Caspofungin clinical studies
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Ahmed Zaghw, M.D. [2]
Clinical Studies
The results of the adult clinical studies are presented by indications in Section 14.1 to 14.4. Results of pediatric clinical trials are in Section 14.5.
- Empirical Therapy in Febrile and Neutropenic Patients
A double-blind study enrolled 1111 febrile, neutropenic (<500 cells/mm3) patients who were randomized to treatment with daily doses of CANCIDAS (50 mg/day following a 70-mg loading dose on Day 1) or AmBisome (3 mg/kg/day). Patients were stratified based on risk category (high-risk patients had undergone allogeneic stem cell transplantation or had relapsed acute leukemia) and on receipt of prior antifungal prophylaxis. Twenty-four percent of patients were high risk and 56% had received prior antifungal prophylaxis. Patients who remained febrile or clinically deteriorated following 5 days of therapy could receive 70 mg/day of CANCIDAS or 5 mg/kg/day of AmBisome. Treatment was continued to resolution of neutropenia (but not beyond 28 days unless a fungal infection was documented).
An overall favorable response required meeting each of the following criteria: no documented breakthrough fungal infections up to 7 days after completion of treatment, survival for 7 days after completion of study therapy, no discontinuation of the study drug because of drug-related toxicity or lack of efficacy, resolution of fever during the period of neutropenia, and successful treatment of any documented baseline fungal infection.
Based on the composite response rates, CANCIDAS was as effective as AmBisome in empirical therapy of persistent febrile neutropenia (see Table 11).
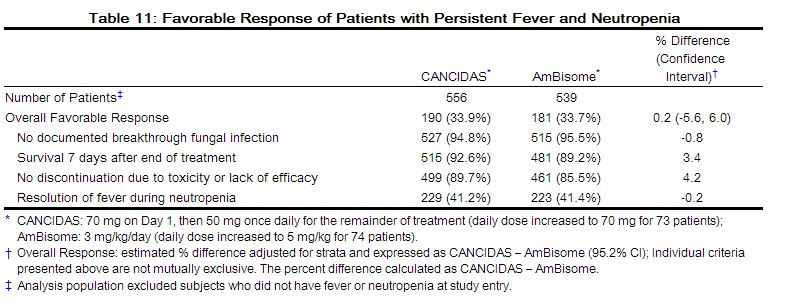 |
The rate of successful treatment of documented baseline infections, a component of the primary endpoint, was not statistically different between treatment groups.
The response rates did not differ between treatment groups based on either of the stratification variables: risk category or prior antifungal prophylaxis.
- Candidemia and the Following other Candida Infections: Intra-Abdominal Abscesse, Peritonitis and Pleural Space Infections
In a randomized, double-blind study, patients with a proven diagnosis of invasive candidiasis received daily doses of CANCIDAS (50 mg/day following a 70-mg loading dose on Day 1) or amphotericin B deoxycholate (0.6 to 0.7 mg/kg/day for non-neutropenic patients and 0.7 to 1 mg/kg/day for neutropenic patients). Patients were stratified by both neutropenic status and APACHE II score. Patients with Candida endocarditis, meningitis, or osteomyelitis were excluded from this study.
Patients who met the entry criteria and received one or more doses of IV study therapy were included in the modified intention-to-treat [MITT] analysis of response at the end of IV study therapy. A favorable response at this time point required both symptom/sign resolution/improvement and microbiological clearance of the Candida infection.
Two hundred thirty-nine patients were enrolled. Patient disposition is shown in Table 12.
 |
Of the 239 patients enrolled, 224 met the criteria for inclusion in the MITT population (109 treated with CANCIDAS and 115 treated with amphotericin B). Of these 224 patients, 186 patients had candidemia (92 treated with CANCIDAS and 94 treated with amphotericin B). The majority of the patients with candidemia were non-neutropenic (87%) and had an APACHE II score less than or equal to 20 (77%) in both arms. Most candidemia infections were caused by C. albicans (39%), followed by C. parapsilosis (20%), C. tropicalis (17%), C. glabrata (8%), and C. krusei (3%).
At the end of IV study therapy, CANCIDAS was comparable to amphotericin B in the treatment of candidemia in the MITT population. For the other efficacy time points (Day 10 of IV study therapy, end of all antifungal therapy, 2-week post-therapy follow-up, and 6- to 8-week post-therapy follow-up), CANCIDAS was as effective as amphotericin B.
Outcome, relapse and mortality data are shown in Table 13.
 |
In this study, the efficacy of CANCIDAS in patients with intra-abdominal abscesses, peritonitis and pleural space Candida infections was evaluated in 19 non-neutropenic patients. Two of these patients had concurrent candidemia. Candida was part of a polymicrobial infection that required adjunctive surgical drainage in 11 of these 19 patients. A favorable response was seen in 9 of 9 patients with peritonitis, 3 of 4 with abscesses (liver, parasplenic, and urinary bladder abscesses), 2 of 2 with pleural space infections, 1 of 2 with mixed peritoneal and pleural infection, 1 of 1 with mixed abdominal abscess and peritonitis, and 0 of 1 with Candida pneumonia.
Overall, across all sites of infection included in the study, the efficacy of CANCIDAS was comparable to that of amphotericin B for the primary endpoint.
In this study, the efficacy data for CANCIDAS in neutropenic patients with candidemia were limited. In a separate compassionate use study, 4 patients with hepatosplenic candidiasis received prolonged therapy with CANCIDAS following other long-term antifungal therapy; three of these patients had a favorable response.
In a second randomized, double-blind study, 197 patients with proven invasive candidiasis received CANCIDAS 50 mg/day (following a 70-mg loading dose on Day 1) or CANCIDAS 150 mg/day. The diagnostic criteria, evaluation time points, and efficacy endpoints were similar to those employed in the prior study. Patients with Candida endocarditis, meningitis, or osteomyelitis were excluded. Although this study was designed to compare the safety of the two doses, it was not large enough to detect differences in rare or unexpected adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A significant improvement in efficacy with the 150-mg daily dose was not seen when compared to the 50-mg dose.
- Esophageal Candidiasis
The safety and efficacy of CANCIDAS in the treatment of esophageal candidiasis was evaluated in one large, controlled, noninferiority, clinical trial and two smaller dose-response studies.
In all 3 studies, patients were required to have symptoms and microbiological documentation of esophageal candidiasis; most patients had advanced AIDS (with CD4 counts <50/mm3).
Of the 166 patients in the large study who had culture-confirmed esophageal candidiasis at baseline, 120 had Candida albicans and 2 had Candida tropicalis as the sole baseline pathogen whereas 44 had mixed baseline cultures containing C. albicans and one or more additional Candida species.
In the large, randomized, double-blind study comparing CANCIDAS 50 mg/day versus intravenous fluconazole 200 mg/day for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, patients were treated for an average of 9 days (range 7-21 days). Favorable overall response at 5 to 7 days following discontinuation of study therapy required both complete resolution of symptoms and significant endoscopic improvement. The definition of endoscopic response was based on severity of disease at baseline using a 4-grade scale and required at least a two-grade reduction from baseline endoscopic score or reduction to grade 0 for patients with a baseline score of 2 or less.
The proportion of patients with a favorable overall response was comparable for CANCIDAS and fluconazole as shown in Table 14.
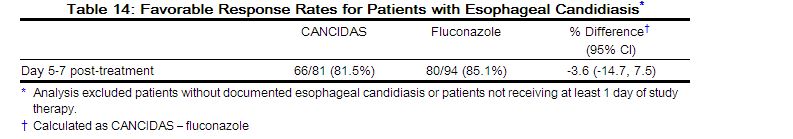 |
The proportion of patients with a favorable symptom response was also comparable (90.1% and 89.4% for CANCIDAS and fluconazole, respectively). In addition, the proportion of patients with a favorable endoscopic response was comparable (85.2% and 86.2% for CANCIDAS and fluconazole, respectively).
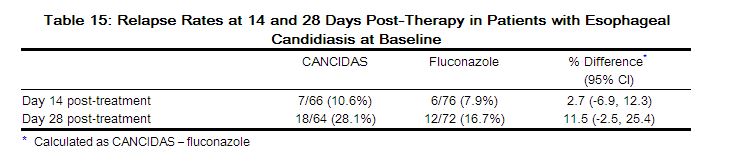
As shown in Table 15, the esophageal candidiasis relapse rates at the Day 14 post-treatment visit were similar for the two groups. At the Day 28 post-treatment visit, the group treated with CANCIDAS had a numerically higher incidence of relapse; however, the difference was not statistically significant.
 |
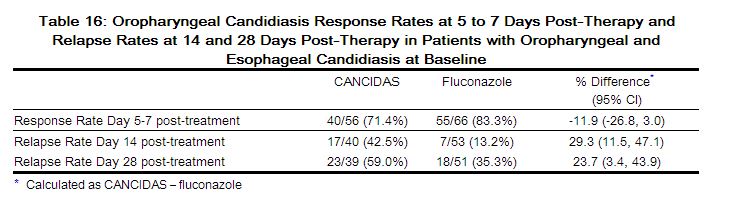
In this trial, which was designed to establish noninferiority of CANCIDAS to fluconazole for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, 122 (70%) patients also had oropharyngeal candidiasis. A favorable response was defined as complete resolution of all symptoms of oropharyngeal disease and all visible oropharyngeal lesions. The proportion of patients with a favorable oropharyngeal response at the 5- to 7-day post-treatment visit was numerically lower for CANCIDAS; however, the difference was not statistically significant. Oropharyngeal candidiasis relapse rates at Day 14 and Day 28 post-treatment visits were statistically significantly higher for CANCIDAS than for fluconazole. The results are shown in Table 16.
 |
The results from the two smaller dose-ranging studies corroborate the efficacy of CANCIDAS for esophageal candidiasis that was demonstrated in the larger study.
CANCIDAS was associated with favorable outcomes in 7 of 10 esophageal C. albicans infections refractory to at least 200 mg of fluconazole given for 7 days, although the in vitro susceptibility of the infecting isolates to fluconazole was not known.
Invasive Aspergillosis
Sixty-nine patients between the ages of 18 and 80 with invasive aspergillosis were enrolled in an open-label, noncomparative study to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of CANCIDAS. Enrolled patients had previously been refractory to or intolerant of other antifungal therapy(ies). Refractory patients were classified as those who had disease progression or failed to improve despite therapy for at least 7 days with amphotericin B, lipid formulations of amphotericin B, itraconazole, or an investigational azole with reported activity against Aspergillus. Intolerance to previous therapy was defined as a doubling of creatinine (or creatinine ≥2.5 mg/dL while on therapy), other acute reactions, or infusion-related toxicity. To be included in the study, patients with pulmonary disease must have had definite (positive tissue histopathology or positive culture from tissue obtained by an invasive procedure) or probable (positive radiographic or computed tomography evidence with supporting culture from bronchoalveolar lavage or sputum, galactomannan enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and/or polymerase chain reaction) invasive aspergillosis. Patients with extrapulmonary disease had to have definite invasive aspergillosis. The definitions were modeled after the Mycoses Study Group Criteria [see References (15)]. Patients were administered a single 70-mg loading dose of CANCIDAS and subsequently dosed with 50 mg daily. The mean duration of therapy was 33.7 days, with a range of 1 to 162 days.
An independent expert panel evaluated patient data, including diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis, response and tolerability to previous antifungal therapy, treatment course on CANCIDAS, and clinical outcome.
A favorable response was defined as either complete resolution (complete response) or clinically meaningful improvement (partial response) of all signs and symptoms and attributable radiographic findings. Stable, nonprogressive disease was considered to be an unfavorable response.
Among the 69 patients enrolled in the study, 63 met entry diagnostic criteria and had outcome data; and of these, 52 patients received treatment for >7 days. Fifty-three (84%) were refractory to previous antifungal therapy and 10 (16%) were intolerant. Forty-five patients had pulmonary disease and 18 had extrapulmonary disease. Underlying conditions were hematologic malignancy (N=24), allogeneic bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant (N=18), organ transplant (N=8), solid tumor (N=3), or other conditions (N=10). All patients in the study received concomitant therapies for their other underlying conditions. Eighteen patients received tacrolimus and CANCIDAS concomitantly, of whom 8 also received mycophenolate mofetil.
Overall, the expert panel determined that 41% (26/63) of patients receiving at least one dose of CANCIDAS had a favorable response. For those patients who received >7 days of therapy with CANCIDAS, 50% (26/52) had a favorable response. The favorable response rates for patients who were either refractory to or intolerant of previous therapies were 36% (19/53) and 70% (7/10), respectively. The response rates among patients with pulmonary disease and extrapulmonary disease were 47% (21/45) and 28% (5/18), respectively. Among patients with extrapulmonary disease, 2 of 8 patients who also had definite, probable, or possible CNS involvement had a favorable response. Two of these 8 patients had progression of disease and manifested CNS involvement while on therapy.
CANCIDAS is effective for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients who are refractory to or intolerant of itraconazole, amphotericin B, and/or lipid formulations of amphotericin B. However, the efficacy of CANCIDAS for initial treatment of invasive aspergillosis has not been evaluated in comparator-controlled clinical studies.
- Pediatric Patients
The safety and efficacy of CANCIDAS were evaluated in pediatric patients 3 months to 17 years of age in two prospective, multicenter clinical trials.
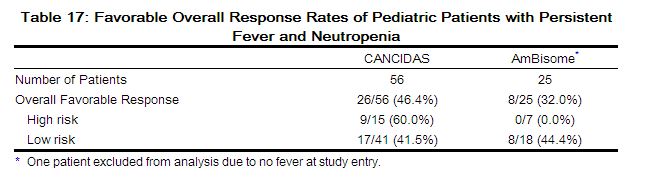
The first study, which enrolled 82 patients between 2 to 17 years of age, was a randomized, double-blind study comparing CANCIDAS (50 mg/m2 IV once daily following a 70-mg/m2 loading dose on Day 1 [not to exceed 70 mg daily]) to AmBisome (3 mg/kg IV daily) in a 2:1 treatment fashion (56 on caspofungin, 26 on AmBisome) as empirical therapy in pediatric patients with persistent fever and neutropenia. The study design and criteria for efficacy assessment were similar to the study in adult patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients were stratified based on risk category (high-risk patients had undergone allogeneic stem cell transplantation or had relapsed acute leukemia). Twenty-seven percent of patients in both treatment groups were high risk. Favorable overall response rates of pediatric patients with persistent fever and neutropenia are presented in Table 17.
 |
The second study was a prospective, open-label, non-comparative study estimating the safety and efficacy of caspofungin in pediatric patients (ages 3 months to 17 years) with candidemia and other Candida infections, esophageal candidiasis, and invasive aspergillosis (as salvage therapy). The study employed diagnostic criteria which were based on established EORTC/MSG criteria of proven or probable infection; these criteria were similar to those criteria employed in the adult studies for these various indications. Similarly, the efficacy time points and endpoints used in this study were similar to those employed in the corresponding adult studies [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3, and 14.4)]. All patients received CANCIDAS at 50 mg/m2 IV once daily following a 70-mg/m2 loading dose on Day 1 (not to exceed 70 mg daily). Among the 49 enrolled patients who received CANCIDAS, 48 were included in the efficacy analysis (one patient excluded due to not having a baseline Aspergillus or Candida infection). Of these 48 patients, 37 had candidemia or otherCandida infections, 10 had invasive aspergillosis, and 1 patient had esophageal candidiasis. Most candidemia and other Candida infections were caused by C. albicans (35%), followed by C. parapsilosis (22%), C. tropicalis (14%), and C. glabrata (11%). The favorable response rate, by indication, at the end of caspofungin therapy was as follows: 30/37 (81%) in candidemia or other Candida infections, 5/10 (50%) in invasive aspergillosis, and 1/1 in esophageal candidiasis.[1]
References
Adapted from the FDA Package Insert.