Clinical classification of acute myocardial infarction: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
'''Type 5:''' Myocardial infarction associated with ''<u>'''Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery'''</u>'' | '''Type 5:''' Myocardial infarction associated with ''<u>'''Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery'''</u>'' | ||
For the main article on cardiac markers see the chapter on [[Cardiac marker|cardiac markers]]. For the main article on the diagnosis of STEMI, see the chapter on [[Clinical classification of acute myocardial infarction]]. | |||
==Overview== | |||
Cardiac markers or cardiac enzymes are proteins that are present in cardiac myocytes that should not be in the bloodstream. When cardiac injury occurs (such as in acute MI), these intracellular proteins are then released into the bloodstream. Along with the patient's history and the electrocardiogram, the release of these enzymes forms the basis of the diagnosis of ST elevation myocardial infarction. | |||
==History== | |||
Until the 1980s, the enzymes [[Aspartate transaminase|SGOT]] and [[lactate dehydrogenase|LDH]] were used to assess cardiac injury. In the early 1980s it was found that disproportional elevation of the ''MB'' subtype of the enzyme [[creatine kinase]] (CK) was very specific for myocardial injury. More recently, troponin has been used as an even more specific marker of myonecrosis. Current guidelines are generally in favor of [[troponin]] sub-units I or T, which are very specific for damage to myocytes.<ref name="pmid16918269">{{cite journal |author=Eisenman A |title=Troponin assays for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome: where do we stand? |journal=Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther |volume=4 |issue=4 |pages=509–14 |year=2006 |month=July |pmid=16918269 |doi=10.1586/14779072.4.4.509 |url=}}</ref> <ref name="pmid12087140">{{cite journal |author=Aviles RJ, Askari AT, Lindahl B, ''et al'' |title=Troponin T levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes, with or without renal dysfunction |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=346 |issue=26 |pages=2047–52 |year=2002 |month=June |pmid=12087140 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa013456 |url=}}</ref><ref>[http://www.cmaj.ca/cgi/content/full/167/6/671 Summary of "Troponin T levels in patients..." for laymen]</ref> | |||
==Clinical Application of Cardiac Markers== | |||
It is important to note that it may take hours for cardiac enzymes to rise following injury to the myocardium, and that they may not be elevated on presentation. For this reason, cardiac enzymes and ECGs are checked every 6 to 8 hours over the course of the first 24 hours to "rule out" acute MI. These enzyme measures over the first 24 hours are used to gauge the size of an MI: higer peak levels and a greater area under the curve of enzyme release are associated with larger MIs and poorer prognosis. | |||
=="False Positive" Troponin Elevations That Are Not Due to Thrombotic Coronary Occlusion== | |||
It is important to note that cardiac troponins are a marker of all heart muscle damage, not just myocardial infarction. There are other "false positive" causes of troponin elevation that directly or indirectly lead to heart muscle damage can also therefore increase troponin levels:<ref name="pmid15867411">{{cite journal |author=Jeremias A, Gibson CM |title=Narrative review: alternative causes for elevated cardiac troponin levels when acute coronary syndromes are excluded |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=142 |issue=9 |pages=786–91 |year=2005 |month=May |pmid=15867411 |doi= |url=}}</ref> <ref>Ammann P, Pfisterer M, Fehr T, Rickli H. Raised cardiac troponins. ''[[British Medical Journal|BMJ]]'' 2004;328:1028-9. PMID 15117768.</ref> | |||
* Cardiac: | |||
** Cardiac [[amyloidosis]] and other cardiac infiltrative disorders | |||
** [[Cardiac contusion]] | |||
** [[Cardiothoracic surgery|Cardiac surgery]] and [[heart transplant]] | |||
** [[Defibrillation]] | |||
** Closure of [[atrial septal defect]]s | |||
** [[Coronary artery vasospasm]] | |||
** [[Dilated cardiomyopathy]] | |||
** [[Heart failure]] | |||
** [[Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] | |||
** [[Hypotension]] | |||
** [[Myocarditis]] | |||
** [[Angioplasty|Percutaneous coronary intervention]] | |||
** [[Pericarditis]] | |||
** [[Pulmonary hypertension]] | |||
** [[Radiofrequency ablation]] | |||
** [[Supraventricular tachycardia]] including [[atrial fibrillation]] | |||
* Non-cardiac: | |||
** Critical illness, e.g. [[sepsis]] | |||
** High-dose [[chemotherapy]] | |||
** [[Hypovolemia]] | |||
** [[Intracranial hemorrhage]] | |||
** Primary [[pulmonary hypertension]] | |||
** [[Pulmonary embolism]] | |||
** [[Renal failure]] | |||
** [[Subarachnoid hemorrhage]] | |||
** Scorpion [[venom]] | |||
** [[Stroke]] | |||
** [[Sympathomimetic]] ingestion | |||
** Very heavy [[exercise]] (e.g. marathon) | |||
==External links== | |||
* [http://www.themdtv.org The MD TV: Comments on Hot Topics, State of the Art Presentations in Cardiovascular Medicine, Expert Reviews on Cardiovascular Research] | |||
* [http://www.clinicaltrialresults.org Clinical Trial Results: An up to date resource of Cardiovascular Research] | |||
* [http://hp2010.nhlbihin.net/atpiii/calculator.asp?usertype=pub Risk Assessment Tool for Estimating Your 10-year Risk of Having a Heart Attack] - based on information of the [[Framingham Heart Study]], from the United States [[National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute]] | |||
* [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/heartattack.html Heart Attack] - overview of resources from [[MedlinePlus]]. | |||
* [http://ww2.heartandstroke.ca/Page.asp?PageID=1975&ArticleID=5288 Heart Attack Warning Signals] from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada | |||
* [http://www.regionalpci-stemi.org/index.html Regional PCI for STEMI Resource Center] - Evidence based online resource center for the development of regional PCI networks for acute STEMI | |||
* [http://www.stemisystems.org/ STEMI Systems] - Articles, profiles, and reviews of the latest publications involved in STEMI care. Quarterly newsletter. | |||
* [http://d2b.acc.org/ American College of Cardiology (ACC) Door to Balloon (D2B) Initiative.] | |||
* [http://www.americanheart.org/heartattack American Heart Association's Heart Attack web site] - Information and resources for preventing, recognizing and treating heart attack. | |||
Revision as of 16:03, 29 April 2009
| Myocardial infarction | |
 | |
|---|---|
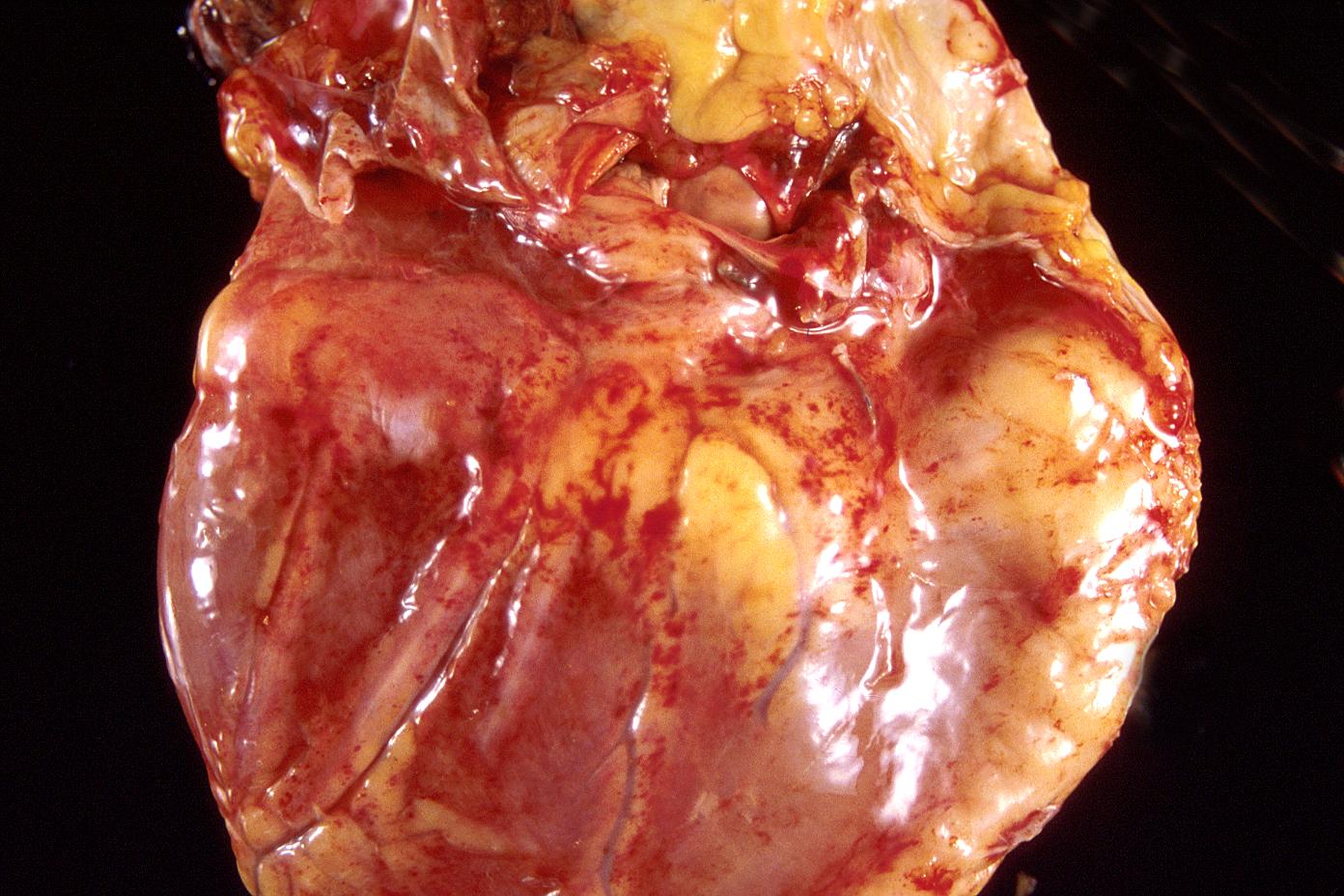
| Acute Myocardial infarction; Posterior wall. Image courtesy of Professor Peter Anderson DVM PhD and published with permission © PEIR, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Department of Pathology | |
| ICD-10 | I21-I22 |
| ICD-9 | 410 |
| DiseasesDB | 8664 |
| MedlinePlus | 000195 |
| eMedicine | med/1567 emerg/327 ped/2520 |
| Cardiology Network |
 Discuss Clinical classification of acute myocardial infarction further in the WikiDoc Cardiology Network |
| Adult Congenital |
|---|
| Biomarkers |
| Cardiac Rehabilitation |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
| CT Angiography |
| Echocardiography |
| Electrophysiology |
| Cardiology General |
| Genetics |
| Health Economics |
| Hypertension |
| Interventional Cardiology |
| MRI |
| Nuclear Cardiology |
| Peripheral Arterial Disease |
| Prevention |
| Public Policy |
| Pulmonary Embolism |
| Stable Angina |
| Valvular Heart Disease |
| Vascular Medicine |
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. [1]
Associate Editor-In-Chief: Cafer Zorkun, M.D., Ph.D. [2]
Prior MI Classification Schemes
There have been several prior classification schemes for characterizing MI:
1. Transmural (necrosis of full thickness of ventricle) vs. non transmural (necrosis of partial thickness of ventricle)
2. Q wave vs. non Q wave: Based upon the development of electrocardiographic Q waves representing electrically inert tissue.
3. ST elevation MI (STEMI) and Non ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)
At one time it was thought that Transmural MI and Q wave MI were synonymous. However, not all Q wave MIs are transmural, and not all transmural MIs are associated with Q waves.
Likewise, not all ST elevation MIs go on to cause q waves. Non ST elevation MIs can result in q waves.
Thus, ST elevation MI should not be equated with transmural MI or q wave MI. Likewise, Non ST elevation MI should not be equated with non transmural MI or non q wave MI. These 3 designations reflect three separate but overlapping characterization schemes.
New MI Clinical Classification System
A new clinical evidence based classification system has been introduced by Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD, et al. and jointly sponsored by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), European Society of Cardiology (ESC), and the World Heart Federation (WHF).[1]
Criteria for Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction
"The term myocardial infarction should be used when there is evidence of myocardial necrosis in a clinical setting consistent with myocardial ischemia. Under these conditions any one of the following criteria meets the diagnosis for acute myocardial infarction". [1]
Below are the criteria quoted from the Thygesen article:
- Detection of rise and/or fall of cardiac biomarkers (preferably Troponin) with at least one of the following
- Sudden unexpected cardiac death, including cardiac arrest, often with symptoms suggestive of myocardial ischemia, accompanied by presumably new ST segment elevation, or new LBBB, and/or evidence of fresh thrombus in a coronary artery by angiography and/or at autopsy, if death has occurred before blood samples could be obtained, or at a time before the appearance of cardiac biomarkers in the blood
- In patients with normal baseline troponin values, a greater than 3 times increase above the 99th percentile of the upper limit of normal of cardiac biomarkers has been designated as the definition of PCI related myocardial infarction. A subtype related to documented stent thrombosis is recognized.
- For patients with CABG surgery; (In patients with normal baseline troponin values) increases of cardiac biomarkers greater than 5 times, (> 5 times the 99th percentile upper limit of normal) and either new pathological Q waves or new LBBB or angiographically evidence of new graft or native vessel occlusion have been designated as defining CABG surgery related myocardial infarction.
- Pathological findings of acute myocardial infarction.
Criteria for Prior Myocardial Infarction
If any of the following are present, then a diagnosis of prior myocardial infarction is established:[1]
- Development of new pathological Q waves with or without symptoms
- Imaging evidence of a region of loss of viable myocardium that is thinned and fails to contract in the absence of a non ischemic cause.
- Pathological findings of healed or healing myocardial infarction.
Classification
Five types of MI are now recognized and classified as follows: [1]
Type 1: Spontaneous myocardial infarction related to ischemia due to a primary coronary event, such as plaque erosion and/or rupture, fissuring, or dissection.
Type 2: Myocardial infarction secondary to ischemia due to an imbalance of O2 supply and demand, as from coronary spasm or embolism, anemia, arrhythmias, hypertension, or hypotension
Type 3: Sudden unexpected cardiac death, including cardiac arrest, often with symptoms suggesting ischemia with new ST segment elevation; new left bundle branch block; or pathologic or angiographic evidence of fresh coronary thrombus (in the absence of reliable biomarker findings)
Type 4:
- a. Myocardial infarction associated with Percutaneous Coronary Interventions (PCI)
- b. Myocardial infarction associated with documented stent thrombosis.
Type 5: Myocardial infarction associated with Coronary Artery Bypass Graft surgery
For the main article on cardiac markers see the chapter on cardiac markers. For the main article on the diagnosis of STEMI, see the chapter on Clinical classification of acute myocardial infarction.
Overview
Cardiac markers or cardiac enzymes are proteins that are present in cardiac myocytes that should not be in the bloodstream. When cardiac injury occurs (such as in acute MI), these intracellular proteins are then released into the bloodstream. Along with the patient's history and the electrocardiogram, the release of these enzymes forms the basis of the diagnosis of ST elevation myocardial infarction.
History
Until the 1980s, the enzymes SGOT and LDH were used to assess cardiac injury. In the early 1980s it was found that disproportional elevation of the MB subtype of the enzyme creatine kinase (CK) was very specific for myocardial injury. More recently, troponin has been used as an even more specific marker of myonecrosis. Current guidelines are generally in favor of troponin sub-units I or T, which are very specific for damage to myocytes.[2] [3][4]
Clinical Application of Cardiac Markers
It is important to note that it may take hours for cardiac enzymes to rise following injury to the myocardium, and that they may not be elevated on presentation. For this reason, cardiac enzymes and ECGs are checked every 6 to 8 hours over the course of the first 24 hours to "rule out" acute MI. These enzyme measures over the first 24 hours are used to gauge the size of an MI: higer peak levels and a greater area under the curve of enzyme release are associated with larger MIs and poorer prognosis.
"False Positive" Troponin Elevations That Are Not Due to Thrombotic Coronary Occlusion
It is important to note that cardiac troponins are a marker of all heart muscle damage, not just myocardial infarction. There are other "false positive" causes of troponin elevation that directly or indirectly lead to heart muscle damage can also therefore increase troponin levels:[5] [6]
- Cardiac:
- Cardiac amyloidosis and other cardiac infiltrative disorders
- Cardiac contusion
- Cardiac surgery and heart transplant
- Defibrillation
- Closure of atrial septal defects
- Coronary artery vasospasm
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Heart failure
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hypotension
- Myocarditis
- Percutaneous coronary intervention
- Pericarditis
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Supraventricular tachycardia including atrial fibrillation
- Non-cardiac:
- Critical illness, e.g. sepsis
- High-dose chemotherapy
- Hypovolemia
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary embolism
- Renal failure
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Scorpion venom
- Stroke
- Sympathomimetic ingestion
- Very heavy exercise (e.g. marathon)
External links
- The MD TV: Comments on Hot Topics, State of the Art Presentations in Cardiovascular Medicine, Expert Reviews on Cardiovascular Research
- Clinical Trial Results: An up to date resource of Cardiovascular Research
- Risk Assessment Tool for Estimating Your 10-year Risk of Having a Heart Attack - based on information of the Framingham Heart Study, from the United States National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute
- Heart Attack - overview of resources from MedlinePlus.
- Heart Attack Warning Signals from the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada
- Regional PCI for STEMI Resource Center - Evidence based online resource center for the development of regional PCI networks for acute STEMI
- STEMI Systems - Articles, profiles, and reviews of the latest publications involved in STEMI care. Quarterly newsletter.
- American College of Cardiology (ACC) Door to Balloon (D2B) Initiative.
- American Heart Association's Heart Attack web site - Information and resources for preventing, recognizing and treating heart attack.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Thygesen K, Alpert JS, White HD; et al. (2007). "Universal definition of myocardial infarction". Circulation. 116 (22): 2634–53. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.187397. PMID 17951284. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Eisenman A (2006). "Troponin assays for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and acute coronary syndrome: where do we stand?". Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 4 (4): 509–14. doi:10.1586/14779072.4.4.509. PMID 16918269. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Aviles RJ, Askari AT, Lindahl B; et al. (2002). "Troponin T levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes, with or without renal dysfunction". N. Engl. J. Med. 346 (26): 2047–52. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa013456. PMID 12087140. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Summary of "Troponin T levels in patients..." for laymen
- ↑ Jeremias A, Gibson CM (2005). "Narrative review: alternative causes for elevated cardiac troponin levels when acute coronary syndromes are excluded". Ann. Intern. Med. 142 (9): 786–91. PMID 15867411. Unknown parameter
|month=ignored (help) - ↑ Ammann P, Pfisterer M, Fehr T, Rickli H. Raised cardiac troponins. BMJ 2004;328:1028-9. PMID 15117768.