |||
[[ | ! | ||
= | |- bgcolor="Pink" | ||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Overview|Overview]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Classification|Classification]] | |||
: [[Diabetes mellitus type 1]] | |||
: [[Diabetes mellitus type 2]] | |||
: [[Gestational diabetes]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Differential diagnosis|Differential Diagnosis]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Complications|Complications]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Screening|Screening]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Diagnosis|Diagnosis]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|- bgcolor="Pink" | |||
! | |||
[[Diabetes mellitus#Prevention|Prevention]] | |||
|- | |||
! | |||
|} | |||
--------------------------- | |||
<div style="-webkit-user-select: none;"> | |||
{| class="infobox" style="position: fixed; top: 65%; right: 10px; margin: 0 0 0 0; border: 0; float: right;" | |||
|- | |||
| {{#ev:youtube|https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zucxZw069kw|350}} | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{CMG}} | |||
{{Glomerulonephritis}} | |||
==Pathophysiology== | |||
===Microscopic Pathology=== | |||
[http://www.peir.net Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
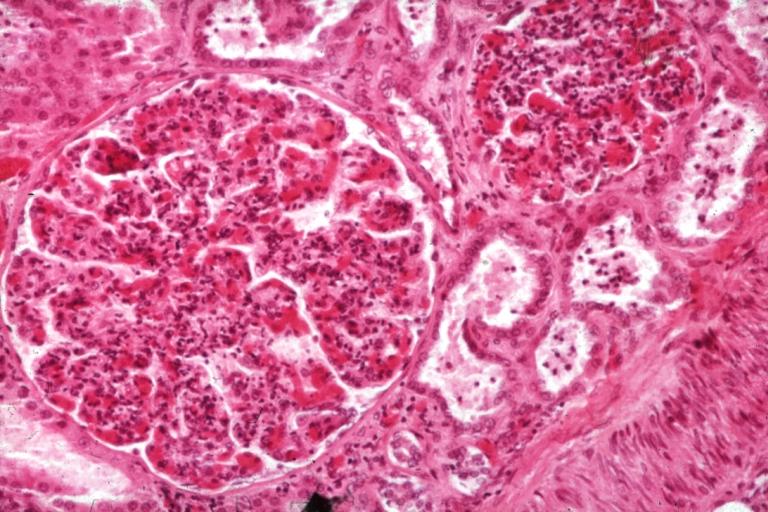
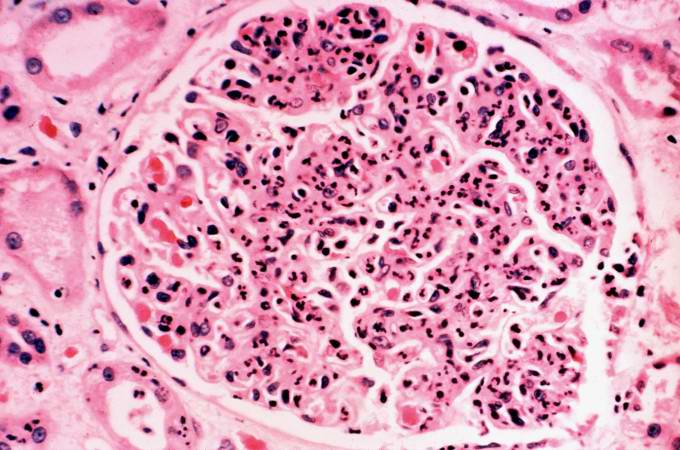
image:Acute GN 1.jpg|Glomerulonephritis: Micro H&E med mag; an excellent example of AGN with many neutrophils | |||
image:Acute GN 2.jpg|Acute Glomerulonephritis: Micro H&E high mag; an excellent example of acute exudative glomerulonephritis. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
<br> | |||
===Glomerulonephritis Videos=== | |||
====Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis==== | |||
{{#ev:youtube|CqSyj4cVZPE}} | |||
: | |||
====Chronic glomerulonephritis==== | |||
{{#ev:youtube|eA1vYarRAWo}} | |||
: | |||
===Images=== | |||
[http://www.peir.net Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology] | |||
: | |||
|- | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
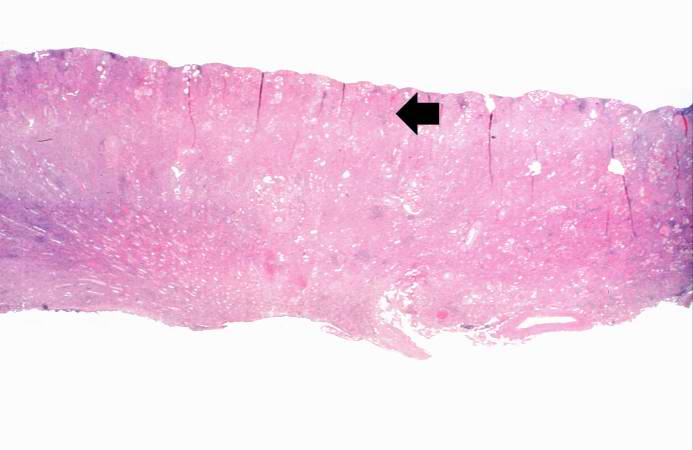
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 1.jpg|This is a low-power photomicrograph of a saggital section of end stage chronic glomerulonephritis (GN). Note the marked thinning of the cortex (arrow). | |||
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 2.jpg|This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (arrows) and glomeruli with thick basement membranes. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
<div align="left"> | |||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 3.jpg|This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (1) and glomeruli with thickened basement membranes (2). | |||
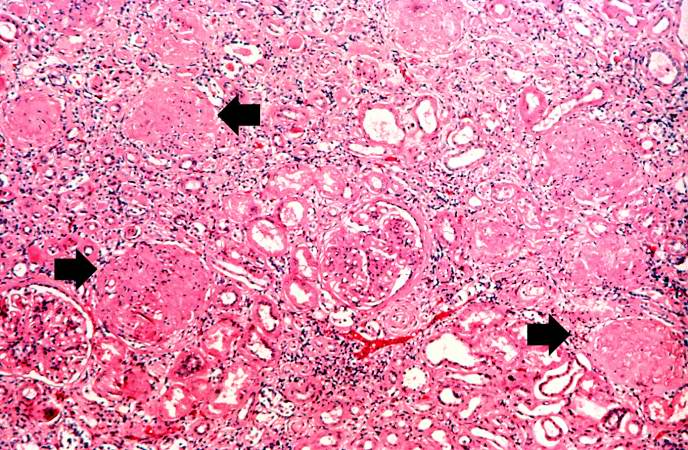
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 4.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of interstitial and vascular lesions in end stage renal disease. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
== | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
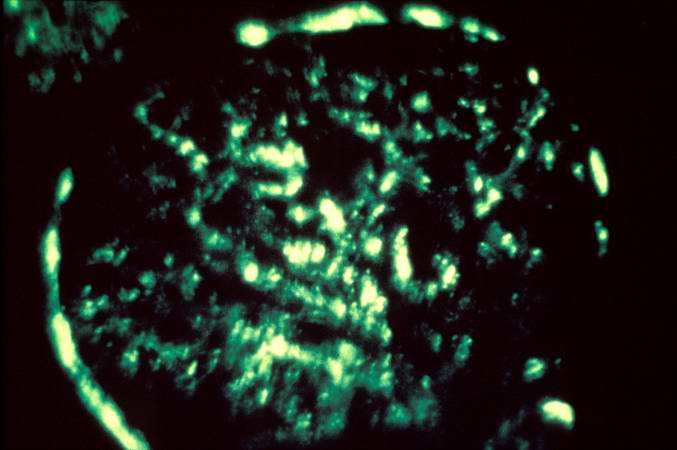
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 5.jpg|This is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of granular membranous immunofluorescence (immune complex disease). The antibody used for these studies was specific for IgG. | |||
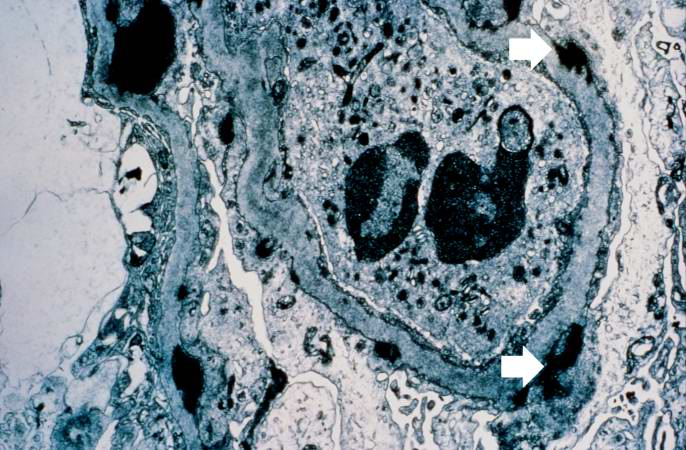
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 6.jpg|This is an electron micrograph of subepithelial granular electron dense deposits (arrows) which correspond to the granular immunofluorescence seen in the previous image. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
== | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
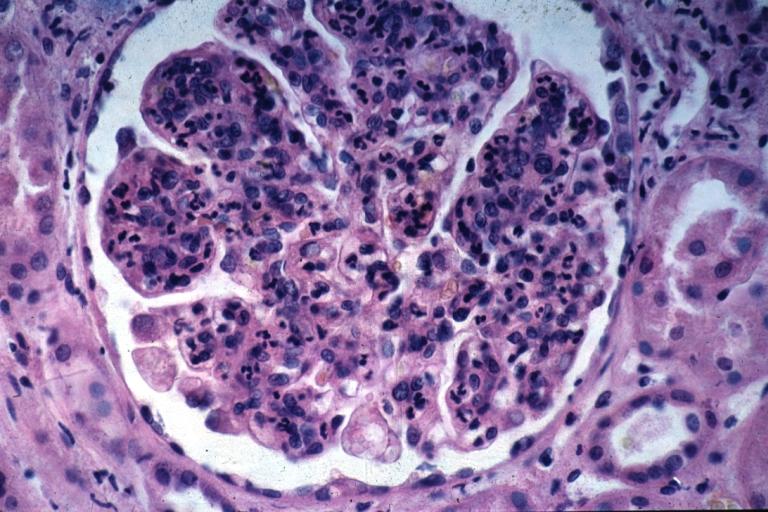
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 7.jpg|This is a photomicrograph of a glomerulus from another case with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. In this case the immune complex glomerular disease is ongoing with necrosis and accumulation of neutrophils in the glomerulus. | |||
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 8.jpg|This immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a case of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis shows a granular immunofluorescence pattern consistent with immune complex disease. The primary antibody used for this staining was specific for IgG; however antibodies for complement would show a similar pattern. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
== | <div align="left"> | ||
<gallery heights="175" widths="175"> | |||
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 9.jpg|This electron micrograph demonstrates scattered subepithelial dense deposits (arrows) and a polymorphonuclear leukocyte in the lumen. | |||
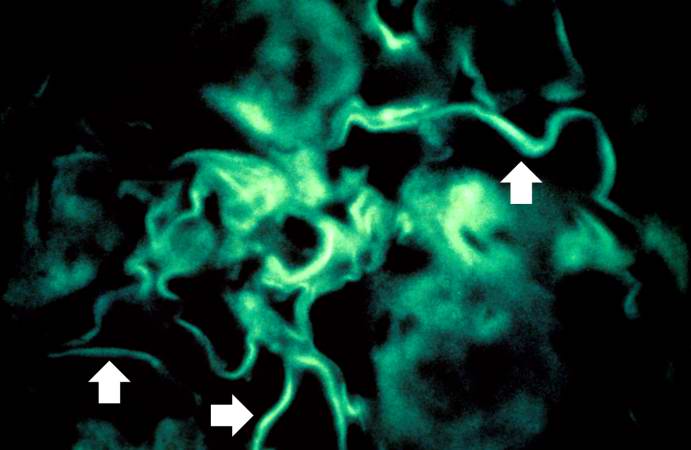
Image:Glomerulonephritis case 10.jpg|For comparison this is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome. The linear (arrows) immunofluorescence is characteristic of Goodpasture's syndrome. | |||
</gallery> | |||
</div> | |||
== | ===Images:=== | ||
*[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/Crescentic%20Glomerulonephritis.html Crescentic GN] | |||
*[http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/Chronic%20Glomerulonephritis1.html Chronic GN] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Organ disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Inflammations]] | |||
[[Category:Kidney diseases]] | |||
[[Category:Needs overview]] | |||
=== | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | |||
-------------------------------------------------- | |||
===Common Causes=== | |||
*[[Churg-strauss syndrome]] | |||
*[[Cryoglobulinaemia]] | |||
*[[Diabetes mellitus type 2]] | |||
*[[Dibasic aminoaciduria type 2]] | |||
*[[Endocarditis]] | |||
*[[Glycogenosis type 1a]] | |||
*[[Henoch-schönlein purpura ]] | |||
*[[Hepatitis b]] | |||
*[[Hereditary onycho-osteodysplasia]] | |||
*[[Hypersensitivity vasculitis]] | |||
*[[Iga nephropathy]] | |||
*[[Lepromatous leprosy]] | |||
*[[Mixed essential cryoglobulinaemia]] | |||
*[[Myeloma]] | |||
*[[Paraneoplastic syndrome]] | |||
*[[Polyarteritis nodosa]] | |||
*[[Radiotherapy]] | |||
*[[Schimke immunoosseous dysplasia]] | |||
*[[Secondary syphilis]] | |||
*[[Serum sickness]] | |||
*[[Sickle cell disease]] | |||
*[[Systemic lupus erythematosus]] | |||
*[[Vasculitis]] | |||
*[[Wegener's granulomatosis]] | |||
*[[Wiskott-aldrich syndrome]] | |||
-------------------------------------- | |||
__NOTOC__ | |||
{{Glomerulonephritis}} | |||
{{CMG}}; {{AE}}{{HK}} | |||
== | ==Overview== | ||
Glomerulonephritis may be proliferative or non-proliferative and may be associated with [[Nephrotic syndrome|nephrotic]] or [[Nephritic syndrome|nephritic]] features. The various types of glomerulonephritides should be differentiated from each other based on associations, presence of [[pitting edema]], hemeturia, [[hypertension]], [[hemoptysis]], [[oliguria]], peri-orbital edema, [[hyperlipidemia]], type of [[antibodies]], [[Light microscope|light]] and [[Electron microscopy|electron microscopic]] features. | |||
=== | ==Differential Diagnosis== | ||
The following table differentiates between various types of glomerulonephritides: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! rowspan="3" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Glomerulonephritis | |||
! rowspan="3" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Sub-entity | |||
! rowspan="3" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Causes and associations | |||
! colspan="7" rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |History and Symtoms | |||
! colspan="9" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Laboratory Findings | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Nephrotic features | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Nephritic features | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |ANCA | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody (Anti-GBM antibody) | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Immune complex formation | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Light microscope | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Electron microscope | |||
! rowspan="2" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Immunoflourescence pattern | |||
|- | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |History | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Pitting edema | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Hemeturia (pre-dominantly microscopic) | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Hypertension | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Hemoptysis | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Oliguria | |||
! align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Peri-orbital edema | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="3" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Non-proliferative | |||
!Minimal change disease | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O (glomerular epithelial protein 1- GLEPP1) | |||
| | |||
* Young children | |||
* Recent infection and immunization | |||
* Atopy | |||
* Hodgkin lymphoma | |||
* Thrombosis (due to urinary loss of antithrombin-III) | |||
| | |||
+ | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
+/- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
+ | |||
| | |||
+ | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
- | |||
| | |||
* Normal | |||
| | |||
* Fusion of podocytes | |||
| | |||
- | |||
|- | |||
!Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* HIV | |||
* Heroine use | |||
* Sickle cell disease | |||
* Interferon | |||
* Severe obesity | |||
* Mixed cryoglobunemia (Hepatitis C) | |||
| | |||
* Adults | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Focal (some glomeruli) and segmental (only part of glomerulus) | |||
| | |||
* Effacement of podocytes | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
!Membranous glomerulonephritis | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Hepatitis B and C | |||
* Solid tumors | |||
* Systemic lupus erythmatosus | |||
* Drugs (NSAIDS, penclliamine, gold, captopril) | |||
| | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Thick glomerular basement membrance | |||
| | |||
* Sub-epithelial immune complex depositis with 'spike and dome' appearance | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| rowspan="7" align="center" style="background:#4479BA; color: #FFFFFF;" + |Proliferative | |||
!IgA nephropathy | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Viral infections | |||
| | |||
* Young children | |||
* History of mucosal infections (e.g. gastroenteritis) and upper respiratory tract infection | |||
* 2-3 days after infection (synpharyngitic) | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
| - | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| + | |||
| | |||
* Crescent formation | |||
| | |||
* Mesangial proliferation | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
! rowspan="5" |Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis | |||
| | |||
* Goodpasture syndrome | |||
| | |||
* Young adults | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| - | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Hypercellular and inflamed glomeruli (Crescent formation) | |||
| | |||
* Diffuse thickening of the glomerular basement membrane with absence of subepithelial and subendothelial deposits | |||
|<nowiki>+ (Linear)</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Post infectious glomerulonephritis | |||
| | |||
* Streptococcal skin infections | |||
* Streptococcal pharyngitis | |||
* 2-3 weeks after infection | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Hypercellular and inflamed glomeruli | |||
| | |||
* Sub-epithelial immune complex deposits | |||
| + (Granular) | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Granulomatosis with polyangitis (Wegner's granulomatosis) | |||
| | |||
* Necrotizing granulomas (Nasopharynx, lungs, kidneys) | |||
* [[Conjunctivitis]] | |||
* Ulceration of the [[cornea]] | |||
* [[Episcleritis]] | |||
* Peripheral neuropathy | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+ (C-ANCA)</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Hypercellular and inflamed glomeruli (Crescent formation) | |||
|<nowiki>- (pauci-immune)</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Churg Strauss syndrome | |||
| | |||
* Necrotizing granulomas (Lungs and kidneys) | |||
* Asthma | |||
* Peripheral neuropathy | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
+ (C-ANCA) | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Hypercellular and inflamed glomeruli (Crescent formation) | |||
|<nowiki>- (pauci-immune)</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
* Microscopic polyngitis | |||
| | |||
* Necrotizing vasculitis (no granuloma) | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| + | |||
| | |||
+ (P-ANCA) | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Hypercellular and inflamed glomeruli (Crescent formation) | |||
|<nowiki>- (pauci-immune)</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|- | |||
!Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis | |||
| | |||
* Idiopathic | |||
* Hepatitis B and C (Type 1) | |||
* C3 nepritic factor (Type2) | |||
| | |||
* Hemeturia | |||
* Oliguria | |||
* Periorbital edema | |||
* Hypertension | |||
|<nowiki>+/-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>-</nowiki> | |||
|<nowiki>+</nowiki> | |||
| | |||
* Thick glomerular basement membrane (Tram-track appearance) | |||
| | |||
* Mesangial proliferation and leukocyte infiltration | |||
|<nowiki>+ (Granular)</nowiki> | |||
|} | |||
== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category: | {{WH}} | ||
{{WS}} | |||
[[Category:Needs content]] | |||
[[Category:Disease]] | |||
[[Category:Organ disorders]] | |||
[[Category:Inflammations]] | |||
[[Category:Kidney diseases]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:42, 28 July 2020
|
Diabetes mellitus Main page |
|
Patient Information |
|---|
| https://https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zucxZw069kw%7C350}} |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
|
Glomerulonephritis Main page |
|
|---|
Pathophysiology
Microscopic Pathology
-
Glomerulonephritis: Micro H&E med mag; an excellent example of AGN with many neutrophils
-
Acute Glomerulonephritis: Micro H&E high mag; an excellent example of acute exudative glomerulonephritis.
Glomerulonephritis Videos
Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis
{{#ev:youtube|CqSyj4cVZPE}}
Chronic glomerulonephritis
{{#ev:youtube|eA1vYarRAWo}}
Images
-
This is a low-power photomicrograph of a saggital section of end stage chronic glomerulonephritis (GN). Note the marked thinning of the cortex (arrow).
-
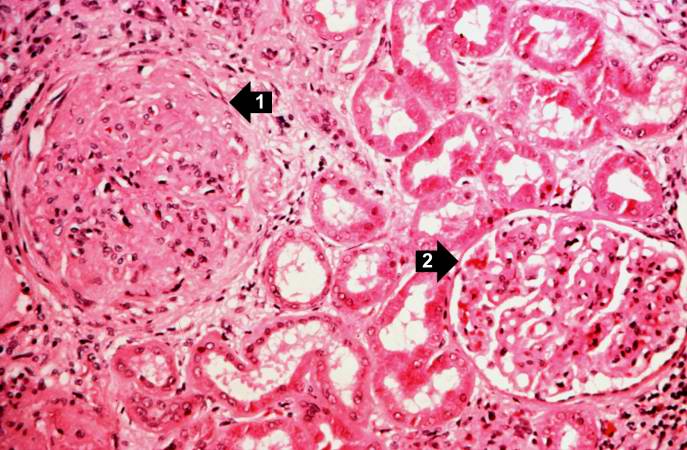
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (arrows) and glomeruli with thick basement membranes.
-
This is a higher-power photomicrograph of hyalinized glomeruli (1) and glomeruli with thickened basement membranes (2).
-
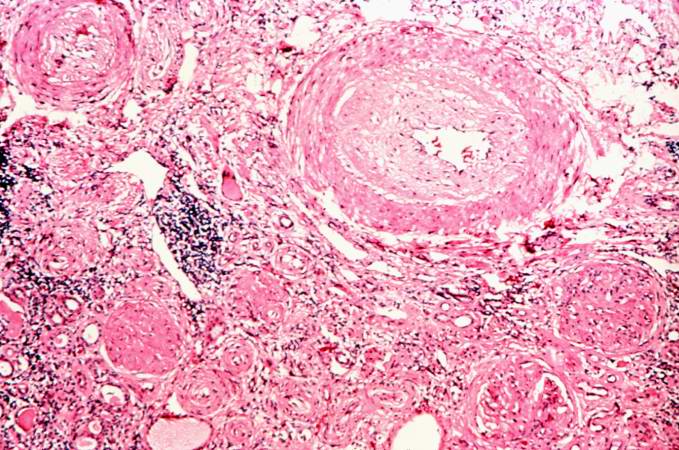
This is a photomicrograph of interstitial and vascular lesions in end stage renal disease.
-
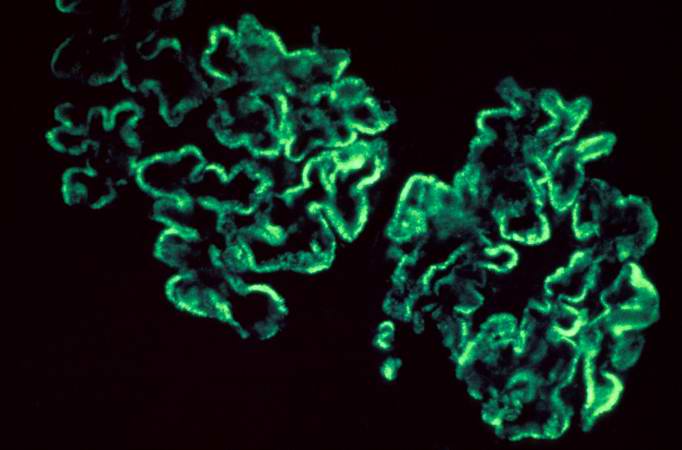
This is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of granular membranous immunofluorescence (immune complex disease). The antibody used for these studies was specific for IgG.
-
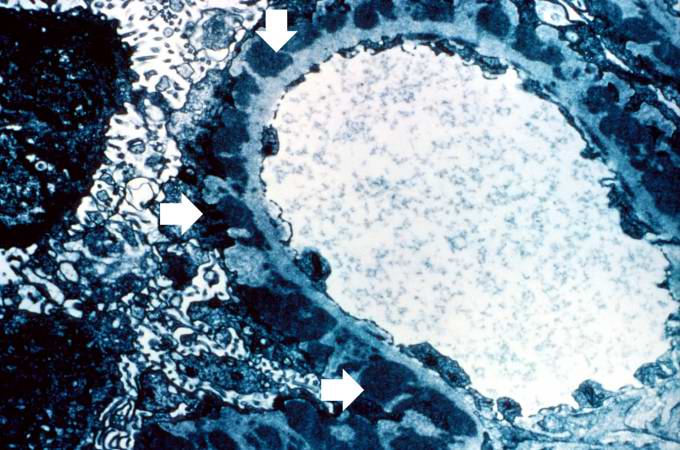
This is an electron micrograph of subepithelial granular electron dense deposits (arrows) which correspond to the granular immunofluorescence seen in the previous image.
-
This is a photomicrograph of a glomerulus from another case with acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. In this case the immune complex glomerular disease is ongoing with necrosis and accumulation of neutrophils in the glomerulus.
-
This immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a case of acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis shows a granular immunofluorescence pattern consistent with immune complex disease. The primary antibody used for this staining was specific for IgG; however antibodies for complement would show a similar pattern.
-
This electron micrograph demonstrates scattered subepithelial dense deposits (arrows) and a polymorphonuclear leukocyte in the lumen.
-
For comparison this is an immunofluorescent photomicrograph of a glomerulus from a patient with Goodpasture's syndrome. The linear (arrows) immunofluorescence is characteristic of Goodpasture's syndrome.
Images:
References
Common Causes
- Churg-strauss syndrome
- Cryoglobulinaemia
- Diabetes mellitus type 2
- Dibasic aminoaciduria type 2
- Endocarditis
- Glycogenosis type 1a
- Henoch-schönlein purpura
- Hepatitis b
- Hereditary onycho-osteodysplasia
- Hypersensitivity vasculitis
- Iga nephropathy
- Lepromatous leprosy
- Mixed essential cryoglobulinaemia
- Myeloma
- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- Polyarteritis nodosa
- Radiotherapy
- Schimke immunoosseous dysplasia
- Secondary syphilis
- Serum sickness
- Sickle cell disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Vasculitis
- Wegener's granulomatosis
- Wiskott-aldrich syndrome
|
Glomerulonephritis Main page |
|
|---|
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [2]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Syed Hassan A. Kazmi BSc, MD [3]
Overview
Glomerulonephritis may be proliferative or non-proliferative and may be associated with nephrotic or nephritic features. The various types of glomerulonephritides should be differentiated from each other based on associations, presence of pitting edema, hemeturia, hypertension, hemoptysis, oliguria, peri-orbital edema, hyperlipidemia, type of antibodies, light and electron microscopic features.
Differential Diagnosis
The following table differentiates between various types of glomerulonephritides:
| Glomerulonephritis | Sub-entity | Causes and associations | History and Symtoms | Laboratory Findings | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia | Nephrotic features | Nephritic features | ANCA | Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody (Anti-GBM antibody) | Immune complex formation | Light microscope | Electron microscope | Immunoflourescence pattern | ||||||||||
| History | Pitting edema | Hemeturia (pre-dominantly microscopic) | Hypertension | Hemoptysis | Oliguria | Peri-orbital edema | ||||||||||||
| Non-proliferative | Minimal change disease |
|
|
+ |
- |
- |
- |
+/- |
- |
+ |
+ |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
|
- |
| Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis |
|
|
+ | - | - | - | +/- | - | + | + | - | - | - | - |
|
|
- | |
| Membranous glomerulonephritis |
|
+ | - | - | - | +/- | - | + | + | - | - | - | + |
|
|
- | ||
| Proliferative | IgA nephropathy |
|
|
+/- | + | + | - | + | +/- | - | - | + | - | - | + |
|
|
- |
| Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis |
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + |
|
|
+ (Linear) | |
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | - | - | + |
|
|
+ (Granular) | ||
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | + (C-ANCA) | - | - |
|
- (pauci-immune) | +/- | ||
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
+ (C-ANCA) |
- | - |
|
- (pauci-immune) | - | ||
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | - | + |
+ (P-ANCA) |
- | - |
|
- (pauci-immune) | - | ||
| Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis |
|
|
+/- | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | - | - | + |
|
|
+ (Granular) | |