Ethmoid bone
|
WikiDoc Resources for Ethmoid bone |
|
Articles |
|---|
|
Most recent articles on Ethmoid bone Most cited articles on Ethmoid bone |
|
Media |
|
Powerpoint slides on Ethmoid bone |
|
Evidence Based Medicine |
|
Clinical Trials |
|
Ongoing Trials on Ethmoid bone at Clinical Trials.gov Clinical Trials on Ethmoid bone at Google
|
|
Guidelines / Policies / Govt |
|
US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Ethmoid bone
|
|
Books |
|
News |
|
Commentary |
|
Definitions |
|
Patient Resources / Community |
|
Patient resources on Ethmoid bone Discussion groups on Ethmoid bone Patient Handouts on Ethmoid bone Directions to Hospitals Treating Ethmoid bone Risk calculators and risk factors for Ethmoid bone
|
|
Healthcare Provider Resources |
|
Causes & Risk Factors for Ethmoid bone |
|
Continuing Medical Education (CME) |
|
International |
|
|
|
Business |
|
Experimental / Informatics |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
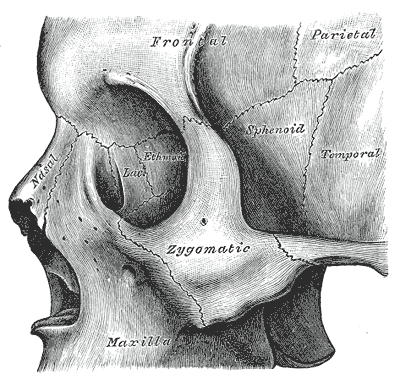
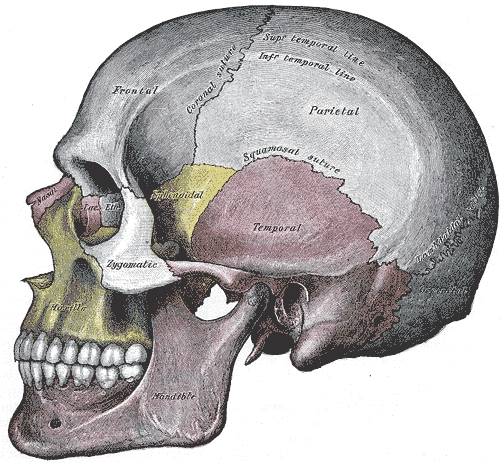
The ethmoid bone (from Greek ethmos, "sieve") is a bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. As such, it is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction.
Parts
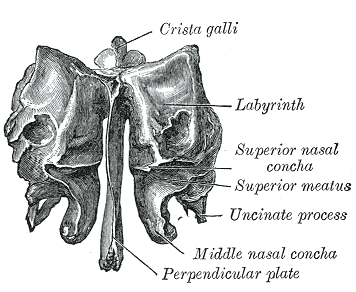
The ethmoid bone consists of four parts:
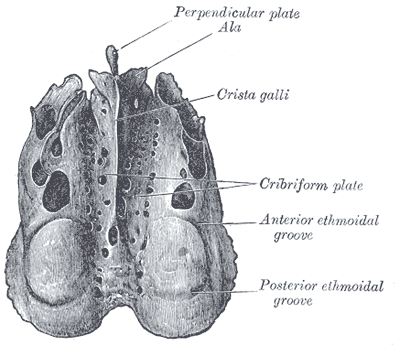
- the horizontal Cribriform plate (lamina cribrosa), part of the cranial base
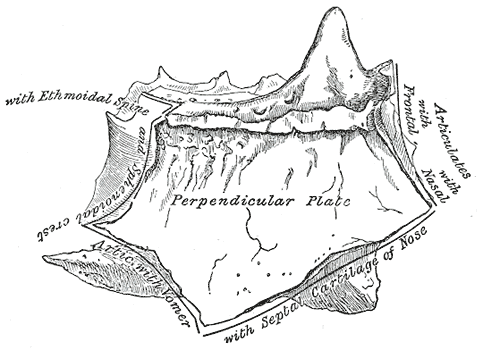
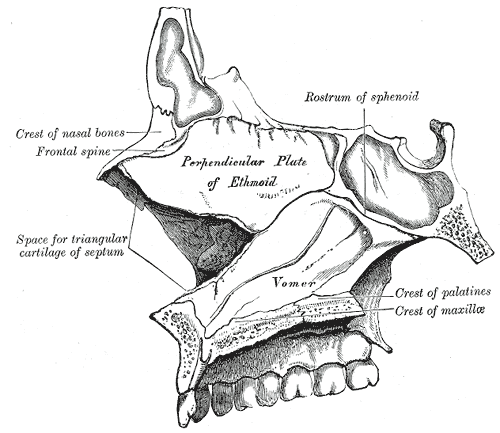
- the vertical Perpendicular plate (lamina perpendicularis), which is part of the nasal septum
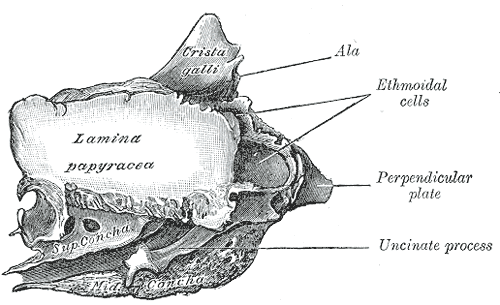
- the two lateral masses or labyrinths.
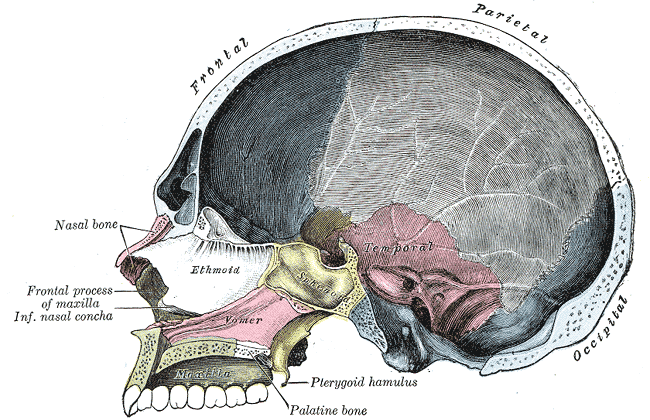
Articulations
The ethmoid articulates with fifteen bones:
- four of the cranium—the frontal, the sphenoid, and the two sphenoidal conchae
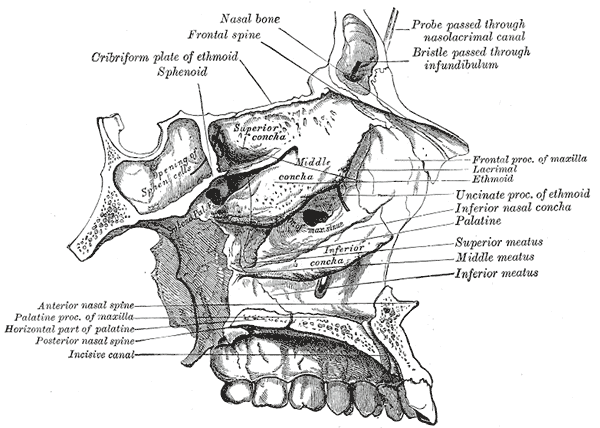
- eleven of the face—the two nasals, two maxillae, two lacrimals, two palatines, two inferior nasal conchae, and the vomer
Injuries
The ethmoid bone is very delicate and is easily injured by a sharp upward blow to the nose, such as a person might suffer by striking an automobile dashboard in a collision. The force of a blow can drive bone fragments through the cribiform plate into the meninges or brain tissue. Such injuries are often evidenced by leakage of cerebrospinal fluid into the nasal cavity, and may be followed from the nasal cavity to the brain.
Blows to the head can also shear off the olfactory nerves that pass though the ethmoid bone and cause anosmia, an irreversible loss of the sense of smell and a great reduction in the sense of taste (most of which depends on smell). This not only deprives life of some of its pleasures, but can also be dangerous, as when a person fails to smell smoke, gas, or spoiled food.
Fracture of the lamina papyracea, the lateral plate of the ethmoid labyrinth bone, permits communication between the nasal cavity and the ipsilateral orbit through the inferomedial orbital wall, resulting in orbital emphysema. Increased pressure within the nasal cavity, as seen during sneezing, for example, leads to temporary exophthalmos.
Role in magnetoception
Some birds and other migratory animals have deposits of biological magnetite in their ethmoid bones which allow them to sense the direction of the Earth's magnetic field. Humans have a similar magnetite deposit, but it is believed to be vestigial. [2]
Additional images
-
Ethmoid bone from above.
-
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid.
-
Ethmoid bone (frontal view).
-
Ethmoid bone from the right side.
-
Sphenoid bone visible center right.
-
Side view of the skull.
-
The skull from the front.
-
Medial wall of left orbit.
-
Base of the skull. Upper surface.
-
Medial wall of left nasal fossa.
-
Roof, floor, and lateral wall of left nasal cavity.
-
Lateral wall of nasal cavity, showing ethmoid bone in position.
See also
External links
Template:Gray's Template:OrbitalBones Template:Cranium
ar:عظم غربالي ca:Etmoide de:Siebbein it:Osso etmoide lv:Sietiņkauls lt:Akytkaulis nl:Zeefbeen simple:Ethmoid bone sl:Sitka uk:Ґратчаста кістка