Ziehl-Neelsen stain
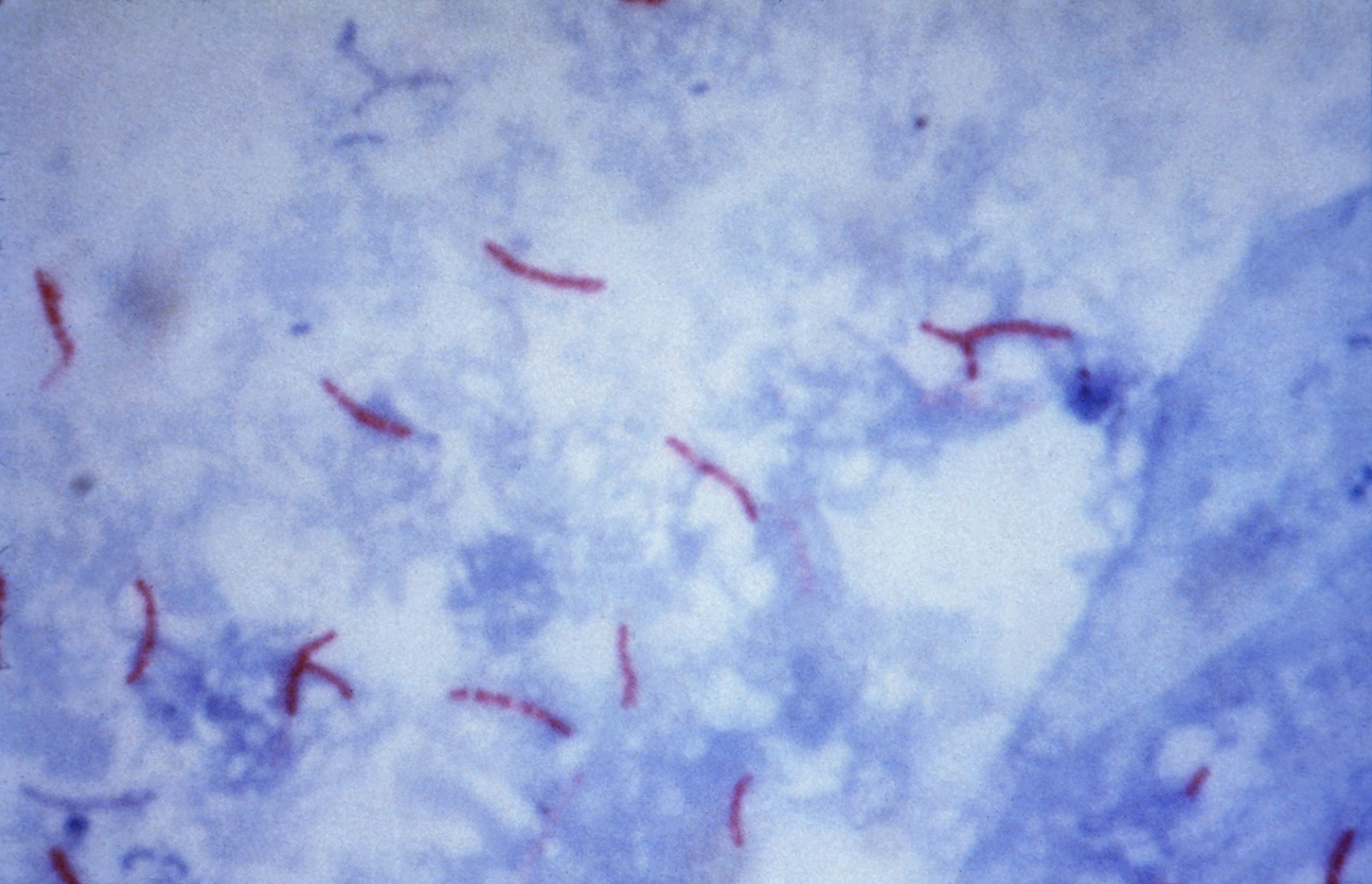
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain, also known as the acid-fast stain, was first described by two German doctors; Franz Ziehl (1859 to 1926), a bacteriologist and Friedrich Neelsen (1854 to 1894), a pathologist. It is a special bacteriological stain used to identify acid-fast Mycobacteria. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is the most important of this group, as it is responsible for the disease called tuberculosis (TB). It can also be used to stain few other bacteria like Nocardia. The reagents used are Ziehl-Neelsen carbolfuchsin, acid alcohol and methylene blue.
Background
In 1877 the German pathologist Edwin Klebs (1834 to 1913) whilst at Zürich (Switzerland) published a paper describing an organism he had isolated from tuberculous material and with which he was able to reproduce tuberculosis. He named the organism 'Monas tuberculosum.' In 1880 Dr Max Schuller duplicated the results of Klebs but found that the ability of material to induce tuberculosis persisted only to the second generation. In 1881 Professor Jean Joseph Henri Toussaint of the Veterinary School at Toulouse described similar organisms isolated from the blood of tuberculosis patients. These organisms were from the descriptions undoubtedly micrococci and thus contaminants of the inocula.
In 1881 the German physician Emanuel Aufrecht (1844 to 1933) physician-in-chief of the department of internal medicine at the Magdeburg City Hospital described the constant presence of rod shaped bacteria lying within the tubercules. His paper omitted to say how the organisms were demonstrated.
In 1882 Robert Koch (1843 to 1910) published a paper in Berlin klin. Wochenschr. 15 wherein he described an unusual bacterium with which he was able to reproduce tuberculosis. The German pathologist Paul Clemens von Baumgarten (1848 to 1928) professor of pathological anatomy at Leipzig published a paper ten days later confirming Koch's findings.
Koch's original method of staining the tubercule bacilli was to use an alkaline mixture of aniline dyes. This requires staining for 20 to 24 hours at room temperature or 30 to 60 minutes at 40 °C. On May 1, 1882 Professor Paul Ehrlich (1854-1915) published an improvement on Koch's method. Both methods held that the solution must be alkaline.
Ziehl described a new method in a paper published on 12 August 1882 which showed that the solutions could be acidic rather than alkaline. The new stain was less damaging to tissue preparations of tubercules while still permitting the visualisation of the causative organisms. With minor modifications this is the stain in routine use today.
These stains were enormously important in convincing doctors and scientists worldwide that the real cause of tuberculosis had been found in contrast to the false positives described earlier.
Procedure
- Add Ziehl-Neelsen carbol fuchsin to the slide for five minutes while applying heat.
- Follow with a gentle wash with water to cool the slide.
- Acid alcohol is now added to decolorize the slide.
- Wash the slide in water again and counterstain with methylene blue for one to two minutes.
- The acid-fast bacteria retain the red color, and therefore look hot pink or red. Non acid-fast bacteria will stain a blue color.
References
Online protocol examples
- Ziehl-Neelsen protocol (PDF format).
de:Ziehl-Neelsen-Färbung it:Colorazione di Ziehl-Neelsen he:צביעה יציבת חומצה nl:Ziehl-Neelsen-kleuring fi:Ziehl-Neelsenin värjäys