Lidocaine (injection)
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Alonso Alvarado, M.D. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Lidocaine (injection) is a Adrenergic receptor agonist that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of ventricular arrhythmias such as those occurring in relation to acute myocardial infarction, or during cardiac manipulation, such as cardiac surgery. Common adverse reactions include a list of adverse reactions, separated by commas..
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Developed by: (Organisation)
- Class of Recommendation: (Class) (Link)
- Strength of Evidence: (Category A/B/C) (Link)
- Dosing Information/Recommendation
- (Dosage)
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition 1
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 2
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Condition 3
- Dosing Information
- (Dosage)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to local anesthetics of the amide type.
- Stokes-Adams syndrome.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Patients with severe degrees of sinoatrial, atrioventricular, or intraventricular block in the absence of an artificial pacemaker.
Warnings
- Systemic toxicity may result in manifestations of central nervous system depression (sedation) or irritability (twitching), which may progress to frank convulsions accompanied by respiratory depression and/or arrest. Early recognition of premonitory signs, assurance of adequate oxygenation and, where necessary, establishment of artificial airway with ventilatory support are essential to management of this problem. Should convulsions persist despite ventilatory therapy with oxygen, small increments of anticonvulsant drugs may be used intravenously. Examples of such agents include benzodiazepines (e.g., diazepam), ultra short-acting barbiturates (e.g., thiopental or thiamylal), or a short-acting barbiturate (e.g., pentobarbital or secobarbital). If the patient is under anesthesia, a short-acting muscle relaxant (e.g., succinylcholine) may be used. Longer acting drugs should be used only when recurrent convulsions are evidenced.
- Should circulatory depression occur, vasopressors may be used.
- Constant electrocardiographic monitoring is essential to the proper administration of lidocaine hydrochloride. Signs of excessive depression of cardiac electrical activity such as sinus node dysfunction, prolongation of the P-R interval and QRS complex or the appearance or aggravation of arrhythmias, should be followed by flow adjustment and, if necessary, prompt cessation of the intravenous infusion of this agent. Occasionally, acceleration of ventricular rate may occur when lidocaine hydrochloride is administered to patients with atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation.
Precautions
General
- Caution should be employed in the use of lidocaine hydrochloride in patients with severe liver disease or kidney disease because accumulation of the drug or metabolites may occur.
- Lidocaine hydrochloride should be used with caution in the treatment of patients with hypovolemia, severe congestive heart failure, shock, and all forms of heart block. In patients with sinus bradycardia or incomplete heart block, the administration of lidocaine hydrochloride intravenously for the elimination of ventricular ectopic beats, without prior acceleration in heart rate (e.g., by atropine, isoproterenol or electric pacing), may promote more frequent and serious ventricular arrhythmias or complete heart block.
- Dosage should be reduced for children and for debilitated and/or elderly patients, commensurate with their age and physical status.
- The safety of amide local anesthetic agents in patients with genetic predisposition to malignant hyperthermia has not been fully assessed; therefore, lidocaine should be used with caution in such patients.
- In hospital environments where drugs known to be triggering agents for malignant hyperthermia (fulminant hypermetabolism) are administered, it is suggested that a standard protocol for management should be available.
- It is not known whether lidocaine may trigger this reaction; however, large doses resulting in significant plasma concentrations, as may be achieved by intravenous infusion, pose potential risk to these individuals. Recognition of early unexplained signs of tachycardia, tachypnea, labile blood pressure and metabolic acidosis may precede temperature elevation. Successful outcome is dependent on early diagnosis, prompt discontinuance of the triggering agent and institution of treatment including oxygen therapy, supportive measures and dantrolene.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Condition 2
Central Nervous System
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Cardiovascular
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Respiratory
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Gastrointestinal
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Hypersensitive Reactions
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Miscellaneous
- (list/description of adverse reactions)
Postmarketing Experience
(Description)
Drug Interactions
- Drug 1
- Drug 2
- Drug 3
- Drug 4
- Drug 5
Drug 1
(Description)
Drug 2
(Description)
Drug 3
(Description)
Drug 4
(Description)
Drug 5
(Description)
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category (FDA):
(Description)
Pregnancy Category (AUS):
(Description)
Labor and Delivery
(Description)
Nursing Mothers
(Description)
Pediatric Use
(Description)
Geriatic Use
(Description)
Gender
(Description)
Race
(Description)
Renal Impairment
(Description)
Hepatic Impairment
(Description)
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
(Description)
Immunocompromised Patients
(Description)
Others
(Description)
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
(Oral/Intravenous/etc)
Monitoring
Condition 1
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 2
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
Condition 3
(Description regarding monitoring, from Warnings section)
IV Compatibility
Solution
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Y-Site
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Admixture
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Syringe
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
TPN/TNA
Compatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Not Tested
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Variable
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Incompatible
- Solution 1
- Solution 2
- Solution 3
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Chronic Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
(Description)
Management
(Description)
Pharmacology
Lidocaine (injection)
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ? | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | ? |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | ? |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | ? |
| Mol. mass | ? |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Mechanism of Action
Studies of the effects of therapeutic concentrations of lidocaine on the electrophysiological properties of mammalian Purkinje fibers have shown that lidocaine attenuates phase 4 diastolic depolarization, decreases automaticity and causes a decrease or no change in excitability and membrane responsiveness.
Structure
Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection USP, is a sterile, aqueous solution of lidocaine, an antiarrhythmic agent, prepared with the aid of hydrochloric acid. It is intended for intravenous administration by either direct injection or continuous infusion.
Lidocaine hydrochloride is designated 2-(Diethylamino)-2’, 6’-acetoxylidide monohydrochloride and isrepresented by the following structural formula:
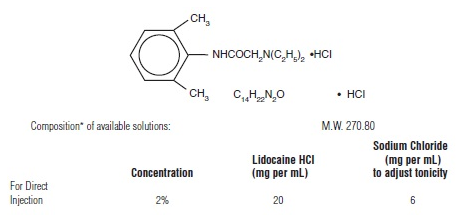
- pH of the above solution adjusted with sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid to finished product pH limits between 5 and 7.
The medication and fluid pathway of these disposable syringes are sterile and nonpyrogenic in the original, unopened package with component caps in place. These dosage forms do not contain preservatives; once the unit is assembled and used, any remaining portion of the solution must be discarded with the entire unit.
Pharmacodynamics
Action potential duration and effective refractory period of Purkinje fibers are decreased, while the ratio of effective refractory period to action potential duration is increased. Action potential duration and effective refractory period of ventricular muscle are also decreased. Effective refractory period of the AV node may increase, decrease or remain unchanged, and atrial effective refractory period is unchanged. Lidocaine raises the ventricular fibrillation threshold. No significant interactions between lidocaine and the autonomic nervous system have been described and consequently lidocaine has little or no effect on autonomic tone.
Clinical electrophysiological studies with lidocaine have demonstrated no change in sinus node recovery time or sinoatrial conduction time. AV nodal conduction time is unchanged or shortened, and His-Purkinje conduction time is unchanged.
Hemodynamics
At therapeutic doses, lidocaine has minimal hemodynamic effects in normal subjects and in patients with heart disease. Lidocaine has been shown to cause no, or minimal, decrease in ventricular contractility, cardiac output, arterial pressure or heart rate.
Pharmacokinetics
Lidocaine is rapidly metabolized by the liver, and less than 10% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine. Oxidative N dealkylation, a major pathway of metabolism, results in the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide. The pharmacological/toxicological activities of these metabolites are similar to, but less potent than, lidocaine. The primary metabolite in urine is a conjugate of 4-hydroxy-2,6,-dimethylaniline.
The elimination half-life of lidocaine following an intravenous bolus injection is typically 1.5 to 2 hours. There are data that indicate that the half-life may be 3 hours or longer following infusions of greater than 24 hours.
Because of the rapid rate at which lidocaine is metabolized, any condition that alters liver function, including changes in liver blood flow, which could result from severe congestive heart failure in shock, may alter lidocaine kinetics. The half-life may be two-fold or more, greater in patients with liver dysfunction. Renal dysfunction does not affect lidocaine kinetics, but may increase the accumulation of metabolites. Therapeutic effects of lidocaine are generally associated with plasma levels at 6 to 25 μmole/L (1.5 to 6 mcg free base per mL). The blood to plasma distribution ratio is approximately 0.84. Objective adverse manifestations become increasingly apparent with increasing plasma levels above 6 mcg free base per mL.
The plasma protein binding of lidocaine is dependent on drug concentration, and the fraction bound decreases with increasing concentration. At concentrations of 1 to 4 mcg free base per mL, 60 to 80 percent of lidocaine is protein bound. In addition to lidocaine concentration, the binding is dependent on the plasma concentration of the α-1-acid glycoprotein.
Lidocaine readily crosses the placental and blood-brain barriers. Dialysis has negligible effects on the kinetics of lidocaine.
Nonclinical Toxicology
(Description)
Clinical Studies
Condition 1
(Description)
Condition 2
(Description)
Condition 3
(Description)
How Supplied
(Description)
Storage
There is limited information regarding Lidocaine (injection) Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Lidocaine (injection) |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Lidocaine (injection) |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
(Patient Counseling Information)
Precautions with Alcohol
Alcohol-Lidocaine interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
There is limited information regarding Lidocaine (injection) Brand Names in the drug label.
Look-Alike Drug Names
- (Paired Confused Name 1a) — (Paired Confused Name 1b)
- (Paired Confused Name 2a) — (Paired Confused Name 2b)
- (Paired Confused Name 3a) — (Paired Confused Name 3b)
Drug Shortage Status
Drug Shortage
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.