Lymphangitis carcinomatosa: Difference between revisions
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
*It is understood that lymphangitis carcinomatosa is the result of the [[tumoral]] [[Spread of the cancer|spread]] into the [[lymphatics]], following [[Hematogen|hematogenous]] seeding of the [[lungs]].<ref name="BiswasSriram2015">{{cite journal|last1=Biswas|first1=Abhishek|last2=Sriram|first2=Peruvemba S.|title=Getting the Whole Picture: Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis|journal=The American Journal of Medicine|volume=128|issue=8|year=2015|pages=837–840|issn=00029343|doi=10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.04.007}}</ref> | *It is understood that lymphangitis carcinomatosa is the result of the [[tumoral]] [[Spread of the cancer|spread]] into the [[lymphatics]], following [[Hematogen|hematogenous]] seeding of the [[lungs]].<ref name="BiswasSriram2015">{{cite journal|last1=Biswas|first1=Abhishek|last2=Sriram|first2=Peruvemba S.|title=Getting the Whole Picture: Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis|journal=The American Journal of Medicine|volume=128|issue=8|year=2015|pages=837–840|issn=00029343|doi=10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.04.007}}</ref> | ||
*The [[pathogenesis]] is also characterized by retrograde [[Spread of the cancer|spread]] into [[lymphatics]] from the [[mediastinal]] and [[hilar]] [[lymph nodes]] in the [[lungs]].<ref name="Beattie1956">{{cite journal|last1=Beattie|first1=J.W.|title=Lymphangitis carcinomatosa|journal=British Journal of Tuberculosis and Diseases of the Chest|volume=50|issue=2|year=1956|pages=120–129|issn=03660869|doi=10.1016/S0366-0869(56)80046-4}}</ref> | *The [[pathogenesis]] is also characterized by retrograde [[Spread of the cancer|spread]] into [[lymphatics]] from the [[mediastinal]] and [[hilar]] [[lymph nodes]] in the [[lungs]].<ref name="Beattie1956">{{cite journal|last1=Beattie|first1=J.W.|title=Lymphangitis carcinomatosa|journal=British Journal of Tuberculosis and Diseases of the Chest|volume=50|issue=2|year=1956|pages=120–129|issn=03660869|doi=10.1016/S0366-0869(56)80046-4}}</ref> | ||
*Both the peripheral [[lymphatics]] coursing in the interlobular [[septa]] and beneath the [[pleura]], and the central [[lymphatics]] coursing in the bronchovascular [[interstitium]] are involved. | *Both the peripheral [[lymphatics]] coursing in the interlobular [[septa]] and beneath the [[pleura]], and the central [[lymphatics]] coursing in the bronchovascular [[interstitium]] are involved.<ref name="urlLymphangitic carcinomatosis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org">{{cite web |url=https://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymphangitic-carcinomatosis?iframe=true&lang=us |title=Lymphangitic carcinomatosis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org |format= |work= |accessdate=}}</ref> | ||
*There are no specific [[genetic]] [[mutations]] associated with the [[development]] of | *There are no specific [[genetic]] [[mutations]] associated with the [[development]] of lymphangitis carcinomatosa.<ref name="MoubaxWuyts2012">{{cite journal|last1=Moubax|first1=Kim|last2=Wuyts|first2=Wim|last3=Vandecaveye|first3=Vincent|last4=Prenen|first4=Hans|title=Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis as a primary manifestation of gastric carcinoma in a young adult: a case report and review of the literature|journal=BMC Research Notes|volume=5|issue=1|year=2012|pages=638|issn=1756-0500|doi=10.1186/1756-0500-5-638}}</ref> | ||
*On [[gross pathology]], characteristic findings of [[lymphangitis]] carcinomatosa include:<ref name="lymph">Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Libre Pathology. https://librepathology.org/wiki/Pulmonary_lymphangitic_carcinomatosis</ref> | *On [[gross pathology]], characteristic findings of [[lymphangitis]] carcinomatosa include:<ref name="lymph">Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Libre Pathology. https://librepathology.org/wiki/Pulmonary_lymphangitic_carcinomatosis</ref> | ||
:*No remarkable findings | :*No remarkable findings | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
:*[[Pneumonitis|Radiation pneumonitis]] | :*[[Pneumonitis|Radiation pneumonitis]] | ||
:*[[Lymphocytic]] [[interstitial pneumonitis]] | :*[[Lymphocytic]] [[interstitial pneumonitis]] | ||
*Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis occurs in 6%–8% of patients with pulmonary metastases | *[[Pulmonary]] lymphangitic carcinomatosis occurs in 6%–8% of [[Patient|patients]] with [[pulmonary]] [[Metastasis|metastases]]. | ||
==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ==Epidemiology and Demographics== | ||
* | *Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is a [[rare]] [[disease]]. | ||
*The [[prevalence]] of [[lymphangitis]] carcinomatosa is approximately 0.03 per 100,000 individuals worldwide.<ref name="radio">Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymphangitic-carcinomatosis</ref> | *The [[prevalence]] of [[lymphangitis]] carcinomatosa is approximately 0.03 per 100,000 individuals worldwide.<ref name="radio">Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymphangitic-carcinomatosis</ref> | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 21 October 2019
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Swathi Venkatesan, M.B.B.S.[2] Sogand Goudarzi, MD [3]
Synonyms and keywords: Lymphangitis carcinomatosis; Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis
Overview
Lymphangitis carcinomatosa also known as carcinomatous lymphangitis, is an inflammation of the lymph vessels secondary to a malignancy. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa was first discovered by Gabriel Andral, a French pathologist, in 1829. The pathogenesis of lymphangitis carcinomatosa is characterized by the tumoral spread into the lymphatics, following hematogenous seeding of the lungs. The pathogenesis is also characterized by retrograde spread into lymphatics from the mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes in the lungs. Common causes of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include breast cancer (most common), lung cancer, colon cancer, stomach cancer, prostate cancer, cervical cancer, and thyroid cancer. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is a rare disease. The prevalence of lymphangitis carcinomatosa is approximately 0.03 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is more commonly observed among patients aged between 40 to 49 years old. Computed tomography is the imaging modality of choice for lymphangitis carcinomatosa. On CT, characteristic findings of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include subpleural nodules, thickening on the interlobar fissures, pleural effusion, and hilar and mediastinal nodal enlargement (40-50%). The mainstay therapy for lymphangitis carcinomatosa is systemic chemotherapy (chemotherapeutic regimen depends on the tumor histology).
Historical Perspective
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa was first discovered by Gabriel Andral, a distinguished French pathologist and professor at the University of Paris in 1829.[1]
- Andral's case report on postmortem findings of lymphangitis carcinomatosa followed after a case report on a woman who had died from cancer of the uterus; there had been extensive spread of the cancer in the pelvis, mesentery and thoracic duct-there was no mention of pulmonary or pleural involvement.[2]
- Andral is remembered for his pioneer investigations of blood chemistry.
- Gabriel Andral is considered to be the founder of scientific hematology, and is credited with its integration into clinical and analytical medicine.
Classification
- There is no established system for the classification of lymphangitis carcinomatosa.[3]
Pathophysiology
- It is understood that lymphangitis carcinomatosa is the result of the tumoral spread into the lymphatics, following hematogenous seeding of the lungs.[4]
- The pathogenesis is also characterized by retrograde spread into lymphatics from the mediastinal and hilar lymph nodes in the lungs.[5]
- Both the peripheral lymphatics coursing in the interlobular septa and beneath the pleura, and the central lymphatics coursing in the bronchovascular interstitium are involved.[6]
- There are no specific genetic mutations associated with the development of lymphangitis carcinomatosa.[7]
- On gross pathology, characteristic findings of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include:[8]
- No remarkable findings
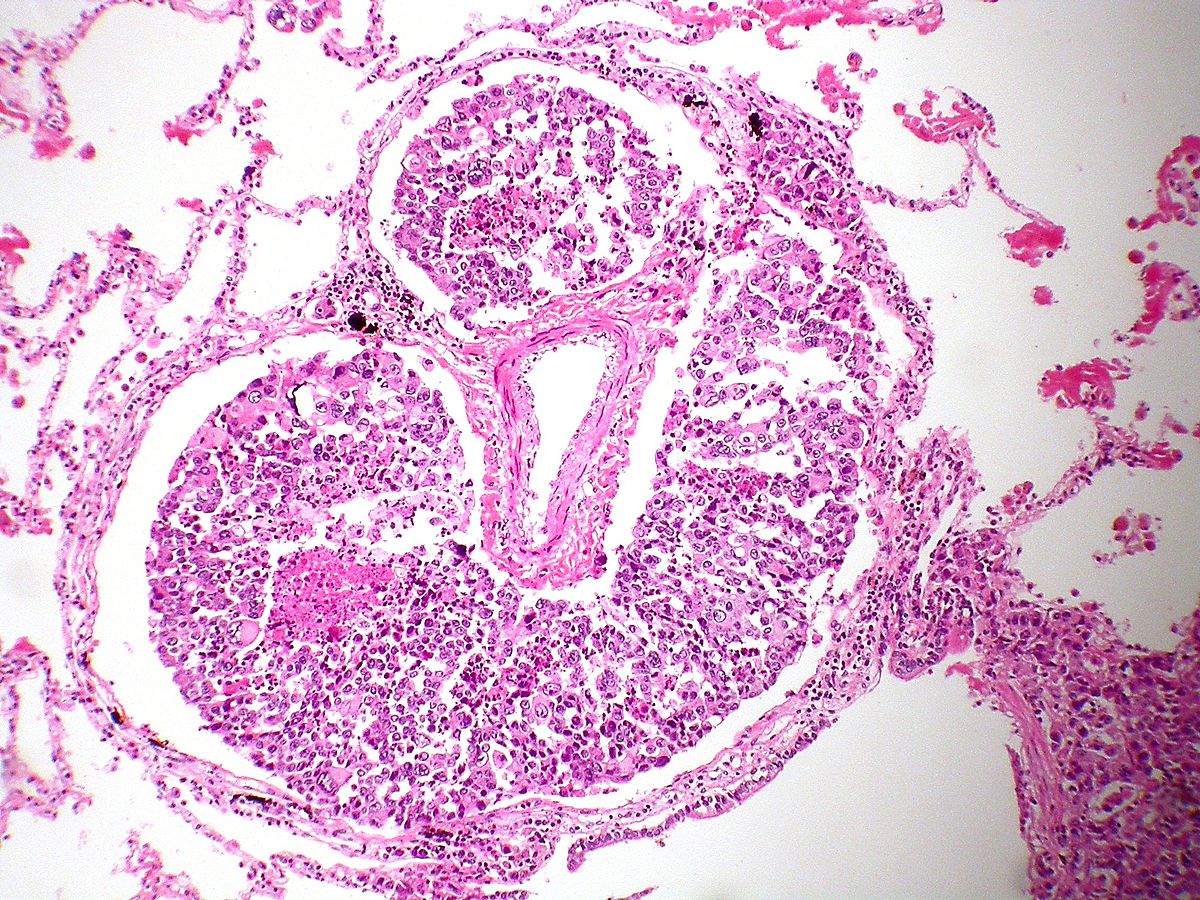
- On microscopic histopathological analysis, characteristic findings of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include:[8]
Causes
Differentiating Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa from Other Diseases
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa must be differentiated from other diseases that cause thickened interlobular septae (on imaging finding), dyspnea, fatigue, and weight-loss, such as:[9][10]
- Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis occurs in 6%–8% of patients with pulmonary metastases.
Epidemiology and Demographics
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is a rare disease.
- The prevalence of lymphangitis carcinomatosa is approximately 0.03 per 100,000 individuals worldwide.[11]
Age
- Patients of all age groups may develop lymphangitis carcinomatosa.
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is more commonly observed among patients aged 40–49 years old.[11]
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is more commonly observed among middle aged adults.
Gender
- The condition affects males more than the females
- Affects a younger population than that affected with most malignancies
Race
- There is no racial predilection for lymphangitis carcinomatosa.
Risk Factors
- Common risk factors in the development of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include:[11]
Natural History, Complications and Prognosis
- The majority of patients with lymphangitis carcinomatosa are symptomatic at the time of diagnosis.[12]
- There are two theories as to how this condition occurs[13]
- The first theory states there is haematogenous metastasis producing obliterative endarteritis and then tumor cells subsequently egress through vascular walls into the perivascular lymphatics.
- The second theory states there may be diffuse retrograde permeation and embolization of lymphatics after involvement of the hilar lymph nodes.
- Early clinical features include dyspnea, fatigue, and weight-loss.
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa may precede or obscure or dominate any local symptoms and present as a diagnostic problem in dyspnoea.[14]
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa may also occur during the evolution of a growth, which has already been identified during life, in which case diagnosis becomes relatively easier.
- If left untreated, patients with lymphangitis carcinomatosa may progress to develop acute respiratory failure.
- Common complications of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include:[9]
- Prognosis is generally poor, and the mean survival rate of patients after diagnosis of lymphangitis carcinomatosa is approximately 6 months.
- Approximately half of patients succumbing to their illness within a year of diagnosis.
- Occasionally, long-term survival is encountered.
Diagnosis
Symptoms
- Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is usually asymptomatic.[15]
- Symptoms of lymphangitis carcinomatosa may include the following:[11]
- Hemoptysis
- Chronic coughing
- Chest pain
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
Physical Examination
- Patients with lymphangitis carcinomatosa usually appear pale and malnourished.
- Physical examination may be remarkable for:[11]
Auscultation
- Present pleural friction rub
- Present egophony
- Crackling or bubbling noises
- Present whispered pectoriloquy
- Decreased/absent breath sounds
Percussion
- Dull percussion
- Reduced chest expansion
Laboratory Findings
- There are no specific laboratory findings associated with lymphangitis carcinomatosa.[16]
- Even if histologically confirmed, the chest radiograph is normal in 30–50% of cases.
Imaging Findings
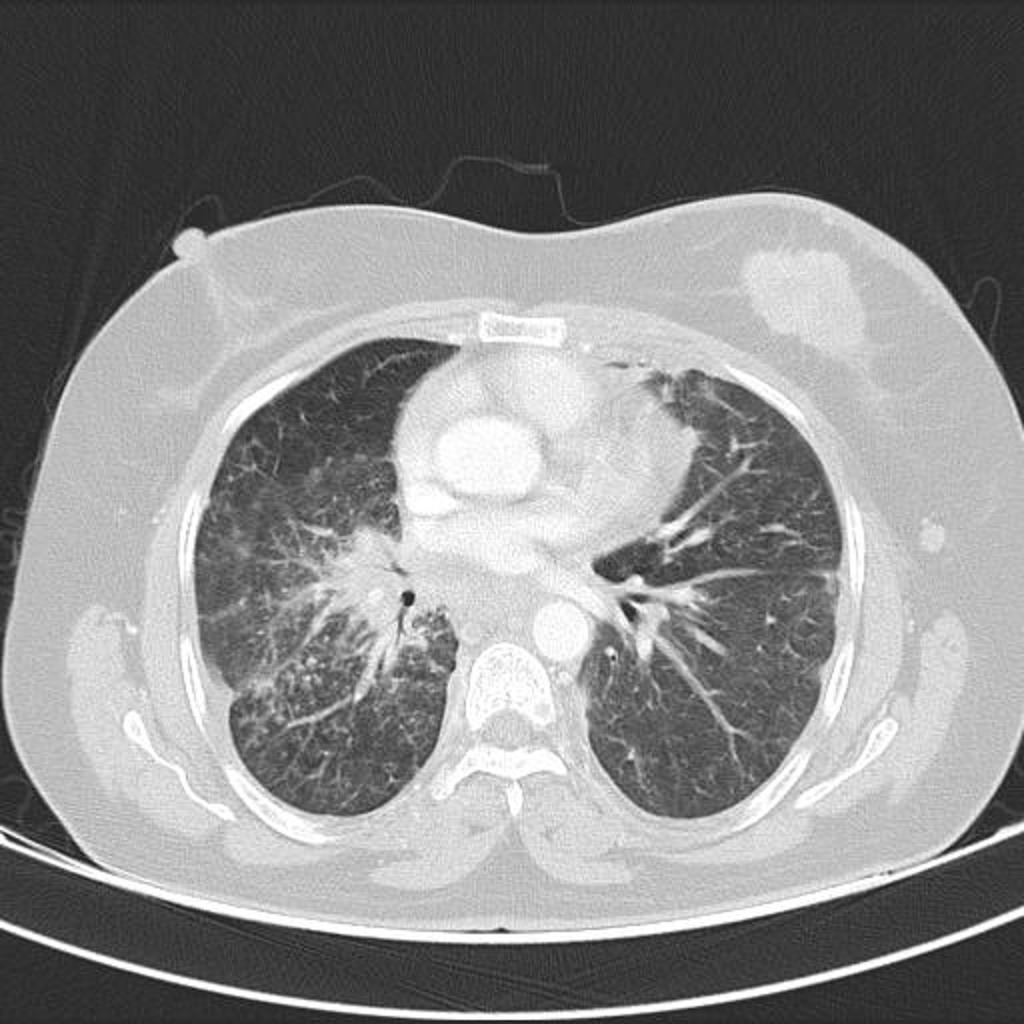
- Computed tomography is the imaging modality of choice for lymphangitis carcinomatosa.[11]
- The most important feature about CT scan is the detection of peripheral and central changes.
- On CT, characteristic findings of lymphangitis carcinomatosa include:[11]
- Subpleural nodules, and thickening on the interlobar fissures
- Pleural effusion
- Hilar and mediastinal nodal enlargement (40-50%)
- Relatively little destruction of overall lung architecture
- Involvement of the peripheral (interlobular septa) and central lymphatic system
- Distribution of changes is variable, but most are asymmetric and patchy
- Usually bilateral (may be unilateral especially in cases of lung and breast cancer)
- Radiographic appearances can most easily be divided into those due to the involvement of the peripheral and central lymphatic system.
- Involvement may be diffusely of both, or predominantly of one compartment or the other.
- Distribution of changes is variable, but most are asymmetric and patchy; it is usually bilateral but may be unilateral, specifically in cases of lung and breast cancer.
Treatment
Medical Therapy
- The mainstay therapy for lymphangitis carcinomatosa is systemic chemotherapy (chemotherapeutic regimen depends on the tumor histology).[11]
Surgery
Prevention
- There are no primary preventive measures available for lymphangitis carcinomatosa. [4]
- Once diagnosed and successfully treated, patients with lymphangitis carcinomatosa are followed-up periodically.
- Follow-up testing may include respiratory function tests and disease progression monitorization.
References
- ↑ Doyle, L (2018). "Gabriel Andral (1797-1876) and the First Reports of Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 82 (8): 491–493. doi:10.1177/014107688908200814. ISSN 0141-0768.
- ↑ Doyle, L (2018). "Gabriel Andral (1797-1876) and the First Reports of Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa". Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. 82 (8): 491–493. doi:10.1177/014107688908200814. ISSN 0141-0768.
- ↑ Aslam HM, Zhi C, Nadeem M, Arsalan M, Wallach SL (April 2019). "A Case of Rapidly Deteriorating Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis in a Patient with Stage IV Pancreatic Cancer". Cureus. 11 (4): e4421. doi:10.7759/cureus.4421. PMC 6559437 Check
|pmc=value (help). PMID 31245208. - ↑ 4.0 4.1 Biswas, Abhishek; Sriram, Peruvemba S. (2015). "Getting the Whole Picture: Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis". The American Journal of Medicine. 128 (8): 837–840. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.04.007. ISSN 0002-9343.
- ↑ Beattie, J.W. (1956). "Lymphangitis carcinomatosa". British Journal of Tuberculosis and Diseases of the Chest. 50 (2): 120–129. doi:10.1016/S0366-0869(56)80046-4. ISSN 0366-0869.
- ↑ "Lymphangitic carcinomatosis | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org".
- ↑ Moubax, Kim; Wuyts, Wim; Vandecaveye, Vincent; Prenen, Hans (2012). "Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis as a primary manifestation of gastric carcinoma in a young adult: a case report and review of the literature". BMC Research Notes. 5 (1): 638. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-5-638. ISSN 1756-0500.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Libre Pathology. https://librepathology.org/wiki/Pulmonary_lymphangitic_carcinomatosis
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Thomas, A.; Lenox, R. (2008). "Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis as a primary manifestation of colon cancer in a young adult". Canadian Medical Association Journal. 179 (4): 338–340. doi:10.1503/cmaj.080142. ISSN 0820-3946.
- ↑ Aslam, Hafiz M; Zhi, Cassandra; Nadeem, Muhammad; Arsalan, Mohammad; Wallach, Sara L (2019). "A Case of Rapidly Deteriorating Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis in a Patient with Stage IV Pancreatic Cancer". Cureus. doi:10.7759/cureus.4421. ISSN 2168-8184.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 11.6 11.7 Lymphangitis carcinomatosa. Radiopedia. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/lymphangitic-carcinomatosis
- ↑ Raja, Anand; Seshadri, Ramakrishnan Ayloor; Sundersingh, Shirley (2011). "Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa: Report of a Case and Review of Literature". Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology. 1 (3): 274–276. doi:10.1007/s13193-011-0047-9. ISSN 0975-7651.
- ↑ Khachekian, Arsineh; Shargh, Sean; Arabian, Sarkis (2015). "Pulmonary Lymphangitic Carcinomatosis From Metastatic Gastric Adenocarcinoma: Case Report". The Journal of the American Osteopathic Association. 115 (5): 332. doi:10.7556/jaoa.2015.064. ISSN 0098-6151.
- ↑ Jaswal, Sofia; Ahuja, Vanita; Aggarwal, Deepak; Kaur, Harkirat (2019). "Incidental finding of pulmonary lymphangitis carcinomatosa in a patient of chest trauma". Indian Journal of Anaesthesia. 63 (1): 70. doi:10.4103/ija.IJA_581_18. ISSN 0019-5049.
- ↑ Raja, Anand; Seshadri, Ramakrishnan Ayloor; Sundersingh, Shirley (2011). "Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa: Report of a Case and Review of Literature". Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology. 1 (3): 274–276. doi:10.1007/s13193-011-0047-9. ISSN 0975-7651.
- ↑ Gilchrist, F. J.; Alton, H.; Brundler, M.-A.; Edwards, L.; Plunkett, A.; Rao, S. (2011). "Pulmonary lymphangitic carcinomatosis presenting as severe interstitial lung disease in a 15-year-old female". European Respiratory Review. 20 (121): 208–210. doi:10.1183/09059180.00000911. ISSN 0905-9180.