Febuxostat: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 343: | Line 343: | ||
|useInNursing= | |useInNursing= | ||
*Febuxostat is excreted in the milk of rats. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ULORIC is administered to a nursing woman. | |||
|useInPed= | |useInPed= | ||
*Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established. | |||
|useInGeri= | |useInGeri= | ||
*No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients. Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of ULORIC, 16% were 65 and over, while 4% were 75 and over. Comparing subjects in different age groups, no clinically significant differences in safety or effectiveness were observed but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. The Cmax and AUC24 of febuxostat following multiple oral doses of ULORIC in geriatric subjects (≥65 years) were similar to those in younger subjects (18 to 40 years) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | |||
|useInGender= | |useInGender= | ||
| Line 358: | Line 361: | ||
|useInRenalImpair= | |useInRenalImpair= | ||
*No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (Clcr 30 to 89 mL/min). The recommended starting dose of ULORIC is 40 mg once daily. For patients who do not achieve a sUA less than 6 mg/dL after two weeks with 40 mg, ULORIC 80 mg is recommended. | |||
*There are insufficient data in patients with severe renal impairment (Clcr less than 30 mL/min); therefore, caution should be exercised in these patients. | |||
|useInHepaticImpair= | |useInHepaticImpair= | ||
*No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B). No studies have been conducted in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C); therefore, caution should be exercised in these patients. | |||
|useInReproPotential= | |useInReproPotential= | ||
| Line 374: | Line 381: | ||
* Oral | * Oral | ||
|monitoring= | |monitoring= | ||
There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | There is limited information regarding <i>Monitoring</i> of {{PAGENAME}} in the drug label. | ||
<!--IV Compatibility--> | <!--IV Compatibility--> | ||
| Line 397: | Line 400: | ||
====Signs and Symptoms==== | ====Signs and Symptoms==== | ||
* | *ULORIC was studied in healthy subjects in doses up to 300 mg daily for seven days without evidence of dose-limiting toxicities. No overdose of ULORIC was reported in clinical studies. | ||
====Management==== | ====Management==== | ||
* | * Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care should there be an overdose. | ||
===Chronic Overdose=== | ===Chronic Overdose=== | ||
| Line 413: | Line 416: | ||
|drugBox= | |drugBox= | ||
{{Drugbox2 | |||
| Verifiedfields = changed | |||
| verifiedrevid = 459437484 | |||
| IUPAC_name = 2-(3-cyano-4-isobutoxyphenyl)-4-methyl-<br>1,3-thiazole-5-carboxylic acid | |||
| image = Febuxostat00.png | |||
<!--Clinical data--> | |||
| tradename = Uloric, Adenuric, Atenurix | |||
| Drugs.com = {{drugs.com|monograph|febuxostat}} | |||
| MedlinePlus = a609020 | |||
| licence_EU = Adenuric | |||
| licence_US = Febuxostat | |||
| pregnancy_AU = <!-- A / B1 / B2 / B3 / C / D / X --> | |||
| pregnancy_US = C | |||
| pregnancy_category = | |||
| legal_AU = <!-- S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8, S9 or Unscheduled--> | |||
| legal_CA = <!-- Schedule I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, VIII --> | |||
| legal_UK = <!-- GSL, P, POM, CD, or Class A, B, C --> | |||
| legal_US = Rx-only | |||
| legal_status = | |||
| routes_of_administration = Oral | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetic data--> | |||
| bioavailability = ~49% absorbed | |||
| protein_bound = ~99% to albumin | |||
| metabolism = via [[CYP1A2]], [[CYP2C8|2C8]], [[CYP2C9|2C9]], [[UGT1A1]], [[UGT1A3|1A3]], [[UGT1A9|1A9]], [[UGT2B7|2B7]] | |||
| elimination_half-life = ~5-8 hours | |||
| excretion = Urine (~49% mostly as metabolites, 3% as unchanged drug); feces (~45% mostly as metabolites, 12% as unchanged drug) | |||
<!--Identifiers--> | |||
| CAS_number_Ref = {{cascite|changed|??}} | |||
| CAS_number = 144060-53-7 | |||
| ATC_prefix = M04 | |||
| ATC_suffix = AA03 | |||
| ATC_supplemental = | |||
| PubChem = 134018 | |||
| DrugBank_Ref = {{drugbankcite|correct|drugbank}} | |||
| DrugBank = | |||
| ChemSpiderID_Ref = {{chemspidercite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| ChemSpiderID = 118173 | |||
| UNII_Ref = {{fdacite|correct|FDA}} | |||
| UNII = 101V0R1N2E | |||
| KEGG_Ref = {{keggcite|correct|kegg}} | |||
| KEGG = D01206 | |||
| ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | |||
| ChEMBL = 1164729 | |||
<!--Chemical data--> | |||
| chemical_formula = | |||
| C=16 | H=16 | N=2 | Na= | O=3 | S=1 | |||
| molecular_weight = 316.374 g/mol | |||
| smiles = N#Cc1c(OCC(C)C)ccc(c1)c2nc(c(s2)C(=O)O)C | |||
| InChI = 1/C16H16N2O3S/c1-9(2)8-21-13-5-4-11(6-12(13)7-17)15-18-10(3)14(22-15)16(19)20/h4-6,9H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,19,20) | |||
| InChIKey = BQSJTQLCZDPROO-UHFFFAOYAV | |||
| StdInChI_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChI = 1S/C16H16N2O3S/c1-9(2)8-21-13-5-4-11(6-12(13)7-17)15-18-10(3)14(22-15)16(19)20/h4-6,9H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,19,20) | |||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|correct|chemspider}} | |||
| StdInChIKey = BQSJTQLCZDPROO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||
}} | |||
<!--Mechanism of Action--> | <!--Mechanism of Action--> | ||
| Line 419: | Line 480: | ||
|mechAction= | |mechAction= | ||
* | * ULORIC, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, achieves its therapeutic effect by decreasing serum uric acid. ULORIC is not expected to inhibit other enzymes involved in purine and pyrimidine synthesis and metabolism at therapeutic concentrations. | ||
<!--Structure--> | <!--Structure--> | ||
| Line 425: | Line 486: | ||
|structure= | |structure= | ||
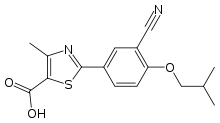
* | * ULORIC (febuxostat) is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. The active ingredient in ULORIC is 2-[3-cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy) phenyl]-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylic acid, with a molecular weight of 316.38. The empirical formula is C16H16N2O3S. | ||
: [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | : [[File:{{PAGENAME}}01.png|thumb|none|600px|This image is provided by the National Library of Medicine.]] | ||
*Febuxostat is a non-hygroscopic, white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in dimethylformamide; soluble in dimethylsulfoxide; sparingly soluble in ethanol; slightly soluble in methanol and acetonitrile; and practically insoluble in water. The melting range is 205°C to 208°C. | |||
*ULORIC tablets for oral use contain the active ingredient, febuxostat, and are available in two dosage strengths, 40 mg and 80 mg. Inactive ingredients include lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium croscarmellose, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. ULORIC tablets are coated with Opadry II, green. | |||
<!--Pharmacodynamics--> | <!--Pharmacodynamics--> | ||
| Line 433: | Line 498: | ||
|PD= | |PD= | ||
*Effect on Uric Acid and Xanthine Concentrations: In healthy subjects, ULORIC resulted in a dose dependent decrease in 24-hour mean serum uric acid concentrations and an increase in 24-hour mean serum xanthine concentrations. In addition, there was a decrease in the total daily urinary uric acid excretion. Also, there was an increase in total daily urinary xanthine excretion. Percent reduction in 24-hour mean serum uric acid concentrations was between 40% and 55% at the exposure levels of 40 mg and 80 mg daily doses. | |||
*Effect on Cardiac Repolarization: The effect of ULORIC on cardiac repolarization as assessed by the QTc interval was evaluated in normal healthy subjects and in patients with gout. ULORIC in doses up to 300 mg daily, at steady-state, did not demonstrate an effect on the QTc interval. | |||
<!--Pharmacokinetics--> | <!--Pharmacokinetics--> | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 24 November 2014
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]; Associate Editor(s)-in-Chief: Vignesh Ponnusamy, M.B.B.S. [2]
Disclaimer
WikiDoc MAKES NO GUARANTEE OF VALIDITY. WikiDoc is not a professional health care provider, nor is it a suitable replacement for a licensed healthcare provider. WikiDoc is intended to be an educational tool, not a tool for any form of healthcare delivery. The educational content on WikiDoc drug pages is based upon the FDA package insert, National Library of Medicine content and practice guidelines / consensus statements. WikiDoc does not promote the administration of any medication or device that is not consistent with its labeling. Please read our full disclaimer here.
Overview
Febuxostat is a xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor that is FDA approved for the {{{indicationType}}} of hyperuricemia in patients with gout. Common adverse reactions include liver function abnormalities, nausea, arthralgia, and rash.
Adult Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Adult)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition3
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition4
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Adult)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Febuxostat in adult patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Febuxostat in adult patients.
Pediatric Indications and Dosage
FDA-Labeled Indications and Dosage (Pediatric)
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding FDA-Labeled Use of Febuxostat in pediatric patients.
Off-Label Use and Dosage (Pediatric)
Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Developed by:
- Class of Recommendation:
- Strength of Evidence:
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Guideline-Supported Use of Febuxostat in pediatric patients.
Non–Guideline-Supported Use
Condition1
- Dosing Information
- Dosage
Condition2
There is limited information regarding Off-Label Non–Guideline-Supported Use of Febuxostat in pediatric patients.
Contraindications
- ULORIC is contraindicated in patients being treated with azathioprine or mercaptopurine.
Warnings
Precautions
- Gout Flare
- After initiation of ULORIC, an increase in gout flares is frequently observed. This increase is due to reduction in serum uric acid levels, resulting in mobilization of urate from tissue deposits.
- In order to prevent gout flares when ULORIC is initiated, concurrent prophylactic treatment with an NSAID or colchicine is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- Cardiovascular Events
- In the randomized controlled studies, there was a higher rate of cardiovascular thromboembolic events (cardiovascular deaths, non-fatal myocardial infarctions, and non-fatal strokes) in patients treated with ULORIC (0.74 per 100 P-Y [95% Confidence Interval (CI) 0.36-1.37]) than allopurinol (0.60 per 100 P-Y [95% CI 0.16-1.53]) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. A causal relationship with ULORIC has not been established. Monitor for signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke.
- Hepatic Effects
- There have been postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking ULORIC, although the reports contain insufficient information necessary to establish the probable cause. During randomized controlled studies, transaminase elevations greater than three times the upper limit of normal (ULN) were observed (AST: 2%, 2%, and ALT: 3%, 2% in ULORIC and allopurinol-treated patients, respectively). No dose-effect relationship for these transaminase elevations was noted [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Obtain a liver test panel (serum alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST], alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) as a baseline before initiating ULORIC.
- Measure liver tests promptly in patients who report symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice. In this clinical context, if the patient is found to have abnormal liver tests (ALT greater than three times the upper limit of the reference range), ULORIC treatment should be interrupted and investigation done to establish the probable cause. ULORIC should not be restarted in these patients without another explanation for the liver test abnormalities.
- Patients who have serum ALT greater than three times the reference range with serum total bilirubin greater than two times the reference range without alternative etiologies are at risk for severe drug-induced liver injury and should not be restarted on ULORIC. For patients with lesser elevations of serum ALT or bilirubin and with an alternate probable cause, treatment with ULORIC can be used with caution.
Adverse Reactions
Clinical Trials Experience
- Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- A total of 2757 subjects with hyperuricemia and gout were treated with ULORIC 40 mg or 80 mg daily in clinical studies. For ULORIC 40 mg, 559 patients were treated for ≥6 months. For ULORIC 80 mg, 1377 subjects were treated for ≥6 months, 674 patients were treated for ≥1 year and 515 patients were treated for ≥2 years.
- Most Common Adverse Reactions
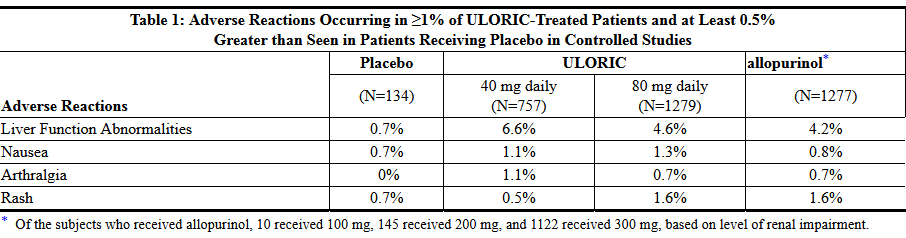
- In three randomized, controlled clinical studies (Studies 1, 2 and 3), which were six to 12 months in duration, the following adverse reactions were reported by the treating physician as related to study drug. Table 1 summarizes adverse reactions reported at a rate of at least 1% in ULORIC treatment groups and at least 0.5% greater than placebo.
T1
- The most common adverse reaction leading to discontinuation from therapy was liver function abnormalities in 1.8% of ULORIC 40 mg, 1.2% of ULORIC 80 mg, and in 0.9% of allopurinol-treated subjects.
- In addition to the adverse reactions presented in Table 1, dizziness was reported in more than 1% of ULORIC-treated subjects although not at a rate more than 0.5% greater than placebo.
- Less Common Adverse Reactions
- In Phase 2 and 3 clinical studies the following adverse reactions occurred in less than 1% of subjects and in more than one subject treated with doses ranging from 40 mg to 240 mg of ULORIC. This list also includes adverse reactions (less than 1% of subjects) associated with organ systems from Warnings and Precautions.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Anemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, leukocytosis/leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia, splenomegaly, thrombocytopenia.
Cardiac Disorders
Angina pectoris, atrial fibrillation/flutter, cardiac murmur, ECG abnormal, palpitations, sinus bradycardia, tachycardia.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders
Deafness, tinnitus, vertigo.
Eye Disorders
Vision blurred.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abdominal distention, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia, flatulence, frequent stools, gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal discomfort, gingival pain, haematemesis, hyperchlorhydria, hematochezia, mouth ulceration, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, vomiting.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Asthenia, chest pain/discomfort, edema, fatigue, feeling abnormal, gait disturbance, influenza-like symptoms, mass, pain, thirst.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Cholelithiasis/cholecystitis, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis, hepatomegaly.
Immune System Disorder
Hypersensitivity.
Infections and Infestations
Herpes zoster.
Procedural Complications
Contusion.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Anorexia, appetite decreased/increased, dehydration, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypokalemia, weight decreased/increased.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Arthritis, joint stiffness, joint swelling, muscle spasms/twitching/tightness/weakness, musculoskeletal pain/stiffness, myalgia.
Nervous System Disorders
Altered taste, balance disorder, cerebrovascular accident, Guillain-Barré syndrome, headache, hemiparesis, hypoesthesia, hyposmia, lacunar infarction, lethargy, mental impairment, migraine, paresthesia, somnolence, transient ischemic attack, tremor.
Psychiatric Disorders
Agitation, anxiety, depression, insomnia, irritability, libido decreased, nervousness, panic attack, personality change.
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Hematuria, nephrolithiasis, pollakiuria, proteinuria, renal failure, renal insufficiency, urgency, incontinence.
Reproductive System and Breast Changes
Breast pain, erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Bronchitis, cough, dyspnea, epistaxis, nasal dryness, paranasal sinus hypersecretion, pharyngeal edema, respiratory tract congestion, sneezing, throat irritation, upper respiratory tract infection.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Alopecia, angio-edema, dermatitis, dermographism, ecchymosis, eczema, hair color changes, hair growth abnormal, hyperhidrosis, peeling skin, petechiae, photosensitivity, pruritus, purpura, skin discoloration/altered pigmentation, skin lesion, skin odor abnormal, urticaria.
Vascular Disorders
Flushing, hot flush, hypertension, hypotension.
Laboratory Parameters
Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged, creatine increased, bicarbonate decreased, sodium increased, EEG abnormal, glucose increased, cholesterol increased, triglycerides increased, amylase increased, potassium increased, TSH increased, platelet count decreased, hematocrit decreased, hemoglobin decreased, MCV increased, RBC decreased, creatinine increased, blood urea increased, BUN/creatinine ratio increased, creatine phosphokinase (CPK) increased, alkaline phosphatase increased, LDH increased, PSA increased, urine output increased/decreased, lymphocyte count decreased, neutrophil count decreased, WBC increased/decreased, coagulation test abnormal, low density lipoprotein (LDL) increased, prothrombin time prolonged, urinary casts, urine positive for white blood cells and protein.
Postmarketing Experience
- Adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ULORIC. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Hepatic failure (some fatal), jaundice, serious cases of abnormal liver function test results, liver disorder.
Immune System Disorders
Anaphylaxis, anaphylactic reaction.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Rhabdomyolysis.
Psychiatric Disorders
Psychotic behavior including aggressive thoughts.
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Tubulointerstitial nephritis.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Generalized rash, Stevens Johnson Syndrome, hypersensitivity skin reactions.
Drug Interactions
- Xanthine Oxidase Substrate Drugs
- ULORIC is an XO inhibitor. Based on a drug interaction study in healthy subjects, febuxostat altered the metabolism of theophylline (a substrate of XO) in humans. Therefore, use with caution when coadministering ULORIC with theophylline.
- Drug interaction studies of ULORIC with other drugs that are metabolized by XO (e.g., mercaptopurine and azathioprine) have not been conducted. Inhibition of XO by ULORIC may cause increased plasma concentrations of these drugs leading to toxicity. ULORIC is contraindicated in patients being treated with azathioprine or mercaptopurine.
- Cytotoxic Chemotherapy Drugs
- Drug interaction studies of ULORIC with cytotoxic chemotherapy have not been conducted. No data are available regarding the safety of ULORIC during cytotoxic chemotherapy.
- In Vivo Drug Interaction Studies
- Based on drug interaction studies in healthy subjects, ULORIC does not have clinically significant interactions with colchicine, naproxen, indomethacin, hydrochlorothiazide, warfarin or desipramine. Therefore, ULORIC may be used concomitantly with these medications.
Use in Specific Populations
Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Category C
- There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ULORIC should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
- Febuxostat was not teratogenic in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 48 mg/kg (40 and 51 times the human plasma exposure at 80 mg/day for equal body surface area, respectively) during organogenesis. However, increased neonatal mortality and a reduction in the neonatal body weight gain were observed when pregnant rats were treated with oral doses up to 48 mg/kg (40 times the human plasma exposure at 80 mg/day) during organogenesis and through lactation period.
- Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) Pregnancy Category
There is no Australian Drug Evaluation Committee (ADEC) guidance on usage of Febuxostat in women who are pregnant.
Labor and Delivery
There is no FDA guidance on use of Febuxostat during labor and delivery.
Nursing Mothers
- Febuxostat is excreted in the milk of rats. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ULORIC is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
- Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under 18 years of age have not been established.
Geriatic Use
- No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients. Of the total number of subjects in clinical studies of ULORIC, 16% were 65 and over, while 4% were 75 and over. Comparing subjects in different age groups, no clinically significant differences in safety or effectiveness were observed but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. The Cmax and AUC24 of febuxostat following multiple oral doses of ULORIC in geriatric subjects (≥65 years) were similar to those in younger subjects (18 to 40 years) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Gender
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Febuxostat with respect to specific gender populations.
Race
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Febuxostat with respect to specific racial populations.
Renal Impairment
- No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment (Clcr 30 to 89 mL/min). The recommended starting dose of ULORIC is 40 mg once daily. For patients who do not achieve a sUA less than 6 mg/dL after two weeks with 40 mg, ULORIC 80 mg is recommended.
- There are insufficient data in patients with severe renal impairment (Clcr less than 30 mL/min); therefore, caution should be exercised in these patients.
Hepatic Impairment
- No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A or B). No studies have been conducted in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C); therefore, caution should be exercised in these patients.
Females of Reproductive Potential and Males
There is no FDA guidance on the use of Febuxostat in women of reproductive potentials and males.
Immunocompromised Patients
There is no FDA guidance one the use of Febuxostat in patients who are immunocompromised.
Administration and Monitoring
Administration
- Oral
Monitoring
There is limited information regarding Monitoring of Febuxostat in the drug label.
IV Compatibility
There is limited information regarding IV Compatibility of Febuxostat in the drug label.
Overdosage
Acute Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
- ULORIC was studied in healthy subjects in doses up to 300 mg daily for seven days without evidence of dose-limiting toxicities. No overdose of ULORIC was reported in clinical studies.
Management
- Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care should there be an overdose.
Chronic Overdose
There is limited information regarding Chronic Overdose of Febuxostat in the drug label.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
- ULORIC, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, achieves its therapeutic effect by decreasing serum uric acid. ULORIC is not expected to inhibit other enzymes involved in purine and pyrimidine synthesis and metabolism at therapeutic concentrations.
Structure
- ULORIC (febuxostat) is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. The active ingredient in ULORIC is 2-[3-cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy) phenyl]-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylic acid, with a molecular weight of 316.38. The empirical formula is C16H16N2O3S.
- Febuxostat is a non-hygroscopic, white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in dimethylformamide; soluble in dimethylsulfoxide; sparingly soluble in ethanol; slightly soluble in methanol and acetonitrile; and practically insoluble in water. The melting range is 205°C to 208°C.
- ULORIC tablets for oral use contain the active ingredient, febuxostat, and are available in two dosage strengths, 40 mg and 80 mg. Inactive ingredients include lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium croscarmellose, silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. ULORIC tablets are coated with Opadry II, green.
Pharmacodynamics
- Effect on Uric Acid and Xanthine Concentrations: In healthy subjects, ULORIC resulted in a dose dependent decrease in 24-hour mean serum uric acid concentrations and an increase in 24-hour mean serum xanthine concentrations. In addition, there was a decrease in the total daily urinary uric acid excretion. Also, there was an increase in total daily urinary xanthine excretion. Percent reduction in 24-hour mean serum uric acid concentrations was between 40% and 55% at the exposure levels of 40 mg and 80 mg daily doses.
- Effect on Cardiac Repolarization: The effect of ULORIC on cardiac repolarization as assessed by the QTc interval was evaluated in normal healthy subjects and in patients with gout. ULORIC in doses up to 300 mg daily, at steady-state, did not demonstrate an effect on the QTc interval.
Pharmacokinetics
There is limited information regarding Pharmacokinetics of Febuxostat in the drug label.
Nonclinical Toxicology
There is limited information regarding Nonclinical Toxicology of Febuxostat in the drug label.
Clinical Studies
There is limited information regarding Clinical Studies of Febuxostat in the drug label.
How Supplied
Storage
There is limited information regarding Febuxostat Storage in the drug label.
Images
Drug Images
{{#ask: Page Name::Febuxostat |?Pill Name |?Drug Name |?Pill Ingred |?Pill Imprint |?Pill Dosage |?Pill Color |?Pill Shape |?Pill Size (mm) |?Pill Scoring |?NDC |?Drug Author |format=template |template=DrugPageImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Pill Name }}
Package and Label Display Panel
{{#ask: Label Page::Febuxostat |?Label Name |format=template |template=DrugLabelImages |mainlabel=- |sort=Label Page }}
Patient Counseling Information
There is limited information regarding Patient Counseling Information of Febuxostat in the drug label.
Precautions with Alcohol
- Alcohol-Febuxostat interaction has not been established. Talk to your doctor about the effects of taking alcohol with this medication.
Brand Names
- ®[1]
Look-Alike Drug Names
- A® — B®[2]
Drug Shortage Status
Price
References
The contents of this FDA label are provided by the National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Empty citation (help)
- ↑ "http://www.ismp.org". External link in
|title=(help)
{{#subobject:
|Page Name=Febuxostat |Pill Name=No image.jpg |Drug Name= |Pill Ingred=|+sep=; |Pill Imprint= |Pill Dosage= |Pill Color=|+sep=; |Pill Shape= |Pill Size (mm)= |Pill Scoring= |Pill Image= |Drug Author= |NDC=
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Febuxostat |Label Name=Febuxostat11.png
}}
{{#subobject:
|Label Page=Febuxostat |Label Name=Febuxostat11.png
}}