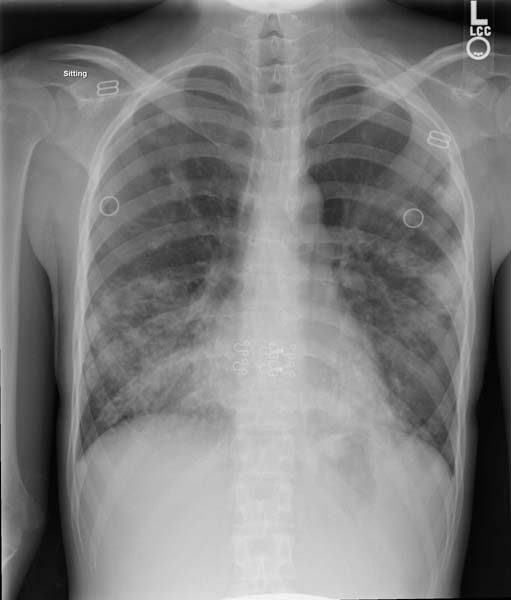
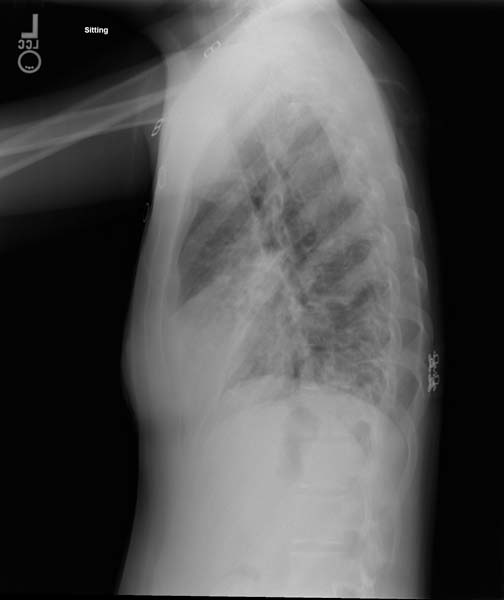
Tuberculosis chest x ray
|
Tuberculosis Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Tuberculosis chest x ray On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Tuberculosis chest x ray |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Tuberculosis chest x ray |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Overview
A posterior-anterior chest radiography is used to detect chest abnormalities. Lesions may appear anywhere in the lungs and may differ in size, shape, density, and cavitation. These abnormalities may suggest TB, but cannot be used to definitively diagnose TB. However, a chest radiograph may be used to rule out the possibility of pulmonary TB in a person who has had a positive reaction to a TST or TB blood test and no symptoms of disease.
Chest X-Ray
A posterior-anterior chest X-ray is the standard view used; other views (lateral or lordotic) or CT scans may be necessary.
In active pulmonary TB, infiltrates or consolidations and/or cavities are often seen in the upper lungs with or without mediastinal or hilar lymphadenopathy or pleural effusions (tuberculous pleurisy). However, lesions may appear anywhere in the lungs. In miliary TB, a pattern of many tiny nodules throughout the lung fields is common. In HIV and other immunosuppressed persons, any abnormality may indicate TB or the chest X-ray may even appear entirely normal.
Old healed tuberculosis usually presents as pulmonary nodules in the hilar area or upper lobes, with or without fibrotic scars and volume loss. Bronchiectasis and pleural scarring may be present.
Nodules and fibrotic scars may contain slowly multiplying tubercle bacilli with the potential for future progression to active tuberculosis. Persons with these findings, if they have a positive tuberculin skin test reaction, should be considered high-priority candidates for treatment of latent infection regardless of age. Conversely, calcified nodular lesions (calcified granuloma) pose a very low risk for future progression to active tuberculosis.
Abnormalities on chest x-rays may be suggestive of, but are never diagnostic of, tuberculosis. However, chest x-rays may be used to rule out the possibility of pulmonary TB in a person who has a positive reaction to the tuberculin skin test and no symptoms of disease.
Common Findings of Early Tuberculosis
Parenchymal Changes
Infiltration
- It is soft, nodular cotton like fluffy tiny opacities that merge into each other.
- Most common location for early lesions are the apico-posterior part (behind the outer borders of clavicle).
Cavity
- Circular, smooth, well defined, thin (acute) or thick walled (chronic), radiolucent area with no air-fluid levels with surrounding infiltrations.
- Commonly seen in the upper zone. Atypical cavities may be seen in lower zones. The common conditions in which lower zone cavities can be found are diabetes and HIV infections.
- Sometimes a radiolucent cavity may be seen within the tuberculosis cavity and is due to the presence of the fungal balls (commonly aspergillosis) within the cavities.
Common Finding in Healing Tuberculosis
Parenchymal Changes
Fibrosis
- Defined as opaque linear streak radiating towards the hilum of the lung.
- Compared to infiltrations, fibrotic changes are more opaque, well defined and may lead to mediastinal shifting or diaphragm pulling toward the affected lesions. A fibrotic lesion near to diaphragm may cause tenting of the diaphragm.
- Compensatory emphysema in cases with extensive fibrosis may be seen.
- Lung volume reduction may be seen.
Calcification
- Calcification looks denser than the bone density.
- It signifies old healed lesions.
- Calcification in hilar zone is due to calcification of the hilar lymph nodes.
Pleural Lesions
Pleural Effusion
- Obliteration and blunting of the costo phrenic angles.
- Depending on the amount of effusion the pleural effusion can be mild (at least 250 - 300 ml of fluid causes a mild obliteration of the costo-phrenic angle), moderate, and massive.
- It may cause mediastinal shifting depending on the amount of effusion.
Advanced Lesions in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A combination of all the lesions may be seen commonly termed as fibrocavitatory lesions.
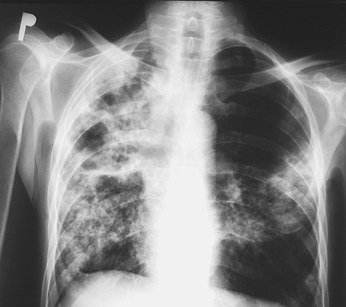
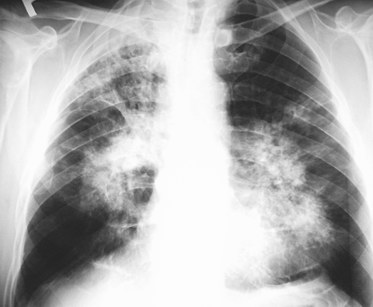
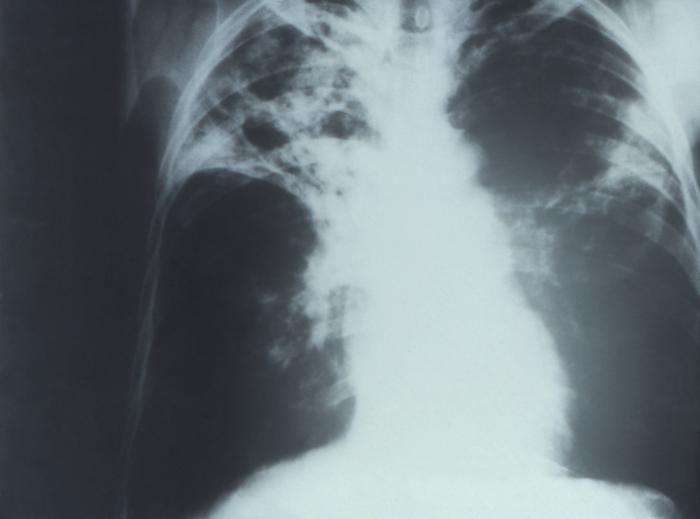
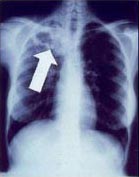
Chest X-Ray Images in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-
Bilateral Pulmonary Tuberculosis
-
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Common Findings of Miliary Tuberculosis on Chest X-Ray
- Fine, pin point approximately 1-2mm in size, discrete, uniform distribution, soft mottlings.
- Commonly found throughout both the lungs.
Chest X-Ray Images in Miliary Tuberculosis
-
Miliary Tuberculosis
-
Miliary Tuberculosis
-
Miliary Tuberculosis
CDC Guidelines for Evaluating Chest X-Ray[1]
A medical examination is mandatory for all refugees coming to the U.S. and all applicants outside the U.S. applying for an immigrant visa. The purpose of the medical examination is to identify applicants with inadmissible health-related conditions such as active tuberculosis. Outside the U.S., medical examinations are performed by approximately 400 physicians (panel physicians) selected by United States Department of State consular officials. In the U.S., medical examinations are performed by approximately 3,000 physicians (civil surgeons) designated by district directors of the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. Guidelines were developed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The chest X-ray and classification worksheet is designed to group findings into categories based on their likelihood of being related to TB or non-TB conditions needing medical follow-up (either at the time of the chest X-ray or after resettlement).
Abnormal Findings
Chest X-Ray Findings that Can Suggest Active TB
This category comprises all findings typically associated with active pulmonary TB. An applicant with any of the following findings must submit sputum specimens for examination.
- Infiltrate or consolidation—Opacification of airspaces within the lung parenchyma. Consolidation or infiltrate can be dense or patchy and might have irregular, ill-defined, or hazy borders.
- Any cavitary lesion—Lucency (darkened area) within the lung parenchyma, with or without irregular margins that might be surrounded by an area of airspace consolidation or infiltrates, or by nodular or fibrotic (reticular) densities, or both. The walls surrounding the lucent area can be thick or thin. Calcification can exist around a cavity.
- Nodule with poorly defined margins—Round density within the lung parenchyma, also called a tuberculoma. Nodules included in this category are those with margins that are indistinct or poorly defined. The surrounding haziness can be either subtle or readily apparent and suggests coexisting airspace consolidation.
- Pleural effusion—Presence of a significant amount of fluid within the pleural space. This finding must be distinguished from blunting of the costophrenic angle, which may or may not represent a small amount of fluid within the pleural space (except in children when even minor blunting must be considered a finding that can suggest active TB).
- Hilar or mediastinal lymphadenopathy (bihilar lymphadenopathy)—Enlargement of lymph nodes in one or both hila or within the mediastinum, with or without associated atelectasis or consolidation.
- Linear, interstitial disease (in children only)—Prominence of linear, interstitial (septal) markings.
- Other—Any other finding suggestive of active TB, such as miliary TB. Miliary findings are nodules of millet size (1 to 2 millimeters) distributed throughout the parenchyma.
Chest X-Ray Findings that Can Suggest Inactive TB
This category includes findings that are suggestive of prior TB, that is inactive. It must be remembered that assessments of the activity of TB cannot be made accurately on the basis of a single radiograph alone. If there is any question of active TB, sputum smears must be obtained. Furthermore, if the applicant has any signs or symptoms of TB, sputum smears must be obtained. Obtaining sputum smears is necessary if there is any question of active TB. Therefore, any applicant might have findings grouped in this category, but still have active TB as suggested by:
- The presence of signs or symptoms of TB (Class B1).
- Sputum smears positive for AFB (Class A).
- Discrete fibrotic scar or linear opacity—Discrete linear or reticular densities within the lung. The edges of these densities should be distinct and there should be no suggestion of airspace opacification or haziness between or surrounding these densities. Calcification can be present within the lesion and then the lesion is called a fibrocalcific scar.
- Discrete nodule(s) without calcification—One or more nodular densities with distinct borders and without any surrounding airspace opacification. Nodules are generally round or have rounded edges. These features allow them to be distinguished from infiltrates or airspace opacities. To be included here, these nodules must be noncalcified. Nodules that are calcified are included in the category: 'Other X-Ray Findings, No follow-up Needed'.
- Discrete fibrotic scar with volume loss or retraction—Discrete linear densities with reduction in the space occupied by the upper lobe. Associated signs include upward deviation of the fissure or hilum on the corresponding side with asymmetry of the volumes of the two thoracic cavities.
- Discrete nodule(s) with volume loss or retraction—One or more nodular densities with distinct borders and no surrounding airspace opacification with reduction in the space occupied by the upper lobe. Nodules are generally round or have rounded edges.
- Other—Any other finding suggestive of prior TB, such as upper lobe bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis is bronchial dilation with bronchial wall thickening.
Other Chest X-Ray Findings
Follow-up
This category includes findings that suggest the need for a follow-up evaluation for non-TB conditions either at the time of the chest X-ray or after resettlement of the applicant in the United States.
- Musculoskeletal abnormalities—New bony fractures or radiographically apparent bony abnormalities that need follow-up.
- Cardiac abnormalities—Cardiac enlargement or anomalies, vascular abnormalities, or any other radiographically apparent cardiovascular abnormality of significant nature to require follow-up.
- Pulmonary abnormalities—Pulmonary finding of a non-TB nature, such as a mass, that needs follow-up.
- Other—Any other finding that the panel physician believes needs follow-up, but is not one of the above.
Follow-up Not Required
This category includes findings that are minor and not suggestive of TB disease. These findings require no follow-up evaluation after resettlement of the applicant.
- Pleural thickening—Irregularity or abnormal prominence of the pleural margin, including apical capping (thickening of the pleura in the apical region). Pleural thickening can be calcified.
- Diaphragmatic tenting—A localized accentuation of the normal convexity of the hemidiaphragm as if 'pulled upwards by a string'.
- Blunting of costophrenic angle (in adults)—Loss of sharpness of one or both costophrenic angles. Blunting can be related to a small amount of fluid in the pleural space or to pleural thickening and, by itself, is a non-specific finding (except in children, when even minor blunting may suggest active TB). In contrast a large pleural effusion, or the presence of a significant amount of fluid in the pleural space, may be a sign of active TB at any age.
- Solitary calcified nodules or granuloma—Discrete calcified nodule or granuloma, or calcified lymph node. The calcified nodule can be within the lung, hila, or mediastinum. The borders must be sharp, distinct, and well defined. This was considered a Class B3 TB in the past; however, Class B3 has been omitted from the classification scheme because it has not been found to be associated with active TB.
- Minor musculoskeletal findings—Minor findings needing no follow-up.
- Minor cardiac findings—Minor findings needing no follow-up.
References
- ↑ {{cite web: url=http://www.cdc.gov/immigrantrefugeehealth/exams/medical-examination.html%7C title= CDC Medical Examination of Immigrants and Refugees