Choline c-11
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ammu Susheela, M.D. [2]
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Choline c-11 is a diagnostic agent that is FDA approved for the treatment of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence and non-informative bone scintigraphy, computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Common adverse reactions include mild injection site reactions.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Indications
- Choline C 11 Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence and non-informative bone scintigraphy, computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
- In these patients, 11 C-choline PET imaging may help identify potential sites of prostate cancer recurrence for subsequent histologic confirmation. Suspected prostate recurrence is based upon elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following initial therapy. In clinical studies, images were produced with PET/CT coregistration.
- Limitation of Use: 11 C-choline PET imaging is not a replacement for histologic verification of recurrent prostate cancer.
- Choline C 11 Injection contains 148 – 1,225 MBq (4 – 33.1 mCi) per milliliter of 11C-choline at end of synthesis (EOS) calibration time in aqueous 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Choline c-11 in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Choline c-11 in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric) in the drug label.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Choline c-11 in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Choline c-11 in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 Contraindications in the drug label.
Warnings
Imaging Errors
- Imaging errors have been reported with 11C-choline PET and PET/CT imaging. A negative image does not rule out the presence of recurrent prostate cancer and a positive image does not confirm the presence of recurrent cancer. 11C-choline uptake is not specific for prostate cancer and may occur with other types of cancer (such as lung carcinoma and brain tumors). Clinical correlation, including histopathological evaluation of the suspected recurrence site, is essential to proper use of the PET imaging information.
- Blood PSA levels < 2 ng/mL have been associated with poor performance of 11C-choline PET imaging (higher numbers of false positive and false negative results).
- Tissue inflammation as well as prostatic hyperplasia have been associated with false positive 11C-choline PET images.
- Concomitant colchicine or androgen-deprivation therapeutic drugs (such as luteinizing hormone-releasing analogs and anti-androgen drugs) may interfere with 11C-choline PET imaging. One published report of 18F-methylcholine PET imaging indicated that discontinuation of colchicine for two weeks resolved the colchicine effect. The impact of discontinuation of androgen-deprivation therapy upon 11C-choline PET imaging has not been established.
Allergic Reactions
- As with any injectable drug product, allergic reactions and anaphylaxis may occur. Emergency resuscitation equipment and personnel should be immediately available.
Radiation Risks
- Choline C 11 Injection contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk for cancer. Safe handling should be ensured to minimize radiation exposure to the patient and health care workers.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 Clinical Trials Experience in the drug label.
Postmarketing Experience
- Exclusive of an uncommon, mild injection site reaction, no adverse reactions to 11C-choline have been reported.
Drug Interactions
- Colchicine and androgen-deprivation therapeutic drugs have been reported to interfere with choline-based PET imaging.
- The impact of androgen-deprivation therapeutic drugs upon 11C-choline PET imaging may depend upon the hormonal responsiveness of a patient’s recurrent prostate cancer. Clinical studies have not established this relationship but published reports suggest 11C-choline PET imaging may be productive in patients with “hormone resistant” recurrent prostate cancer even if the patients are receiving anti-androgen therapy. Imaging may prove unproductive or misleading due to failed or insufficient 11C-choline uptake in patients with hormone-responsive cancer if the patients are receiving androgen-deprivation therapy.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- There are no adequate and well controlled studies with Choline C 11 Injection in pregnant women and the fetal radiation dose from a 11C-choline PET imaging study is unknown. It is not known whether Choline C 11 Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with 11C-choline.
- All radiopharmaceuticals, including Choline C 11 Injection, have a potential to cause fetal harm. The likelihood of fetal harm depends on the stage of fetal development and the magnitude of the radiopharmaceutical dose. Assess pregnancy status before administering Choline C 11 Injection to a female of child bearing potential. Choline C 11 Injection should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Choline c-11 in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Choline c-11 during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Choline C 11 Injection is not indicated for use in women. It is not known whether Choline C 11 Injection is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for radiation exposure to nursing infants from Choline C 11 Injection, nursing mothers should use alternative infant nutrition sources (e.g., stored breast milk or infant formula) and pump and discard breast milk for 8 hours (>10 half lives of radioactive decay for 11C isotope) after administration of the drug or avoid use of the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Choline C 11 Injection have not been established in pediatric patients.
Geriatic Use
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 in geriatric settings.
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic Impairment
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 in patients with hepatic impairment.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Choline c-11 in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Choline c-11 in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 Monitoring in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding the compatibility of Choline c-11 and IV administrations.
Overdosage
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 overdosage. If you suspect drug poisoning or overdose, please contact the National Poison Help hotline (1-800-222-1222) immediately.
Pharmacology
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 Pharmacology in the drug label.
Mechanism of Action
- Choline C 11 Injection is a radiolabeled analog of choline, a precursor molecule essential for the biosynthesis of cell membrane phospholipids. Choline is involved in synthesis of the structural components of cell membranes, as well as modulation of trans-membrane signaling. Increased phospholipid synthesis (i.e., increased uptake of choline) has been associated with cell proliferation and the transformation process that occurs in tumor cells.
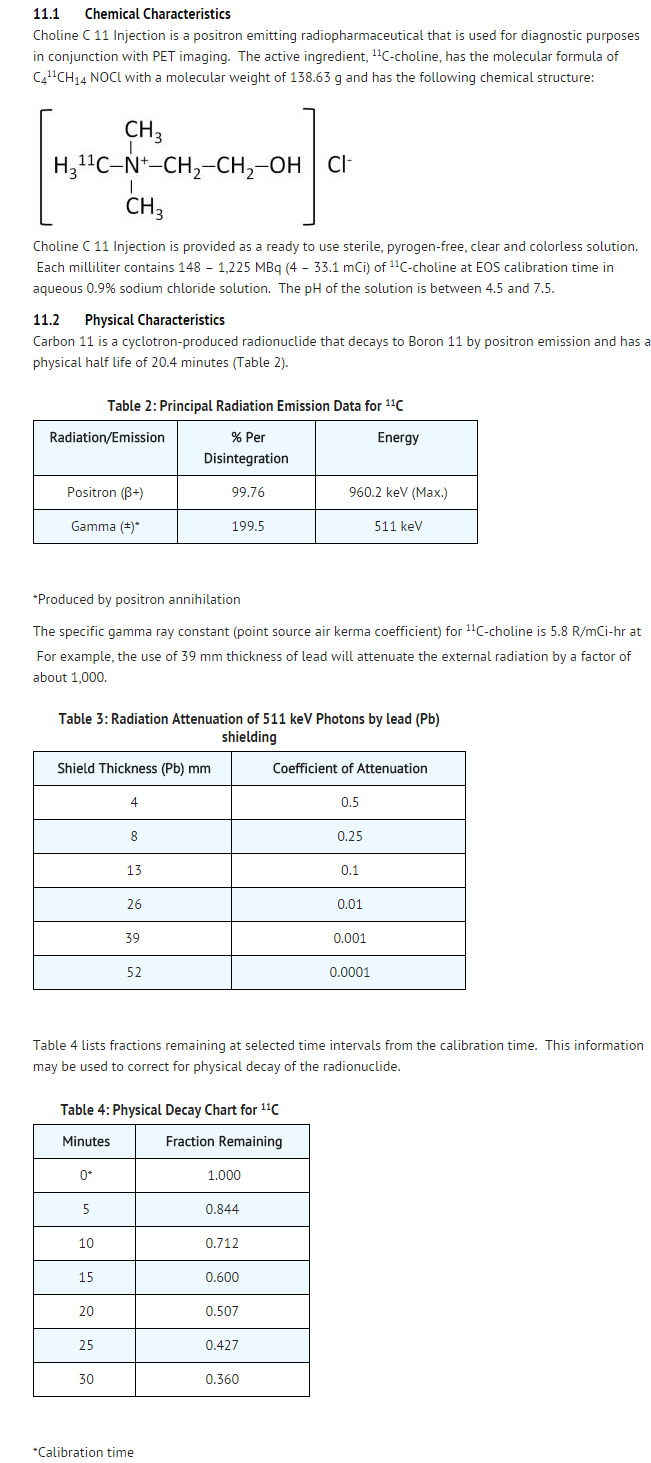
Structure
Pharmacodynamics
- In a study of men with prostatic hyperplasia or primary prostate cancer, PET imaging showed 11C-choline radioactivity accumulated rapidly within the prostate; uptake appeared to peak by five minutes following injection of the drug and activity was retained over the subsequent 30 minute scanning period. Little uptake was observed in the bladder and rectum.
Pharmacokinetics
- Distribution: 11C-choline distributes mainly to the pancreas, kidneys, liver, spleen and colon. Based upon the relatively low urinary excretion of radioactivity, renal distribution is predominantly to the organ itself, rather than via formation of urine.
Metabolism
- Following intravenous administration, 11C-choline undergoes metabolism resulting in the detection of 11C-betaine as the major metabolite in blood. In a study of patients with prostate cancer or brain disorders, the fractional activities of 11C-choline and 11C-betaine in human arterial plasma appeared to reach a plateau within 25 minutes, with 11C-betaine representing 82± 9% of the total 11C detected at that time point. A small amount of unmetabolized 11C-choline was detected within the blood at the final sampling time point (40 minutes).
Elimination
- Urinary excretion of 11C-choline was < 2% of the injected radioactivity at 1.5 hours after injection of the drug. The rate of 11C-choline excretion in urine was 0.014 mL/min.
Nonclinical Toxicology
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
- Long term studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of Choline C 11 Injection. The mutagenic potential of Choline C 11 Injection has not been adequately evaluated; however, any radiopharmaceutical, including Choline C 11 Injection, has the potential to be mutagenic. The effect of Choline C 11 Injection on fertility has not been evaluated.
Clinical Studies
- A systematic review of published reports identified four studies that contained data sufficient to compare 11C-choline PET imaging to histopathology (truth standard) among patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence and non-informative conventional imaging (for most patients, CT or MRI). In general, the suspected recurrence criteria consisted of at least two sequential PSA levels of > 0.2 ng/mL for men who had undergone prostatectomy and PSA levels of ≥ 2 ng/mL above the post-therapy nadir for men who had undergone radiotherapy. The studies were predominantly single clinical site experiences and image acquisition generally surveyed radioactivity distribution from the base of the pelvis to the base of the skull.
- Prospective studies: Two studies examined the ability of 11C-choline PET/CT to detect prostate cancer in pelvic and/or retroperitoneal lymph nodes among patients who had previously undergone radical prostatectomy. Both studies used a truth standard of lymph node histopathology. 11C-choline images were interpreted by readers masked to clinical information; surgical resection of lymph nodes was performed by surgeons aware of the 11C-choline PET/CT results.
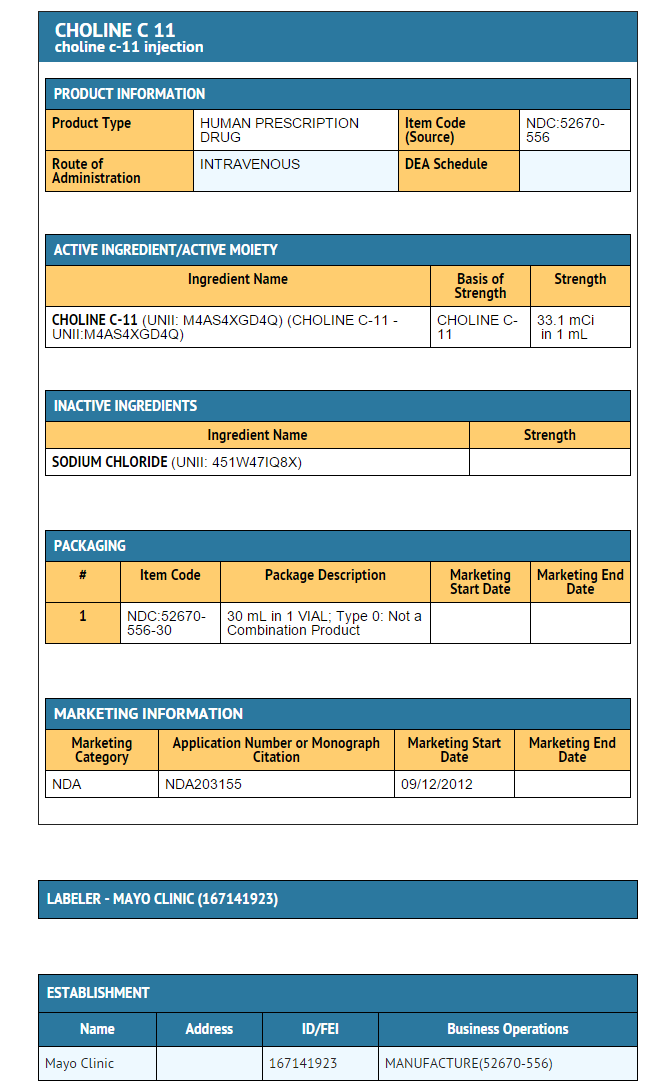
- In Study One3, 25 patients who underwent 11C-choline PET/CT and conventional imaging (CT or MRI) were scheduled to undergo pelvic or pelvic plus retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy following the imaging identification of suspected lymph node metastases. The median PSA was 2.0 ng/mL (range 0.2 to 23.1 ng/mL). The study excluded subjects with metastatic disease detected by bone scintigraphy or isolated prostatic fossa recurrence. Among the 25 patients, 21 had positive 11C-choline PET/CT scans; histopathology verified cancer in 19 of these patients. Lymph node histopathology detected no cancer among the four patients who had surgery based only on positive conventional imaging; 11C-choline PET/CT was negative in all four patients. The study report included information for patients who had non-informative conventional imaging (CT or MRI, bone scintigraphy and transrectal ultrasound), as shown in Table 5.
- In Study Two4, 15 patients were scheduled to undergo pelvic or pelvis plus retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy solely based upon positive 11C-choline PET/CT imaging in the setting of negative conventional imaging (ultrasound and/or CTand/or MRI and/or bone scintigraphy). The median PSA was 2.0 ng/mL (range 1.0 to 8.0 ng/mL); all patients had previously undergone radical prostatectomy. Eight of the 15 patients had cancer verified by lymph node histology; histology detected no cancer in seven patients.
- Retrospective Studies: Two studies were retrospective reviews of patients who underwent 11C-choline PET/CT and had histopathology obtained from biopsy of the prostatic fossa or other suspected recurrence sites.
- In Study Three5, 11C-choline PET/CT imaging was performed among 36 patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence and 13 subjects without suspected recurrence (controls). Prostatic fossa biopsies were performed among the patients with suspected recurrence. All the patients and control subjects had previously undergone radical prostatectomy; patient with suspected recurrence had no evidence of cancer using conventional clinical evaluations, including trans-rectal ultrasound and bone scintigraphy. PET/CT scans were interpreted by readers masked to clinical information. Median PSA was 2.0 ng/mL (range 0.3 – 12.1 ng/mL) for patients with suspected recurrence and 0.1 ng/mL (range 0.0 – 0.2 ng/mL) in control subjects. Prostatic fossa biopsy showed cancer in 33 of the 36 patients with suspected recurrence. PET/CT scans were positive in 25 of the 36 patients; two patients had false positive scans (one scan in a control subject and one scan in a suspected recurrence subject who had no cancer detected on prostatic fossa biopsy). Among the 13 control subjects, 12 had negative PET/CT scans.
- In Study Four6,7, 34 patients with negative conventional imaging underwent 11C-choline PET/CT and subsequently had biopsies of suspected recurrence sites. The median PSA level of the 34 patients was 3.9 ng/mL (range 0.2 – 65.0 ng/mL); 22 of the patients had previously undergone radical prostatectomy and 12 had received other therapy (radiotherapy, anti-androgen therapy or cryotherapy). 11C-choline PET/CT images were positive in 30 patients and negative in four patients. Cancer was verified by histopathology in 29 patients; 25 had positive PET/CT images and four had negative PET/CT images. Five patients with positive PET/CT images did not have cancer confirmed with histopathology.
- As shown in Table 5, within each study at least half the patients with non-informative conventional imaging had positive 11C-choline PET/CT images and histologically verified recurrent prostate cancer.
How Supplied
- Choline C 11 Injection is packaged in a single dose glass vial containing between 148 MBq to 1,225 MBq (4 mCi to 33.1 mCi) per milliliter of 11C-choline at EOS calibration time in aqueous 0.9% sodium chloride solution.
Storage
- Store Choline C 11 Injection at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 – 30°C (59 – 86°F). Use the solution within 120 minutes of EOS calibration.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Choline c-11 |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel

{{#ask: Label Page::Choline c-11 |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
- Instruct patients to drink plenty of water or other fluids (as tolerated) in the four hours before their PET/CT study.
- Instruct patients to void after completion of each image acquisition session and as often as possible for one hour after the PET/CT scan ends.
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Choline c-11 interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- CHOLINE C 11®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
There is limited information regarding Choline c-11 Look-Alike Drug Names in the drug label.
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.