Aortic stenosis gross pathology
|
Aortic Stenosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Percutaneous Aortic Balloon Valvotomy (PABV) or Aortic Valvuloplasty |
|
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) |
|
Case Studies |
|
Aortic stenosis gross pathology On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Aortic stenosis gross pathology |
|
Directions to Hospitals Treating Aortic stenosis gross pathology |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Aortic stenosis gross pathology |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editors-In-Chief: Claudia P. Hochberg, M.D. [2], Abdul-Rahman Arabi, M.D. [3], Keri Shafer, M.D. [4], Priyamvada Singh, MBBS [5], Aysha Anwar, M.B.B.S[6]; Assistant Editor-In-Chief: Kristin Feeney, B.S. [7]
Overview
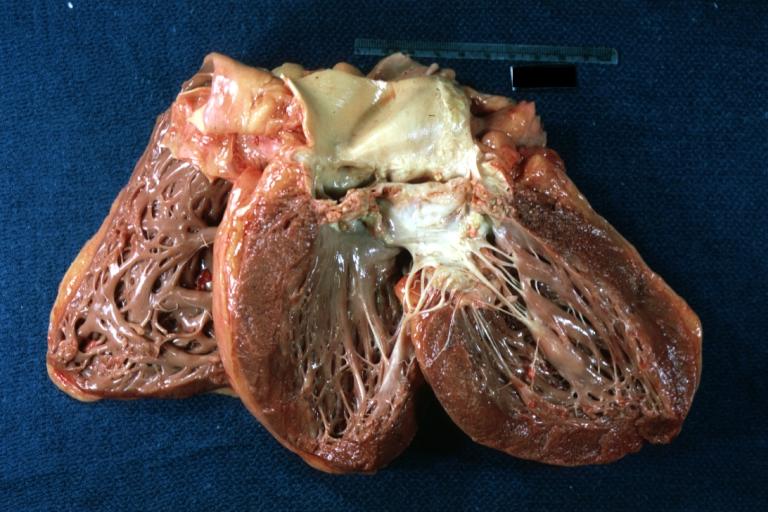
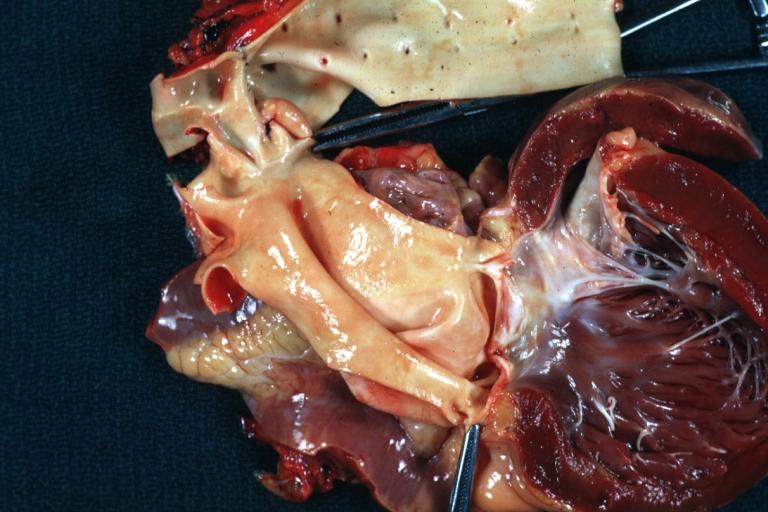
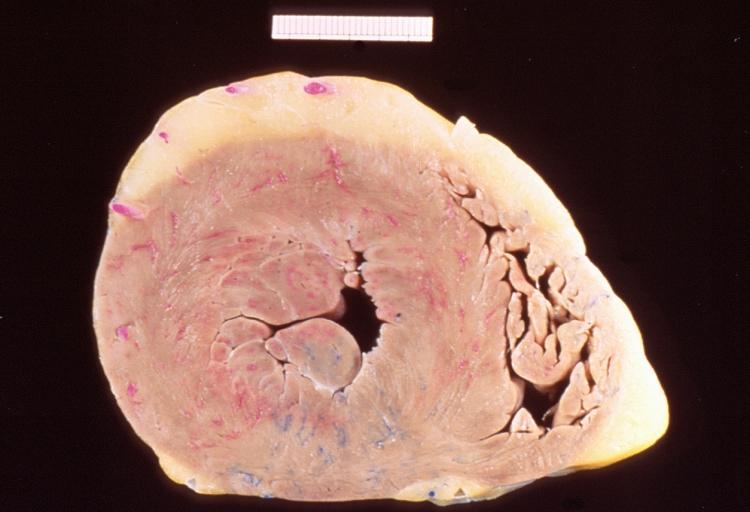
Gross anatomy dissection may be used as a diagnostic tool in the evaluation of aortic stenosis. Common findings associated with aortic stenosis include left ventricular hypertrophy and heart block.
Pathological Findings
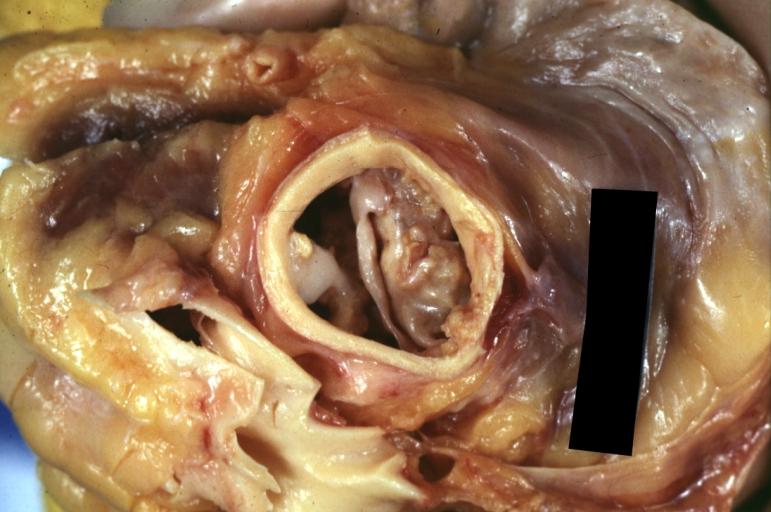
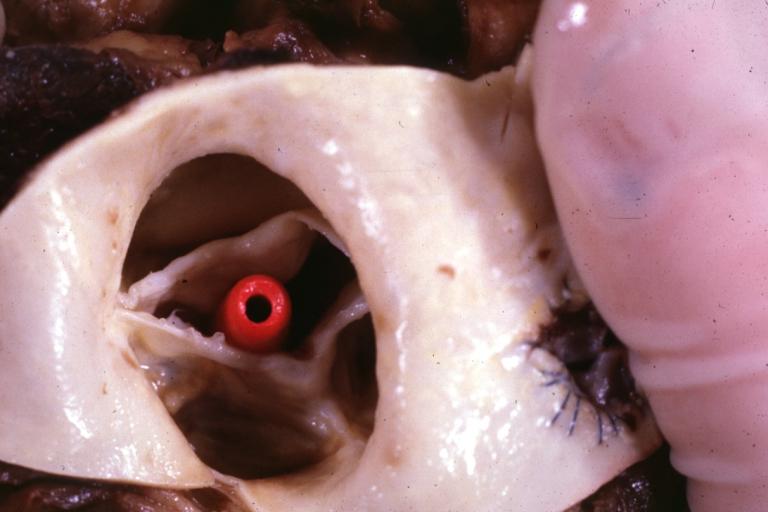
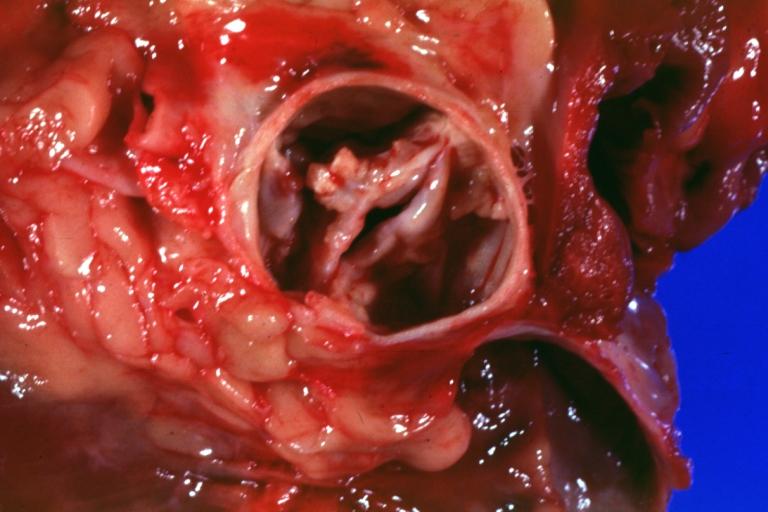
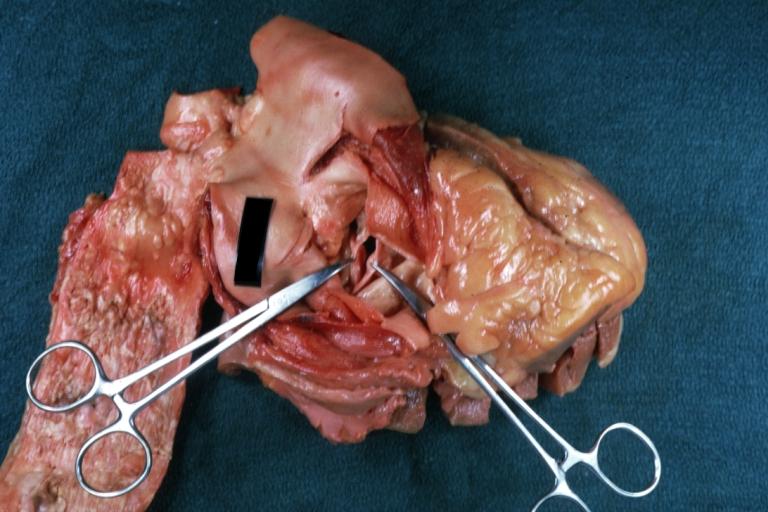
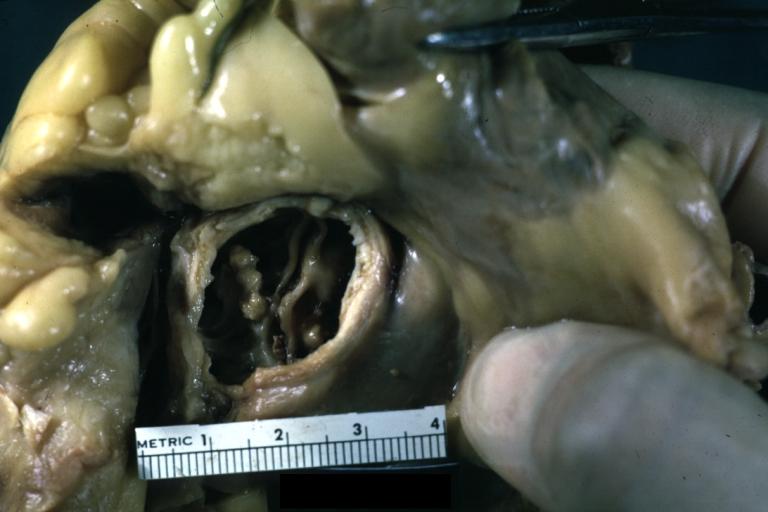
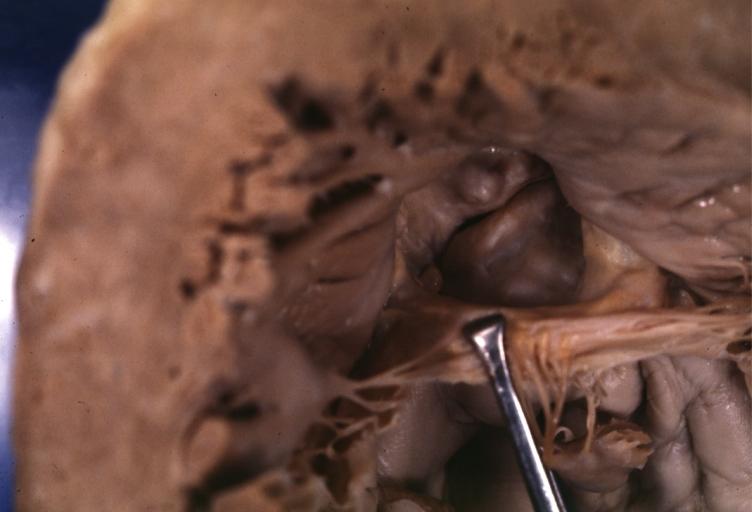
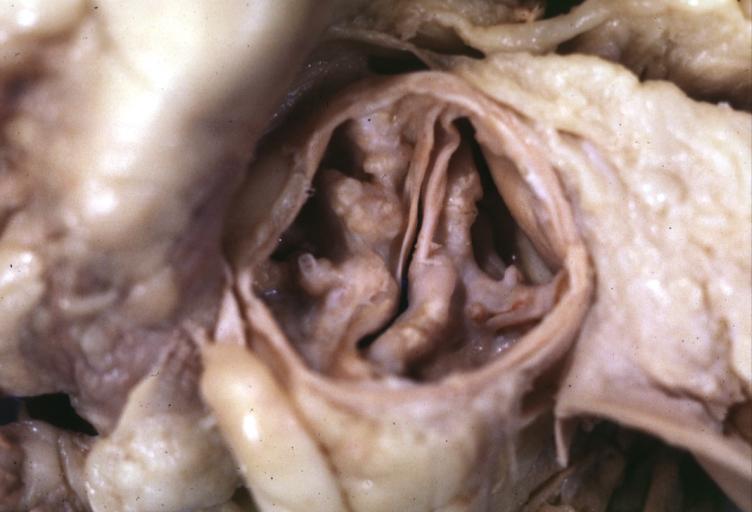
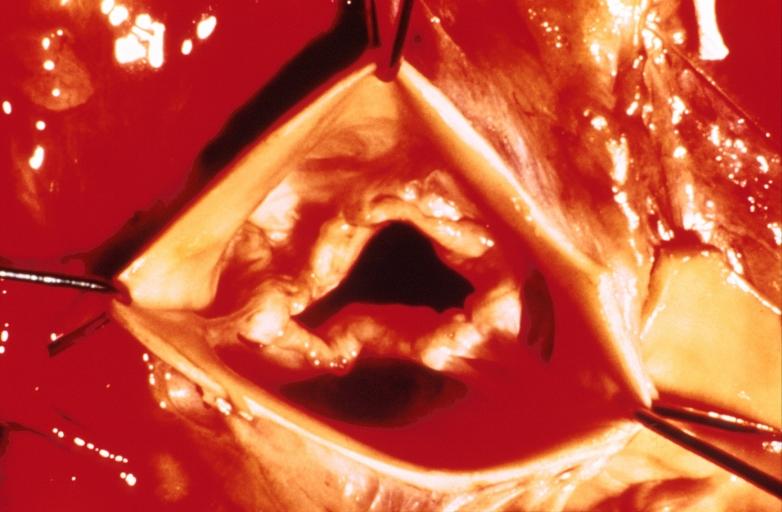
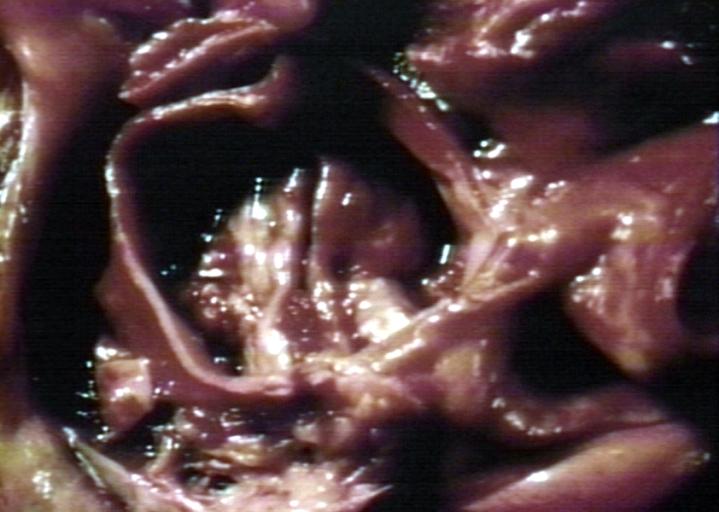
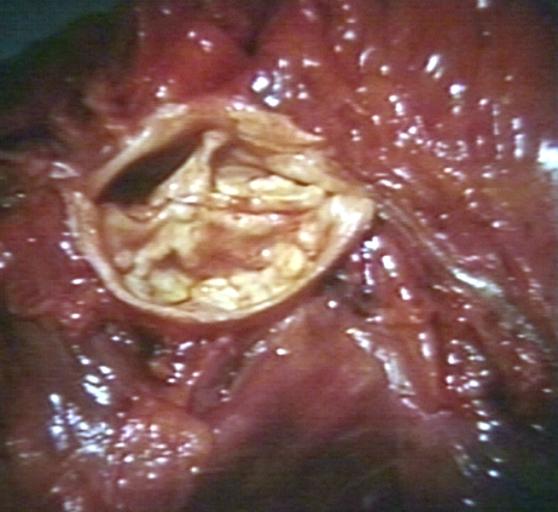
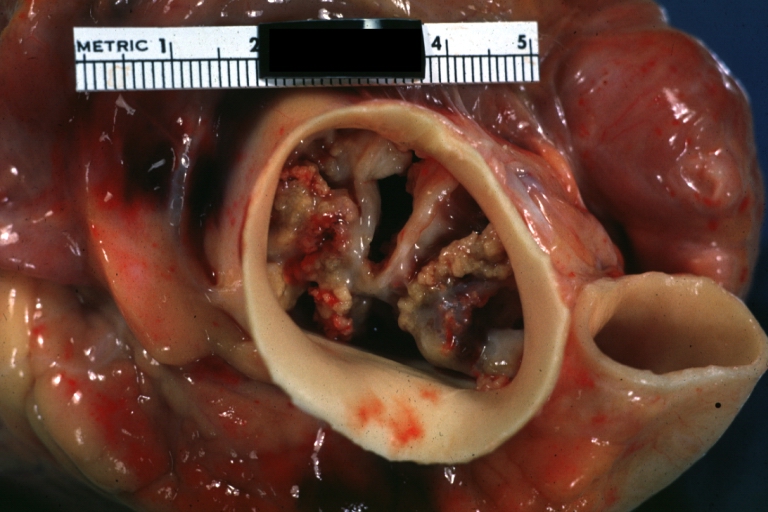
Pathological findings of congenital or acquired aortic stenosis in adults results in thickening and calcification of aortic valve. Following patterns may be seen:[1]
- Calcified bicuspid valve involving anterior or posterior cusps
- Calcified aortic valve cusps with fusion of commissures seen in post rheumatic cases
- Degenerative calcific aortic stenosis which shows sinuses of valsalva filled with calcium deposits seen in age >70
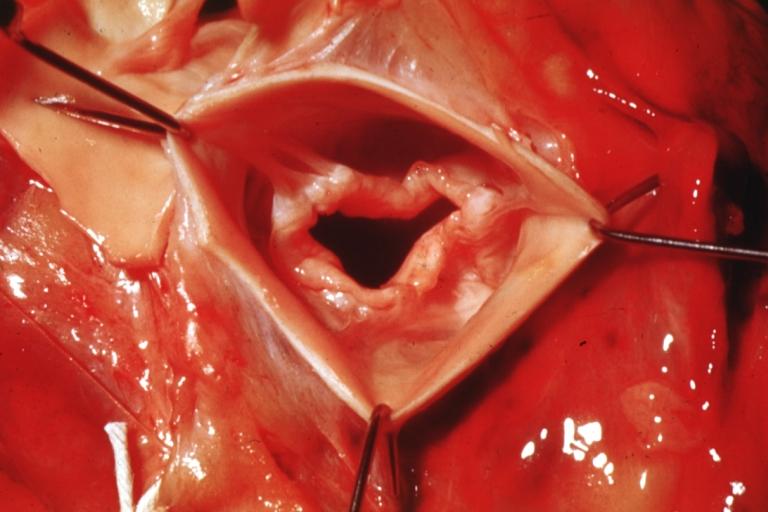
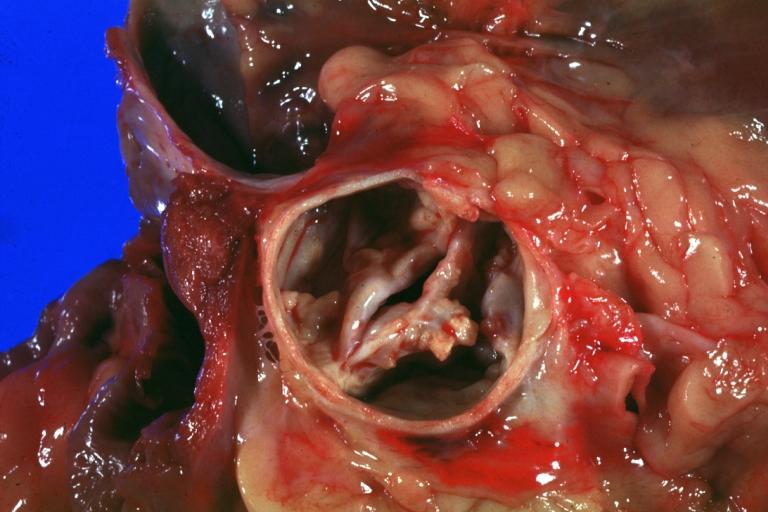
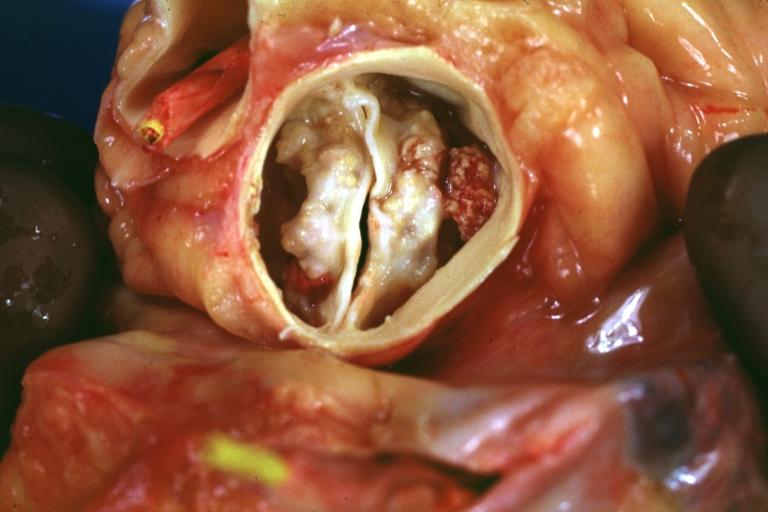
Images shown below are courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission. © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid valve: Gross; excellent image of bicuspid and calcific valve showing a false raphe.
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid valve: Gross; good example of bicuspid valve
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid valve: Gross; image of bicuspid aortic valve, an excellent example
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid valve: Gross; close-up image of bicuspid aortic valve.
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid valve: Gross; close-up image of bicuspid aortic valve.
-
Bicuspid aortic valve
-
Gross natural color opened first portion aortic arch with bicuspid aortic valve shows stenosis and aortic root is dilated
-
Aortic Stenosis Bicuspid: Gross; natural color opened left ventricular outflow tract with calcific masses on valve as well as anterior leaflet mitral valve probably did not cause significant stenosis
-
Bicuspid Aortic Valve with Repaired Aorta Coarctation: Gross natural color opened left ventricular outflow tract with uncomplicated bicuspid aortic valve repaired coarctation barely visible ruptured postoperative young female with ovaries Turner mosaic not ruled out
-
Bicuspid Aortic Stenosis: Gross; fixed tissue
-
Aortic Stenosis, Bicuspid: Gross; fixed tissue view of stenotic valve through ventricular outlet track
-
Aortic Stenosis Bicuspid: Gross; fixed tissue. Bicuspid valve and false raphe classical
-
Bicuspid aortic valve
-
Bicuspid aortic valve
-
Bicuspid aortic valve
-
Left ventricular hypertrophy due to bicuspid aortic valve
-
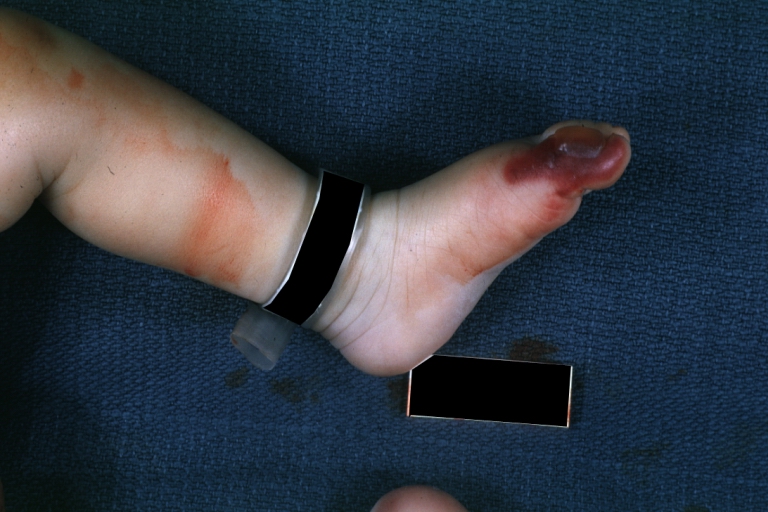
Congenital aortic stenosis: Gangrene toe In Infant: Gross, natural color, 1 month old child with congenital aortic stenosis
-
Unicuspid aortic stenosis
References
- ↑ Normand J, Loire R, Zambartas C (1988). "The anatomical aspects of adult aortic stenosis". Eur Heart J. 9 Suppl E: 31–6. PMID 3402479.