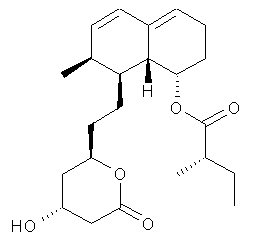
Mevastatin
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| E number | {{#property:P628}} |
| ECHA InfoCard | {{#property:P2566}}Lua error in Module:EditAtWikidata at line 36: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H36O6 |
| Molar mass | 408.534 g/mol |
|
WikiDoc Resources for Mevastatin |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Mevastatin |
|
Media |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Mevastatin at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Mevastatin at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Mevastatin
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Mevastatin Discussion groups on Mevastatin Patient Handouts on Mevastatin Directions to Hospitals Treating Mevastatin Risk calculators and risk factors for Mevastatin
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Mevastatin |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
Mevastatin, compactin, ML-236B is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class.
It was the first compound isolated in the 1970s during research into HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors produced by a mould Penicillium citrinum.
Nowadays, Mevastatin is not used in therapy of hyperlipidemias because of multiple side effects but it is the only source for production of other statin - pravastatin.
Mechanisms of Action
Mevastatin inhibits isoprenoid biosynthesis by inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase (Ki for acid form is 1 nM)1 and therefore blocks protein isoprenylation and reduces plasma cholesterol levels in humans.[1] It causes cells to arrest early in the G1 phase. [2] [3]
Mevastatin is a close structural analog of lovastatin and both agents have the same biochemical and pharmacological activities. Mevastatin is inactive in cell-free assays. In cells however, it is hydrolyzed to the active free acid form by intracellular esterases.
References
- Pages with script errors
- E number from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Cardiology
- Statins
- Drugs