Piperacillin sodium dosage and administration
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Mohamed Moubarak, M.D. [2]
Dosage and Administration
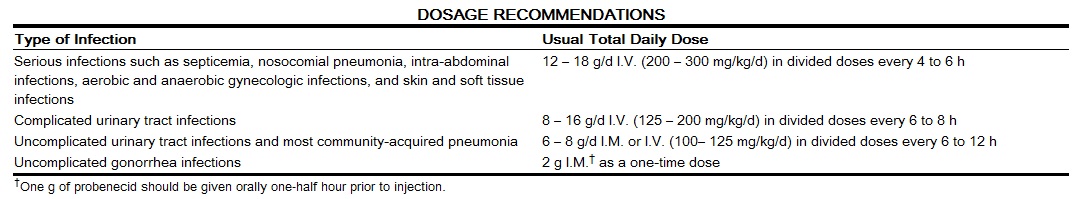
PIPRACIL may be administered by the intramuscular route (see NOTE) or intravenously as a three- to five-minute intravenous injection or as a 20- to 30-minute infusion. The usual dosage of PIPRACIL for serious infections is 3 to 4 g given every four to six hours as a 20- to 30-minute infusion. For serious infections, the intravenous route should be used.
PIPRACIL should not be mixed with an aminoglycoside in a syringe or infusion bottle since this can result in inactivation of the aminoglycoside.
The maximum daily dose for adults is usually 24 g/day, although higher doses have been used.
Intramuscular injections (see NOTE) should be limited to 2 g per injection site. This route of administration has been used primarily in the treatment of patients with uncomplicated gonorrhea and urinary tract infections.
The average duration of PIPRACIL treatment is from seven to ten days, except in the treatment of gynecologic infections, which is from three to ten days; the duration should be guided by the patient's clinical and bacteriological progress. For most acute infections, treatment should be continued for at least 48 to 72 hours after the patient becomes asymptomatic. Antibiotic therapy for S. pyogenes infections should be maintained for at least ten days to reduce the risk of rheumatic fever.
When PIPRACIL is given concurrently with aminoglycosides, both drugs should be used in full therapeutic doses.
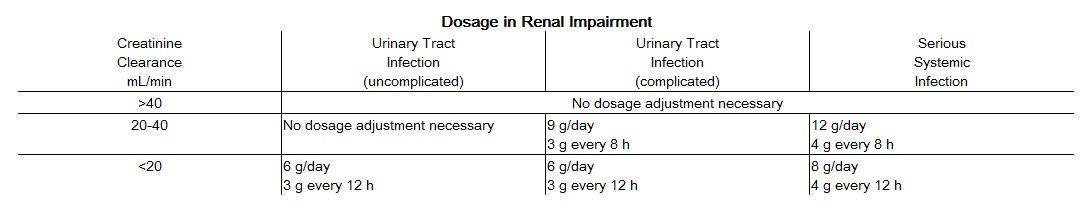
Renal Impairment
For patients on hemodialysis, the maximum daily dose is 6 g/day (2 g every 8 hours). In addition, because hemodialysis removes 30% to 50% of piperacillin in 4 hours, a 1-g additional dose should be administered following each dialysis period.
For patients with renal failure and hepatic insufficiency, measurement of serum levels of piperacillin will provide additional guidance for adjusting dosage.
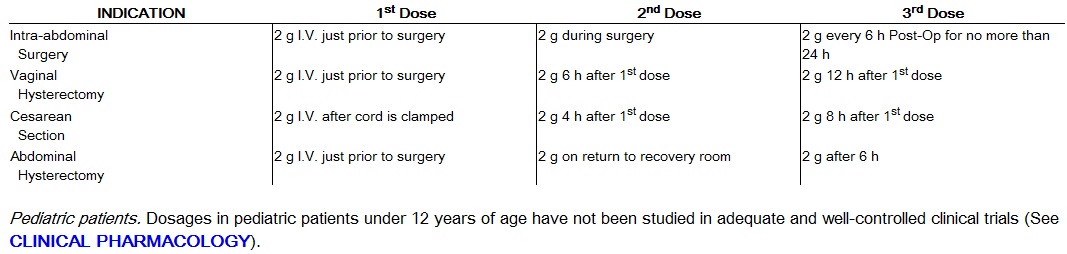
Prophylaxis
When possible, PIPRACIL should be administered as a 20- to 30-minute infusion just prior to anesthesia. Administration while the patient is awake will facilitate identification of possible adverse reactions during drug infusion. (See PRECAUTION, Drug Interactions.)
Intravenous Administration
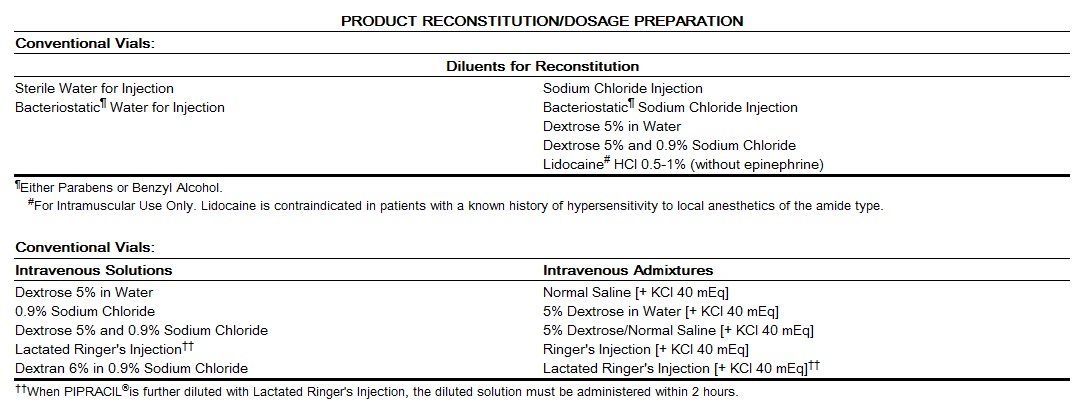
Reconstitution Directions for Conventional Vials: Reconstitute each gram of PIPRACIL with at least 5 mL of a suitable diluent (except Lidocaine HCl 0.5%-1% without epinephrine) listed above. Shake well until dissolved. Reconstituted solution may be diluted to the desired volume (eg, 50 or 100 mL) in the above listed intravenous solutions and admixtures.
DIRECTIONS FOR ADMINISTRATION Intermittent IV Infusion Infuse diluted solution over period of about 30 minutes. During infusion, it is desirable to discontinue the primary intravenous solution.
Intravenous Injection (Bolus)
Reconstituted solution should be injected slowly over a 3-to 5-minute period to help avoid vein irritation.
Intramuscular Administration (Conventional Vials Only)
Reconstitution Directions:Reconstitute each gram of PIPRACIL with 2 mL of a suitable diluent listed above to achieve a concentration of 1 g per 2.5 mL. Shake well until dissolved.
DIRECTIONS FOR ADMINISTRATION When indicated by clinical and bacteriological findings, intramuscularadministration of 6 to 8 g daily of PIPRACIL, in divided doses, may be utilized for initiation of therapy. In addition, intramuscular administration of the drug may be considered for maintenance therapy after clinical and bacteriologic improvement has been obtained with intravenous piperacillin sodium treatment. Intramuscular administration should not exceed 2 g per injection at any one site.
The preferred site is the upper outer quadrant of the buttock (ie, gluteus maximus).
The deltoid area should be used only if well-developed, and then only with caution to avoid radial nerve injury. Intramuscular injections should not be made into the lower or mid-third of the upper arm.
Stability of PIPRACIL Following Reconstitution
PIPRACIL is stable in both glass and plastic containers when reconstituted with recommended diluents and when diluted with the intravenous solutions and intravenous admixtures indicated above.
Pharmacy vials should be used immediately after reconstitution. Discard any unused portion after 24 hours if stored at room temperature (20° to 25°C [68° to 77°F]), or after 48 hours if stored at refrigerated temperature (2° to 8°C [36° to 46°F]). Vials should not be frozen after reconstitution.[1]
References
- ↑ "PIPRACIL (PIPERACILLIN SODIUM) INJECTION, POWDER, LYOPHILIZED, FOR SOLUTION [WYETH PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.]". Text " accessdate" ignored (help)
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.