Posterior interventricular artery: Difference between revisions
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Gerald Chi (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{CMG}} | {{CMG}} | ||
{{Infobox Artery | | {{Infobox Artery | | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
==Overview== | ==Overview== | ||
The posterior interventricular artery (PIV), or posterior descending artery (PDA), is | The posterior interventricular artery (PIV), or posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the [[posterior interventricular sulcus]] to the [[apex of the heart]] where it meets with the [[anterior interventricular artery]]. It supplies the posterior one third of the [[interventricular septum]]. The remaining anterior two thirds is supplied by the anterior interventricular artery which is a septal branch of the [[left anterior descending artery]], which is a branch of [[left coronary artery]]. | ||
It is typically a branch of the [[right coronary artery]] (70%, known as right dominance). Alternatively, the PIV can be a branch of the [[circumflex coronary artery]] (10%, known as left dominance) which itself is a branch of the [[left coronary artery]]. It can also be supplied by an anastomosis of the left and right coronary artery (20%, known as co-dominance).<ref name="Hurst">{{cite book | last=Fuster | first=V | coauthors=Alexander RW, O'Rourke RA | title=Hurst's The Heart | publisher=McGraw-Hill | year=2001 | page=53 | edition=10th | isbn=0-07-135694-0 }}</ref> Variants have been reported.<ref name="pmid9283726">{{cite journal |author=Topaz O, Holdaway B, Bailey NT, Vetrovec GW |title=Anatomic variant of the posterior interventricular coronary artery: implications for coronary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction |journal=Clin Anat |volume=10 |issue=5 |pages=303–6 |year=1997 |pmid=9283726 |doi=10.1002/(SICI)1098-2353(1997)10:5<303::AID-CA2>3.0.CO;2-R}}</ref> | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
==Additional images== | |||
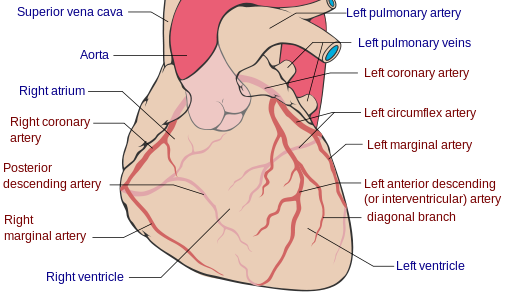
[[File:Coronary arteries.png|thumb|300px|left|Coronary arteries (labeled in red text) and other major landmarks (in blue text). Posterior descending artery is labeled at left.]] | |||
{{Arteries of chest}} | {{Arteries of chest}} | ||
{{Coronary Angiography}} | |||
[[Category:Cardiology]] | [[Category:Cardiology]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 43: | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular system]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular system]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date]] | ||
[[Category:Up-To-Date Cardiology]] | [[Category:Up-To-Date Cardiology]] | ||
{{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | {{WikiDoc Help Menu}} | ||
{{WikiDoc Sources}} | {{WikiDoc Sources}} | ||
Latest revision as of 04:26, 2 September 2013
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Template:Infobox Artery
Overview
The posterior interventricular artery (PIV), or posterior descending artery (PDA), is an artery running in the posterior interventricular sulcus to the apex of the heart where it meets with the anterior interventricular artery. It supplies the posterior one third of the interventricular septum. The remaining anterior two thirds is supplied by the anterior interventricular artery which is a septal branch of the left anterior descending artery, which is a branch of left coronary artery.
It is typically a branch of the right coronary artery (70%, known as right dominance). Alternatively, the PIV can be a branch of the circumflex coronary artery (10%, known as left dominance) which itself is a branch of the left coronary artery. It can also be supplied by an anastomosis of the left and right coronary artery (20%, known as co-dominance).[1] Variants have been reported.[2]
References
- ↑ Fuster, V (2001). Hurst's The Heart (10th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 53. ISBN 0-07-135694-0. Unknown parameter
|coauthors=ignored (help) - ↑ Topaz O, Holdaway B, Bailey NT, Vetrovec GW (1997). "Anatomic variant of the posterior interventricular coronary artery: implications for coronary angioplasty in acute myocardial infarction". Clin Anat. 10 (5): 303–6. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2353(1997)10:5<303::AID-CA2>3.0.CO;2-R. PMID 9283726.
Additional images