Rimantadine adverse reactions
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Adverse Reactions
In 1,027 patients treated with Flumadine in controlled clinical trials at the recommended dose of 200 mg daily, the most frequently reported adverse events involved the gastrointestinal and nervous systems.
Incidence >1%: Adverse events reported most frequently (1-3%) at the recommended dose in controlled clinical trials are shown in the table below.
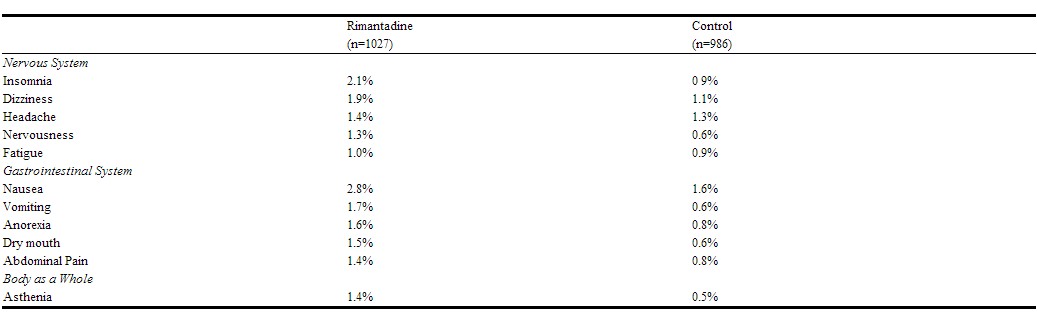 |
Less frequent adverse events (0.3 to 1%) at the recommended dose in controlled clinical trials were: Gastrointestinal System: diarrhea, dyspepsia; Nervous System:impairment of concentration, ataxia, somnolence, agitation, depression; Skin and Appendages: rash; Hearing and Vestibular: tinnitus; Respiratory: dyspnea.
Additional adverse events (less than 0.3%) reported at recommended doses in controlled clinical trials were: Nervous System: gait abnormality, euphoria, hyperkinesia, tremor, hallucination, confusion, convulsions; Respiratory: bronchospasm, cough; Cardiovascular: pallor, palpitation, hypertension, cerebrovascular disorder, cardiac failure, pedal edema, heart block, tachycardia, syncope; Reproduction: non-puerperal lactation; Special Senses: taste loss/change, parosmia.
Rates of adverse events, particularly those involving the gastrointestinal and nervous systems, increased significantly in controlled studies using higher than recommended doses of Flumadine. In most cases, symptoms resolved rapidly with discontinuation of treatment. In addition to the adverse events reported above, the following were also reported at higher than recommended doses: increased lacrimation, increased micturition frequency, fever, rigors, agitation, constipation, diaphoresis, dysphagia, stomatitis, hypesthesia and eye pain.
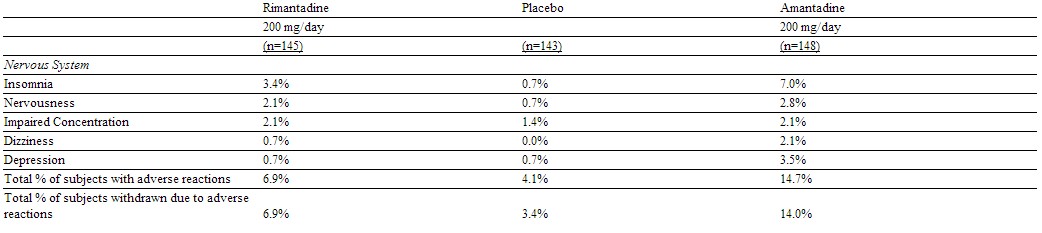
Adverse Reactions in Trials of Rimantadine and Amantadine: In a six-week prophylaxis study of 436 healthy adults comparing rimantadine with amantadine and placebo, the following adverse reactions were reported with an incidence >1 %.
 |
GERIATRIC USE: Approximately 200 patients over the age of 64 were evaluated for safety in controlled clinical trials with Flumadine® (rimantadine hydrochloride). Geriatric subjects who received either 200 mg or 400 mg of rimantadine daily for 1 to 50 days experienced considerably more central nervous system and gastrointestinal adverse events than comparable geriatric subjects receiving placebo. Central nervous system events including dizziness, headache, anxiety, asthenia, and fatigue, occurred up to two times more often in subjects treated with rimantadine than in those treated with placebo. Gastrointestinal symptoms, particularly nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain occurred at least twice as frequently in subjects receiving rimantadine than in those receiving placebo. The gastrointestinal symptoms appeared to be dose related. In patients over 64, the recommended dose is 100 mg, daily (see Clinical Pharmacology and Dosage and Administration).[1]
References
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.