Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid is a combination of stimulant laxative and osmotic laxative that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults. Common adverse reactions include nausea, headache and vomiting.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Colonoscopy - Preparation of bowel for procedure
- Prepopik® (sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution is indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults.
- Prepopik®, supplied as a powder, must be reconstituted with cold water right before its use. There are two dosing regimens, each requires two separate dosing times:
- The preferred method is the "Split-Dose" method and consists of two separate doses: the first dose during the evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose the next day, during the morning prior to the colonoscopy
- The alternative method is the "DayBefore" method and consists of two separate doses: the first dose during the afternoon or early evening before the colonoscopy and the second dose 6 hours later during the evening before the colonoscopy.
- Additional fluids must be consumed after every dose in both dosing regimens. Instruct patients to consume only clear liquids (no solid food or milk) on the day before the colonoscopy up until 2 hours before the time of the colonoscopy. Instruct patients that if they experience severe bloating, distention, or abdominal pain following the first dose, delay the second dose until their symptoms resolve.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- Patients with severely reduced renal function (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute ) which may result in accumulation of magnesium
- Gastrointestinal obstruction or ileus
- Bowel perforation
- Toxic colitis or toxic megacolon
- An allergy to any of the ingredients in Prepopik®
Warnings
Precautions
- Serious Fluid and Serum Chemistry Abnormalities
- Advise patients to hydrate adequately before, during, and after the use of Prepopik®. Use caution in patients with congestive heart failure when replacing fluids. If a patient develops significant vomiting or signs of dehydration including signs of orthostatic hypotension after taking Prepopik®, consider performing post-colonoscopy lab tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) and treat accordingly. Approximately 20% of patients in both arms (Prepopik®, 2L of PEG + E plus two × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets) of clinical trials of Prepopik® had orthostatic changes (changes in blood pressure and/or heart rate) on the day of colonoscopy. In clinical trials orthostatic changes were documented out to seven days post colonoscopy.
- Fluid and electrolyte disturbances can lead to serious adverse events including cardiac arrhythmias or seizures and renal impairment. Fluid and electrolyte abnormalities should be corrected before treatment with Prepopik®. In addition, use caution when prescribing Prepopik® for patients who have conditions or who are using medications that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or that may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmia, and renal impairment.
- Seizures
- There have been reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures with the use of bowel preparation products in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities.
- Use caution when prescribing Prepopik® for patients with a history of seizures and in patients at risk of seizure, such as patients taking medications that lower the seizure threshold (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, patients with known or suspected hyponatremia.
- Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
- As in other magnesium containing bowel preparations, use caution when prescribing Prepopik® for patients with impaired renal function or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function (such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). These patients may be at increased risk for renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Prepopik®. Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients. In patients with severely reduced renal function (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min), accumulation of magnesium in plasma may occur.
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- There have been rare reports of serious arrhythmias associated with the use of ionic osmotic laxative products for bowel preparation. Use caution when prescribing Prepopik® for patients at increased risk of arrhythmias (e.g., patients with a history of prolonged QT, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or cardiomyopathy). Pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs should be considered in patients at increased risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
- Colonic Mucosal Ulceration, Ischemic Colitis and Ulcerative Colitis
- Osmotic laxatives may produce colonic mucosal aphthous ulcerations and there have been reports of more serious cases of ischemic colitis requiring hospitalization. Concurrent use of additional stimulant laxatives with Prepopik® may increase this risk. The potential for mucosal ulcerations should be considered when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspected inflammatory bowel disease.
- Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
- If gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation is suspected, perform appropriate diagnostic studies to rule out these conditions before administering Prepopik®. Use with caution in patients with severe active ulcerative colitis.
- Aspiration
- Patients with impaired gag reflex and patients prone to regurgitation or aspiration should be observed during the administration of Prepopik®. Use with caution in these patients.
- Not for Direct Ingestion
- Each packet must be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and administered at separate times according to the dosing regimen. Ingestion of additional water is important to patient tolerance. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- In randomized, multicenter, controlled clinical trials, nausea, headache, and vomiting were the most common adverse reactions (>1%) following Prepopik® administration. The patients were not blinded to the study drug. Since abdominal bloating, distension, pain/cramping, and watery diarrhea are known to occur in response to colon cleansing preparations, these effects were documented as adverse events in the clinical trials only if they required medical intervention (such as a change in study drug or led to study discontinuation, therapeutic or diagnostic procedures, met the criteria for a serious adverse event), or showed clinically significant worsening during the study that was not in the frame of the usual clinical course, as determined by the investigator.
- Prepopik® was compared for colon cleansing effectiveness with a preparation containing two liters (2L) of polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution (PEG + E) and two 5-mg bisacodyl tablets, all administered the day before the procedure. Table 1 displays the most common adverse reactions in Study 1 and Study 2 for the Prepopik® Split-Dose and Day-Before dosing regimens, respectively, each as compared to the comparator preparation.
- Electrolyte Abnormalities
- In general, Prepopik® was associated with numerically higher rates of abnormal electrolyte shifts on the day of colonoscopy compared to the preparation containing 2L of PEG + E plus two × 5-mg bisacodyl tablets (Table 2). These shifts were transient in nature and numerically similar between treatment arms at the Day 30 visit.
Postmarketing Experience
- The following foreign spontaneous reports have been identified during use of formulations similar to Prepopik®. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Allergic reactions
Cases of hypersensitivity reactions including rash, urticaria, and purpura have been reported.
Electrolyte abnormalities
There have been reports of hypokalemia, hyponatremia and hypermagnesemia with the use of Prepopik® for colon preparation prior to colonoscopy.
Gastrointestinal
Abdominal pain, diarrhea, fecal incontinence, and proctalgia have been reported with the use of Prepopik® for colon preparation prior to colonoscopy. There have been isolated reports of reversible aphthoid ileal ulcers. Ischemic colitis has been reported with the use of Prepopik® for colon preparation prior to colonoscopy. However, a causal relationship between these ischemic colitis cases and the use of Prepopik® has not been established.
Neurologic
There have been reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures associated with and without hyponatremia in epileptic patients.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs That May Increase Risks of Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
- Use caution when prescribing Prepopik® for patients with conditions or who are using medications that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of seizure, arrhythmias, and prolonged QT in the setting of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. This includes patients receiving drugs which may be associated with hypokalemia (such as diuretics or corticosteroids, or drugs where hypokalemia is a particular risk, such as cardiac glycosides) or hyponatremia. Use caution when Prepopik® is used in patients on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) or drugs known to induce Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH), such as tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors, antipsychotic drugs and carbamazepine, as these drugs may increase the risk of water retention and/or electrolyte imbalance. Consider additional patient evaluations as appropriate.
- Potential for Altered Drug Absorption
- Oral medication administered within one hour of the start of administration of Prepopik® solution may be flushed from the GI tract and the medication may not be absorbed.
- Tetracycline and fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine and penicillamine, should be taken at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of Prepopik® to avoid chelation with magnesium.
- Antibiotics
- Prior or concomitant use of antibiotics with Prepopik® may reduce efficacy of Prepopik® as conversion of sodium picosulfate to its active metabolite BHPM is mediated by colonic bacteria.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category B
- Reproduction studies with Prepopik® have been performed in pregnant rats at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg/day (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on the body surface area), and did not reveal any evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to Prepopik®. The reproduction study in rabbits was not adequate, as treatment-related mortalities were observed at all doses. A pre and postnatal development study in rats showed no evidence of any adverse effect on pre and postnatal development at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg twice daily (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on the body surface area). There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, Prepopik® should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Prepopik® is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- The safety and effectiveness of Prepopik® in pediatric patients has not been established.
Geriatic Use
- In controlled clinical trials of Prepopik®, 215 of 1201 (18%) patients were 65 years of age or older. The overall incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar among patients ≥65 years of age (73%) and patients <65 years of age (71%). Among all patients ≥65 years of age, the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing was greater in the Prepopik® group (81.1%) than in the comparator group (70.9%).
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- Patients with impaired renal function or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function (such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may be at increased risk for further renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after the use of Prepopik®. Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients. In patients with severely reduced renal function (creatinine clearance < 30 mL/min), accumulation of magnesium in plasma may occur. The signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia may include, but are not limited to, diminished or absent deep tendon reflexes, somnolence, hypocalcemia, hypotension, bradycardia, muscle, respiratory paralysis, complete heart block, and cardiac arrest.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
- The patient who has taken an overdose should be monitored carefully, and treated symptomatically for complications.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid in the drug label.
Pharmacology
| |
| |
Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| disodium (pyridin-2-ylmethylene)di-4,1-phenylene disulfate | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | A06 A06AB58 (WHO) (combinations) |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 481.409 g/mol |
| SMILES | & |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | Oral |
Mechanism of Action
- Sodium picosulfate is hydrolyzed by colonic bacteria to form an active metabolite: bis-(p-hydroxy-phenyl)-pyridyl-2-methane, BHPM, which acts directly on the colonic mucosa to stimulate colonic peristalsis.
- Magnesium oxide and citric acid react to create magnesium citrate in solution, which is an osmotic agent that causes water to be retained within the gastrointestinal tract.
Structure
- Prepopik® (sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid) for oral solution is available in 2 flavors, orange and cranberry flavor, and is provided in two packets. The contents of each is to be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and consumed.
- Each packet for both flavors contains 10 mg sodium picosulfate, 3.5 g magnesium oxide and 12 g anhydrous citric acid. The product also contains the following inactive ingredients: potassium hydrogen carbonate, saccharine sodium and orange or cranberry flavors. The orange flavor contains acacia gum, lactose, ascorbic acid and butylated hydroxyanisole, and the cranberry flavor contains maltodextrin, glyceryl triacetate (triacetin) and sodium octenyl succinated starch. The following is a description of the three active ingredients:
- Sodium picosulfate is a stimulant laxative.
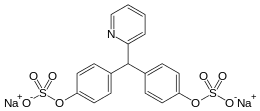
- Sodium picosulfate
- Chemical name: 4,4´-(2-pyridylmethylene) diphenyl bis(hydrogen sulfate) disodium salt, monohydrate
- Chemical formula: C18H13NNa2O8S2.H2O
- Molecular weight: 499.4
- Structural formula:
- Chemical Structure 1.H2O
- Magnesium citrate, which is formed in solution by the combination of magnesium oxide and anhydrous citric acid, is an osmotic laxative.
- Magnesium oxide
- Chemical name: Magnesium oxide
- Chemical formula: Mg O
- Molecular weight: 40.3
- Structural formula: Mg O
- Anhydrous citric acid
- Chemical name: 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid
- Chemical formula: C6H8O7
- Molecular weight: 192.1
- Structural formula:
Pharmacodynamics
- The stimulant laxative activity of sodium picosulfate together with the osmotic laxative activity of magnesium citrate produces a purgative effect which, when ingested with additional fluids, produces watery diarrhea.
Pharmacokinetics
- Sodium picosulfate, which is a prodrug, is converted to its active metabolite, BHPM, by colonic bacteria. After administration of 2 packets of Prepopik® separated by 6 hours, in 16 healthy volunteers, sodium picosulfate reached a mean Cmax of 3.2 ng/mL at approximately 7 hours (Tmax). After the first packet the corresponding values were 2.3 ng/mL at 2 hours. The terminal half-life of sodium picosulfate was 7.4 hours. The fraction of the absorbed sodium picosulfate dose excreted unchanged in urine was 0.19%. Plasma levels of the free BHPM were low, with 13 out of 16 subjects studied having plasma BHPM concentrations below the lower limit of quantification (0.1 ng/mL). Urinary samples show that the majority of excreted BHPM was in the glucuronide-conjugated form. Magnesium oxide and citric acid react in water to create magnesium citrate. Baseline uncorrected magnesium concentration reached a maximum (Cmax) of approximately 1.9 mEq/L, which occurred at 10 hours post initial packet administration (Tmax). This represents an approximately 20% increase from the baseline.
- Drug Interaction Studies
- In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, sodium picosulfate did not inhibit the major CYP enzymes (CYP 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 3A4/5) evaluated. Based on an in vitro study using freshly isolated hepatocyte culture, sodium picosulfate is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6 or CYP3A4/5.
Nonclinical Toxicology
- Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential or studies to evaluate mutagenic potential have not been performed with Prepopik®. However, sodium picosulfate was not mutagenic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma assay and the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test.
- In an oral fertility study in rats, Prepopik® did not cause any significant adverse effect on male or female fertility parameters up to a maximum dose of 2000 mg/kg twice daily (about 1.2 times the recommended human dose based on the body surface area).
Clinical Studies
- The colon cleansing efficacy of Prepopik® was evaluated for non-inferiority against a comparator in two randomized, investigator-blinded, active-controlled, multicenter US trials in patients scheduled to have an elective colonoscopy. In all, 1195 adult patients were included in the primary efficacy analysis: 601 from Study 1, and 594 from Study 2. Patients ranged in age from 18 to 80 years (mean age 56 years); 61% were female and 39% male. Self-identified race was distributed as follows: 90% White, 10% Black, and less than 1% other. Of these, 3% self-identified their ethnicity as Hispanic or Latino.
- Patients randomized to Prepopik® in the two studies were treated with one of two dosing regimens:
- In Study 1, Prepopik® was given by "Split-Dose" (evening before and day of) dosing, where the first packet was taken the evening before the colonoscopy (between 5:00 and 9:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second packet was taken the morning of the colonoscopy (at least 5 hours prior to but no more than 9 hours prior to colonoscopy), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
- In Study 2, Prepopik® was given by "Day-Before" (afternoon/evening before only) dosing, where both packets were taken separately on the day before the colonoscopy, with the first packet taken in the afternoon (between 4:00 and 6:00 PM), followed by five (5) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid, and the second packet taken in the late evening (approximately 6 hours later, between 10:00 PM and 12:00 AM), followed by three (3) 8-ounce glasses of clear liquid.
- The comparator was a preparation containing two liters of polyethylene glycol plus electrolytes solution (PEG + E) and two 5-mg bisacodyl tablets, administered the day before the procedure. All patients in both the Prepopik® and comparator groups were limited to a clear liquid diet on the day before the procedure (24 hours before).
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing, as assessed by blinded colonoscopists using the Aronchick Scale. The Aronchick scale is a tool used to assess overall colon cleansing. Successful colon cleansing was defined as bowel preparations with >90% of the mucosa seen and mostly liquid stool that were graded excellent (minimal suctioning needed for adequate visualization) or good (significant suctioning needed for adequate visualization) by the colonoscopist.
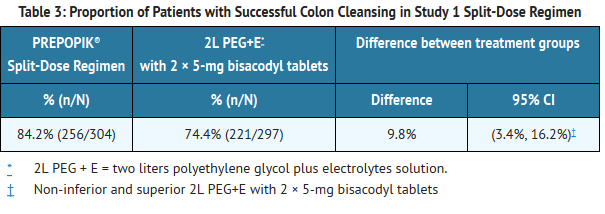
- In both studies, Prepopik® was non-inferior to the comparator. In addition, Prepopik® provided by Split-Dose dosing met the pre-specified criteria for superiority to the comparator for colon cleansing in Study 1. The comparator in that study was administered entirely on the day prior to colonoscopy. See Tables 3 and 4 below.
How Supplied
- Prepopik® is supplied in a carton containing 2 packets, each holding 16.1 grams of powder in orange flavor or 16.2 grams of powder in cranberry flavor for oral solution, along with a pre-marked dosing cup. Each packet for both flavors contains 10 mg sodium picosulfate, 3.5 g magnesium oxide and 12 g anhydrous citric acid. The excipients for both flavors include potassium hydrogen carbonate, sodium saccharin, orange or cranberry flavor. The orange flavor contains acacia gum, lactose, ascorbic acid, and butylated hydroxyanisole, and the cranberry flavor contains maltodextrin, glyceryl triacetate (triacetin) and sodium octenyl succinated starch.
- Storage
- Store at 25°C (77°F). Excursions permitted at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- Orange flavor:
- NDC# 55566-9300-2 Kit, 2 packets and cup
- Cranberry flavor:
- NDC# 55566-9700-1- Kit, 2 packets and cup
Storage
There is limited information regarding Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Ask patients to let you know if they have trouble swallowing or are prone to regurgitation or aspiration.
- Tell patients not to take other laxatives while they are taking Prepopik®.
- Tell patients that if they experience severe bloating, distention or abdominal pain following the first packet of Prepopik®, delay the second administration until the symptoms resolve.
- Instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop signs and symptoms of dehydration.
- Not for Direct Ingestion: Each packet must be dissolved in 5 ounces of cold water and administered at separate times according to the dosing regimen. Ingestion of additional water is important to patient tolerance. Direct ingestion of the undissolved powder may increase the risk of nausea, vomiting, dehydration, and electrolyte disturbances. Inform patients that oral medication administered within one hour of the start of administration of Prepopik® solution may not be absorbed completely.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- PREPOPIK®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |Label Name=sp06.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |Label Name=sp07.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Sodium picosulfate, magnesium oxide, and anhydrous citric acid |Label Name=sp08.png
}}