Hepatic encephalopathy physical examination
|
Hepatic encephalopathy Microchapters |
|
Diagnosis |
|---|
|
Treatment |
|
Case Studies |
|
Hepatic encephalopathy physical examination On the Web |
|
American Roentgen Ray Society Images of Hepatic encephalopathy physical examination |
|
Risk calculators and risk factors for Hepatic encephalopathy physical examination |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1] Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief:
Please help WikiDoc by adding content here. It's easy! Click here to learn about editing.
Overview
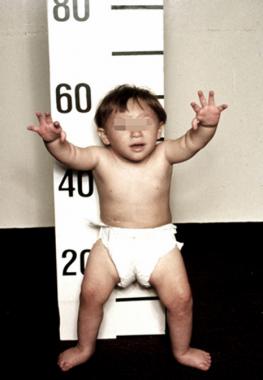
In addition to changed level of consciousness, the hallmark of hepatic encephalopathy on the physical examination is the presence of asterixis. This is detected by having the patient hold out his outstretched arms and hands and cock his wrists back. In the presence of asterixis, there is a non-synchronized, intermittent flapping motion at the wrists. Asterixis is not specific to hepatic encephalopathy. It may also be seen in states such as renal failure and carbon dioxide retention.
Physical Examination
Skin
- Signs of liver disease, such as yellow skin and eyes.
Nose
- Signs of liver disease, such as musty odor to the breath.
Abdomen
- Signs of liver disease, such fluid collection in the abdomen (ascites), and occasionally a musty odor urine.
Neurologic
Nervous system signs may change. Signs include:
- Coarse, "flapping" shaking of the hands when attempting to hold the arms out in front of the body and lift the hands.
- Abnormal mental status, particularly cognitive (thinking) tasks such as connecting numbers with lines.
References
Overview
Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance]. Physical examination of patients with [disease name] is usually remarkable for [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
Common physical examination findings of [disease name] include [finding 1], [finding 2], and [finding 3].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is diagnostic of [disease name].
OR
The presence of [finding(s)] on physical examination is highly suggestive of [disease name].
Physical Examination
- Physical examination of patients with hepatic encephalopathy is usually remarkable for: signs of personality changes, signs of altered level of consciousness, observing jerking movement of the limbs(asterixis), slurred speech, writing disturbances, voice monotonous and Impaired memory.
- The presence of asterixis on physical examination is highly suggestive of hepatic encephalopathy.
Appearance of the Patient
- Patients with [disease name] usually appear [general appearance].
Vital Signs
- High-grade / low-grade fever
- Hypothermia / hyperthermia may be present
- Tachycardia with regular pulse or (ir)regularly irregular pulse
- Bradycardia with regular pulse or (ir)regularly irregular pulse
- Tachypnea / bradypnea
- Kussmal respirations may be present in _____ (advanced disease state)
- Weak/bounding pulse / pulsus alternans / paradoxical pulse / asymmetric pulse
- High/low blood pressure with normal pulse pressure / wide pulse pressure / narrow pulse pressure
Skin
- Cyanosis
- Jaundice
- Pallor
- Bruises
-
Description (Adapted from Dermatology Atlas)
-
Description (Adapted from Dermatology Atlas)
HEENT
- Abnormalities of the head/hair may include ___
- Evidence of trauma
- Icteric sclera
- Nystagmus
- Extra-ocular movements may be abnormal
- Pupils non-reactive to light / non-reactive to accomodation / non-reactive to neither light nor accomodation
- Ophthalmoscopic exam may be abnormal with findings of ___
- Hearing acuity may be reduced
- Weber test may be abnormal (Note: A positive Weber test is considered a normal finding / A negative Weber test is considered an abnormal finding. To avoid confusion, you may write "abnormal Weber test".)
- Rinne test may be positive (Note: A positive Rinne test is considered a normal finding / A negative Rinne test is considered an abnormal finding. To avoid confusion, you may write "abnormal Rinne test".)
- Exudate from the ear canal
- Tenderness upon palpation of the ear pinnae / tragus (anterior to ear canal)
- Inflamed nares / congested nares
- Purulent exudate from the nares
- Facial tenderness
- Erythematous throat with/without tonsillar swelling, exudates, and/or petechiae
Neck
- Jugular venous distension
- Carotid bruits may be auscultated unilaterally/bilaterally using the bell/diaphragm of the otoscope
- Lymphadenopathy (describe location, size, tenderness, mobility, and symmetry)
- Thyromegaly / thyroid nodules
- Hepatojugular reflux
Lungs
- Asymmetric chest expansion / Decreased chest expansion
- Lungs are hypo/hyperresonant
- Fine/coarse crackles upon auscultation of the lung bases/apices unilaterally/bilaterally
- Rhonchi
- Vesicular breath sounds / Distant breath sounds
- Expiratory/inspiratory wheezing with normal / delayed expiratory phase
- Wheezing may be present
- Egophony present/absent
- Bronchophony present/absent
- Normal/reduced tactile fremitus
Heart
- Chest tenderness upon palpation
- PMI within 2 cm of the sternum (PMI) / Displaced point of maximal impulse (PMI) suggestive of ____
- Heave / thrill
- Friction rub
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
- Gallops
- A high/low grade early/late systolic murmur / diastolic murmur best heard at the base/apex/(specific valve region) may be heard using the bell/diaphgram of the otoscope
Abdomen
- Abdominal distention
- Abdominal tenderness in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Rebound tenderness (positive Blumberg sign)
- A palpable abdominal mass in the right/left upper/lower abdominal quadrant
- Guarding may be present
- Hepatomegaly / splenomegaly / hepatosplenomegaly
- Additional findings, such as obturator test, psoas test, McBurney point test, Murphy test
Back
- Point tenderness over __ vertebrae (e.g. L3-L4)
- Sacral edema
- Costovertebral angle tenderness bilaterally/unilaterally
- Buffalo hump
Genitourinary
- A pelvic/adnexal mass may be palpated
- Inflamed mucosa
- Clear/(color), foul-smelling/odorless penile/vaginal discharge
Neuromuscular
- Patient is usually oriented to persons, place, and time
- Altered mental status
- Glasgow coma scale is ___ / 15
- Clonus may be present
- Hyperreflexia / hyporeflexia / areflexia
- Positive (abnormal) Babinski / plantar reflex unilaterally/bilaterally
- Muscle rigidity
- Proximal/distal muscle weakness unilaterally/bilaterally
- ____ (finding) suggestive of cranial nerve ___ (roman numerical) deficit (e.g. Dilated pupils suggestive of CN III deficit)
- Unilateral/bilateral upper/lower extremity weakness
- Unilateral/bilateral sensory loss in the upper/lower extremity
- Positive straight leg raise test
- Abnormal gait (describe gait: e.g. ataxic (cerebellar) gait / steppage gait / waddling gait / choeiform gait / Parkinsonian gait / sensory gait)
- Positive/negative Trendelenburg sign
- Unilateral/bilateral tremor (describe tremor, e.g. at rest, pill-rolling)
- Normal finger-to-nose test / Dysmetria
- Absent/present dysdiadochokinesia (palm tapping test)
Extremities
- Clubbing
- Cyanosis
- Pitting/non-pitting edema of the upper/lower extremities
- Muscle atrophy
- Fasciculations in the upper/lower extremity